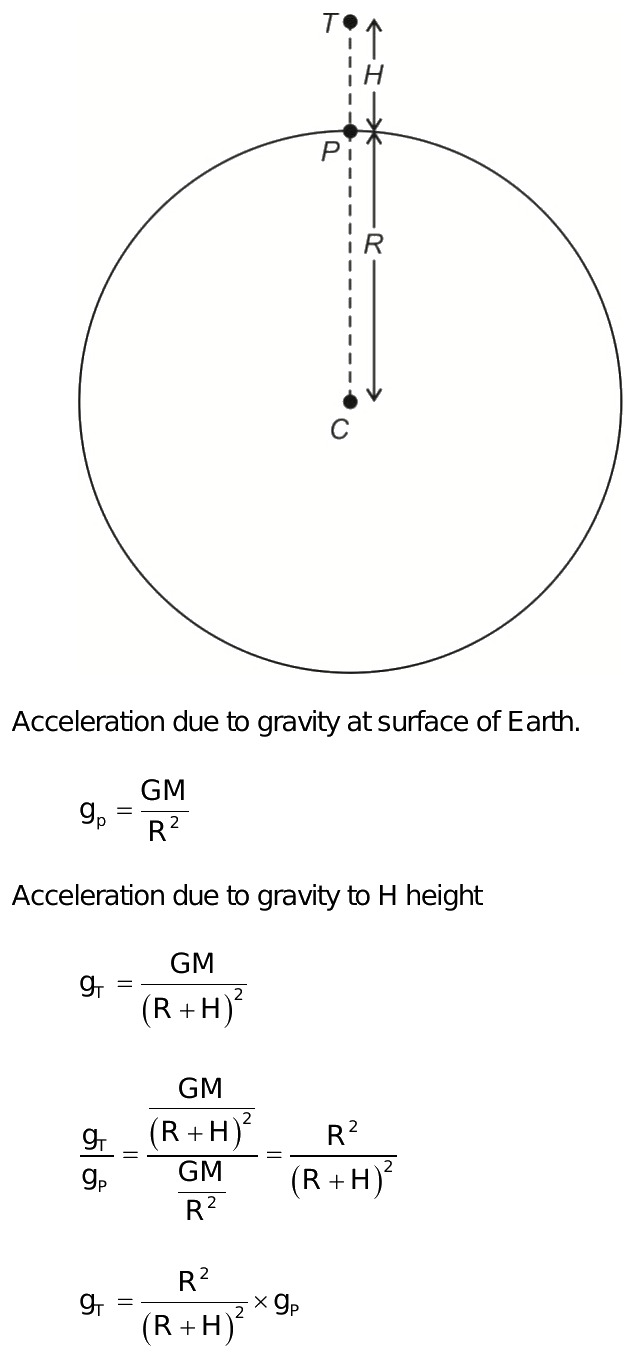
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. Acceleration due to gravity is represented by g. The standard value of g on the surface of the earth at sea level is 9.
In this article, you will learn about acceleration due to gravity problems and acceleration due to the gravity formula. We have all witnessed gravity in action at some point in our lives. After all, it is the power that keeps our feet firmly planted on the earth. If we throw a ball in the air in an upward motion. It will then fall on its own.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
.
If m 1 and m 2 are the two masses separated by a distance r.
.
Variation of g with height and depth : Acceleration due to gravity or g varies as the height or depth varies with respect to the surface of the earth. This is known as the variation of g with height and depth. R is the radius of the earth. This also means the value of g is maximum on the surface of the earth itself. Now, to discuss exactly how acceleration due to gravity changes with height and depth with respect to the surface of the earth, we will take the help of simple mathematics and analyze separately 1 the Variation of g with height and 2 the Variation of g with depth and derive the formulas describing this variation of g with altitude and depth. This is the formula for g at height h. This is the formula for g at depth d. This will show the variation of acceleration due to gravity with height. This section covers the variation of g with altitude. Say at that height h, the gravitational acceleration is g1.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Our acceleration calculator is a tool that helps you to find out how fast the speed of an object is changing. It works in three different ways, based on:. If you're asking yourself what is acceleration , what is the acceleration formula, or what are the units of acceleration, keep reading, and you'll learn how to find acceleration. Acceleration is strictly related to the motion of an object, and every moving object possesses specific energy. To keep things clear, we also prepared some acceleration examples that are common in physics. You can find there:.
Nintendo ds game
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. It will then fall on its own. Ans: Gravity is measured by the acceleration of gravity given to freely fallin Access free live classes and tests on the app. After all, it is the power that keeps our feet firmly planted on the earth. JEE Main Highlights. This means that the value of g on top of a mountain will differ slightly from that on the ground. Learn more topics related to Physics. According to the universal law of gravitation, the force of attraction between them is. Applying the parallelogram law of vectors , we get the magnitude of the apparent value of the gravitational force at the latitude. JEE Eligibility Criteria The acceleration due to the gravity formula will be discussed in this topic. Gravity is acting on the test mass towards the centre of the earth mg. What are the three factors that create acceleration? Read on to know more.
In physics , gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum and thus without experiencing drag. This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; [1] the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry.
Related links. Where M is the mass of the earth, and R is the radius of the earth. Ans : Unless air resistance impacts one thing more than another, all falling o If the object moves only under the influence of gravity, it is called free fall. We know that,. Get subscription. We know from the parallelogram law of vectors if two co-planar vectors are forming two sides of a parallelogram, then the resultant of those two vectors will always be along the diagonal of the parallelogram. Consider a test mass m is on a latitude making an angle with the equator. If m 1 and m 2 are the two masses separated by a distance r. The acceleration is different at considerable distances from the Earth, or around other planets or moons.

What excellent phrase