Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Have you ever used the term bandwidth?
Have you ever felt like you're stuck in a slow internet vortex, where your favorite cat videos take forever to load? Or maybe you've heard people throwing around terms like 'network speed,' 'bandwidth,' and 'throughput' but have no idea what they actually mean. Well, fear not! In this blog post, we're going to dive into the wild world of networking and unravel the mysteries of network speed, bandwidth, and throughput. Network bandwidth, network speed, and network throughput are often used interchangeably in the world of networking, but they are not the same thing.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
If you know throughput and bandwidth levels for your network, you have valuable information for assessing network performance. Throughput tells you how much data was transferred from a source at any given time and bandwidth tells you how much data could theoretically be transferred from a source at any given time. Pretty much all of the products I mention have free trials available, so you can give them a try if you want to put my recommendations to the test. What is Throughput in Networking? How to Optimize Bandwidth Bandwidth vs. Throughput and Bandwidth Explained—Final Thoughts. So, what are throughput and bandwidth? The short answer is speed. Speed is one of the most important things used to measure network performance, and we use throughput and bandwidth to measure it. How fast packets or units of data travel from source to destination or sender to recipient determines how much information can be sent within a given timeframe. Slow network speed equals slow network speed within applications, which equals laggy applications.
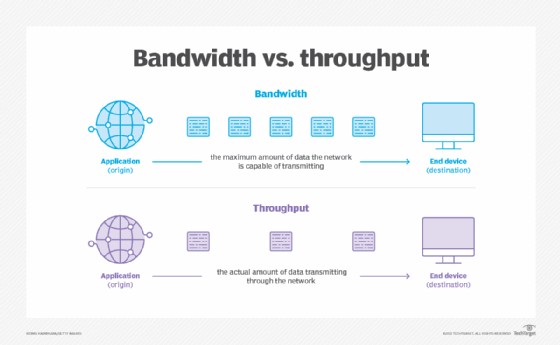
Data throughput meaning is a practical measure of actual packet delivery while bandwidth is a theoretical measure of packet delivery.
.
Throughput is the actual data transfer rate, while bandwidth is the maximum capacity or speed of a network connection. Know more about throughput vs The answer lies in understanding the difference between bandwidth and throughput. Even though these two words are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. Bandwidth measures how much a network can hold, while throughput measures how well it works. Throughput measures how often messages get to where they are supposed to go. It is a practical measure of how packets are actually delivered, not a theoretical measure. The user can find out how many packets are arriving at their destination by looking at the average data throughput. For a high-performance service, packets need to get to their destination.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Bandwidth and throughput are metrics that determine how much data can travel through a network. Understanding it and its differences with bandwidth can help you pick the right internet plan for you and better evaluate your internet speed. Each network has its own bandwidth, established at the time of setting up that network. So when you see an internet service provider advertise a 1 Gbps connection, it means every second it can carry a maximum of one gigabit of data from the source to the destination. A network can only accomplish its bandwidth in ideal, controlled environments. In reality, a network is hindered by a host of factors that can slow it down and take a hit on its efficiency. There could be a leak in the connection, the distance between the sender and the recipient may be too long to quickly exchange requests, or the quality of routers could be poor. More importantly, the bandwidth is a finite and fixed resource. It is shared across all members of a network and how much each member is assigned is based on their internet activities.
How to get 25000 diamonds in free fire
To analyze the bandwidth data, you can use the various charts and graphs available in the Obkio Dashboard, including line charts, bar charts, and pie charts. Network Performance Monitor NPM from SolarWinds is a tried-and-true, multi-vendor network monitoring system specially designed for scalability. Let's use a pipe analogy to better explain the difference between network bandwidth vs. It is typically measured in bits per second bps or bytes per second Bps. When monitoring your network performance, measuring network throughput is a much better indicator of the quality of your network performance rather than bandwidth or speed. These might interest you. When planning or designing a network, it's essential to consider these factors and conduct performance testing to determine the actual achievable throughput for specific applications and use cases. Besides speed and bandwidth, latency is also important to mention when talking about throughput. A quiz to help you determine the severity of shadow IT in your org. Bandwidth refers to the maximum capacity of a pipe, i. Obkio Blog. Alyssa Lamberti Last updated on Mar 9,
When working with networks , particularly in regard to capacity planning or troubleshooting, understanding key terms are important.
Similarly, even if you have a high-bandwidth network connection, the speed at which data can be transmitted over the connection will also depend on other factors such as the latency of the connection, the efficiency of the network protocols being used, and any congestion or packet loss on the network. Download Free Trial. In our example, we used Mbps, megabits per second. Packets lost in transit lead to poor or slow network performance, and low throughput indicates problems like packet loss. Throughput vs. How to Optimize Throughput By far the most important thing to do when optimizing throughput is to minimize network latency. Network speed can vary depending on the type of network, the devices used, and the distance between them. There are many types of applications that not only need good throughput but also need it to be predictable and reliable. Alyssa Lamberti Last updated on Mar 9, It quantifies the amount of data that can be sent or received in a given period, typically expressed in bits per second bps , kilobits per second Kbps , megabits per second Mbps , or gigabits per second Gbps. Therefore, all three metrics are important to measure, but the most important one depends on the context and what you are trying to accomplish. Say goodbye to network headaches. How Do You Measure Throughput? In general, measuring bandwidth involves transferring data and measuring the time it takes to complete the transfer. When this happens, servers have to send the information all over again, causing a delay.

I think it already was discussed.
Your idea is useful
I think, that you are not right. I am assured.