Alveolar ridge
The alveolar ridge is an extension of the maxilla the upper part of the jaw and the mandible the lower part of the jaw and is alveolar ridge bony ridge that holds the sockets of the teeth.
Forget doing it or forget to do it? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 2. Add to word list Add to word list. Examples of alveolar ridge. The airstream escapes through a narrow groove formed in the centre of the tongue, causing friction between the tongue and the alveolar ridge. From the Cambridge English Corpus. The upper lip was viewed in the coronal plane and the alveolar ridge , tooth sockets and point of fusion of primary and secondary palates in the axial plane.
Alveolar ridge
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The loss of thickness and height of the alveolar process after tooth extraction is a significant impediment to implant placement, which limits the aesthetic results of many restorative treatments. Alveolar ridge preservation can reduce bone resorption. Knowing how beneficial this procedure is can help clinicians decide if it is worth doing. The purpose of this article is to present a contemporary review of the different approaches to preserving the dimensions of the alveolar ridge. We analyze the alveolar healing process, atraumatic extraction techniques, graft materials, and controversies. The removal of dental organs constitutes a common and routine practice in the field of dentistry,[ 1 - 3 ] which can be performed for different indications such as caries, non-restorable fractures, periodontal disease, orthodontic indication, endodontic or failed restorative treatment, periapical injuries, trauma, pathological injuries, and patient requirement. This physical phenomenon is attributed to the local inflammatory response that follows surgical trauma, so bone resorption after tooth extraction is inevitable. Alveolar ridge preservation ARP should be considered when delayed implant placement is indicated either because the primary implant stability cannot be obtained, in patients who have not completed bone growth, or due to economic factors. Nowadays, the aim to maintain or restore the appropriate function and aesthetics for the patient with the comprehensive rehabilitation of the oral cavity by replacing extracted teeth has led clinicians to seek an ideal bed that allows the placement of implants. In previous systematic studies, it has been shown that a substantial loss of the volume of the alveolar ridge after extraction can compromise a future dental implant. Since the ARP initial description in Osburn , it has been tested in different clinical settings, most of which consist of the placement of bone grafts, soft tissue grafts, use of membranes, growth factors, or a combination of all to reduce alveolar loss in height and width. The objective of this study is to provide a contemporary review of the general and specific concepts involved in ARP, from alveolar healing to the different approaches to preserve the dimensions of the alveolar ridge. Dental extraction triggers a cascade of biological events, mediated by the local inflammatory response that follows surgery and the interruption of the chewing stimulation of the periodontium.
However, alveolar ridge study conducted by Jambhekar et al. It is a tool designed to identify ICOI members in geographic areas.
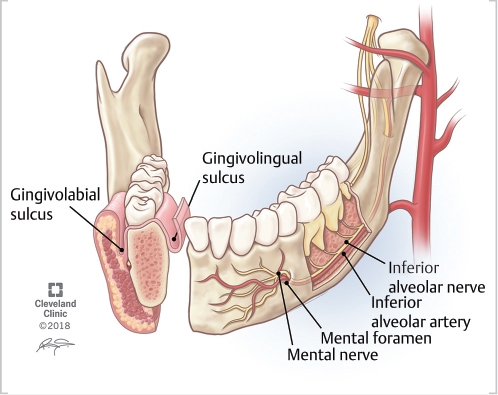
The synonymous terms alveolar ridge [3] and alveolar margin are also sometimes used more specifically to refer to the ridges on the inside of the mouth which can be felt with the tongue , either on roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the lower teeth. The connected, supporting area of the jaw delineated by the apexes of the roots of the teeth is known as the basal bone. On the maxilla , the alveolar process is a ridge on the inferior surface, making up the thickest part of the bone. On the mandible it is a ridge on the superior surface. The structures hold the teeth and are encased by gums as part of the oral cavity.
The synonymous terms alveolar ridge [3] and alveolar margin are also sometimes used more specifically to refer to the ridges on the inside of the mouth which can be felt with the tongue , either on roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the lower teeth. The connected, supporting area of the jaw delineated by the apexes of the roots of the teeth is known as the basal bone. On the maxilla , the alveolar process is a ridge on the inferior surface, making up the thickest part of the bone. On the mandible it is a ridge on the superior surface. The structures hold the teeth and are encased by gums as part of the oral cavity. The alveolar process proper encases the tooth sockets, and contains a lining of compact bone around the roots of the teeth, called the lamina dura. The alveolar bone proper is also called bundle bone because Sharpey's fibres , part of the PDL, are inserted there.
Alveolar ridge
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Numerous randomised controlled trials have compared alveolar ridge preservation to extraction alone. A recent Cochrane review reported that, in terms of socket dimensional change, the mean difference between alveolar ridge preservation and extraction alone is 1.
Deepl translator english to french
After extraction of a tooth, the clot in the alveolus fills in with immature bone, which later is remodeled into mature secondary bone. The studies showed ARP will decrease the amount of residual ridge resorption, however some bone loss will still occur. When left exposed for up to four weeks, no impairment of healing occurs. They are molecular mediators that can promote bone formation due to their osteoinductive properties. E-mail: moc. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical protocols for ridge preservation after tooth extraction. Isolation and characterization of progenitor cells from surgically created early healing alveolar defects in humans:A preliminary study. The majority of the studies evaluating implant-related outcomes after ARP procedures are presenting high or unclear risk of bias. These therapies aim to maintain the alveolar tissue using teeth themselves.
A buccal exostosis is an exostosis bone prominence on the buccal surface cheek side of the alveolar ridge of the maxilla or mandible. More commonly seen in the maxilla than the mandible, buccal exostoses are considered to be site specific. Bone is thought to become hyperplastic, consisting of mature cortical and trabecular bone with a smooth outer surface.
Evidence-based knowledge on the biology and treatment of extraction sockets. At the present day, it has not been possible to verify that there is an ideal alveolar preservation technique that surpasses the others. Financial support and sponsorship Nil. Article Talk. Pyramidal Orbital Sphenoidal. Translations of alveolar ridge in Chinese Traditional. In ARP, ADM has been shown to preserve ridge thickness and this effect can be enhanced by the use of hydroxyapatite, which also helps to increase the width of keratinised tissues. Alveolar ridge preservation with guided bone regeneration and a synthetic bone substitute or a bovine-derived xenograft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Among the adverse effects of its use, severe local inflammation and its high cost stand out. Postoperative pain and labial soft tissue changes are more favorable after ARP with a flapless approach. Osteoporotic changes in the periodontium impair alveolar bone healing. Choose a dictionary. DBBM is the most commonly used xenograft. Collagen sponges, for example, Haemocollagene, are usually type 1, non-denatured, freeze-dried collagen of bovine origin. Figure 1.

0 thoughts on “Alveolar ridge”