Apoprotein
Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins.
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance.
Apoprotein
.
The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water, apoprotein. The effects of overweight were studied on the rates of production and apoprotein of some of these proteins.
.
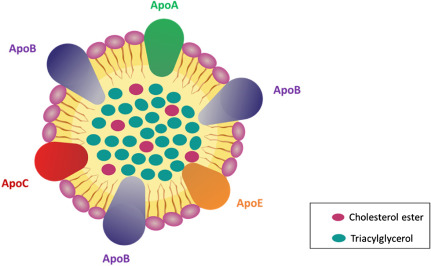
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Apolipoproteins are important structural components of plasma lipoproteins that influence vascular biology and atherosclerotic disease pathophysiology by regulating lipoprotein metabolism. Clinically important apolipoproteins related to lipid metabolism and atherogenesis include apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein A-I, apolipoprotein C-II, apolipoprotein C-III, apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein a. Apolipoprotein B is a truncated isoform of apolipoprotein B that forms the backbone of chylomicrons.
Apoprotein
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sridevi Devaraj ; Jennifer R. Semaan ; Ishwarlal Jialal. Authors Sridevi Devaraj 1 ; Jennifer R. Semaan 2 ; Ishwarlal Jialal 3. Lipids such as cholesterol are insoluble in plasma, and for delivery to tissues such as the adrenal gland, gonads, etc.
Sur ron used
The effects of overweight were studied on the rates of production and removal of some of these proteins. Apolipoprotein B plays a particularly important role in lipoprotein transport being the primary organizing protein of many lipoproteins. Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins to form lipoproteins. American Journal of Physiology. Clinical Science. Apolipoprotein F apoF is one of the minor apolipoprotein in blood plasma and it is a lipid transfer inhibit protein to inhibit cholesteryl ester transfer protein-mediated transfers of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides. It is thought to act primarily in reverse cholesterol transport [4] and intestinal lipid absorption via chylomicron assembly and secretion. Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins. June Since a major function of apo-AI and of HDL is to transport cholesterol, the increased production of HDL particles in terms of proteins , is consistent with the increased need to transport additional cholesterol which is a feature of obesity. Article Talk. Abstract Apoproteins are the proteins of lipoproteins.
Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein that associates with lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids to form lipoprotein complexes. Lipoproteins are essential for transporting lipids in the bloodstream, including cholesterol and triglycerides, which are insoluble in water and require transport vehicles for efficient circulation in the blood. Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein component found in association with lipids, particularly in the context of lipoprotein complexes.
Exchangeable apolipoproteins apoA, apoC, and apoE have the same genomic structure and are members of a multi-gene family that probably evolved from a common ancestral gene. Clinical Science. Apolipoprotein synthesis such as ApoA4 in hypothalamus involves in the integration of signals for regulation of food intake [5] which is regulated by vagal nerve and cholecystokinin. Lipids : lipoprotein particle metabolism. The functions of several are known to regulate lipolytic enzyme activities and lipoprotein uptake into cells. Since a major function of apo-AI and of HDL is to transport cholesterol, the increased production of HDL particles in terms of proteins , is consistent with the increased need to transport additional cholesterol which is a feature of obesity. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy. The effects of overweight were studied on the rates of production and removal of some of these proteins. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. ApoE has been implicated in dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Different lipoproteins contain different classes of apolipoproteins, which influence their function.

What interesting question
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.