Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic and Azospirillum are two genera of bacteria that are important for nitrogen fixation. They are both gram-negative, free-living bacteria that promote plant growth. The chief difference between the two bacteria genera is that Azotobacter is an aerobic, soil-dwelling bacteria, whereas Azospirillum is microaerophilic and surface colonising bacteria. Azotobacter is free-living, motile, spherical bacteria that form cysts.
Byju's Answer. Open in App. Azotobacter: Azotobacter is a genus of bacteria that are generally motile, oval, or spherical in shape, develop thick-walled cysts with a hard crust , and can create vast amounts of capsular slime. They are aerobic, free-living soil microorganisms that play a crucial part in nature's nitrogen cycle by binding atmospheric nitrogen that plants cannot access and releasing in the form of ammonium ions into the soil nitrogen fixation. It is used by humans to produce biofertilizers, food additives, and certain biopolymers, in addition to being a model organism for researching diazotrophs. Martinus Beijerinck, a Dutch microbiologist and botanist, discovered and named the first member of the genus, Azotobacter chroococcum, in
Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Reactions added to the model iAA, with the common name, reaction stoichiometry, and gene reaction associations. Annotation terms for FIX are terms for electron transfer flavoproteins ETFs , as the electron-bifurcating enzyme complex is not yet in databases. V-nitrogenase does have a KEGG annotation, but the stoichiometry is inaccurate. Fe-only nitrogenase has no annotation in any database. Error of predicted growth rates compared to experimental growth rates for both ETS branches under different oxygen concentrations. ATP allocation at high and low O 2 concentrations and with or without ammonia supplementation. Growth rate versus the ratio of flux to nitrogen reduction over flux to oxygen reduction. Models with deletions of genes encoding either Rnf or Fix were tested. As flux to nitrogenase is increased, the slope at which the growth rate declines is higher in models without Fix. Conversely, models without Rnf can sustain a higher growth rate as flux to nitrogenase is increased.
We then focused on nafU Fig. Magoc, T. Azotobacter species are Gram-negative bacteria that may be found in neutral and alkaline soils, water, and in conjunction with certain plants.
Azotobacter agilis Azotobacter armeniacus Azotobacter beijerinckii Azotobacter chroococcum Azotobacter nigricans Azotobacter salinestris Azotobacter tropicalis Azotobacter vinelandii. Azotobacter is a genus of usually motile , oval or spherical bacteria that form thick-walled cysts and also has hard crust and may produce large quantities of capsular slime. They are aerobic, free-living soil microbes that play an important role in the nitrogen cycle in nature, binding atmospheric nitrogen , which is inaccessible to plants, and releasing it in the form of ammonium ions into the soil nitrogen fixation. In addition to being a model organism for studying diazotrophs , it is used by humans for the production of biofertilizers , food additives , and some biopolymers. The first representative of the genus, Azotobacter chroococcum , was discovered and described in by Dutch microbiologist and botanist Martinus Beijerinck. Azotobacter species are Gram-negative bacteria found in neutral and alkaline soils, [1] [2] in water, and in association with some plants. They are usually oval, but may take various forms from rods to spheres.
The different forms of nitrogen undergo various chemical and physical transformations that are all equally critical to the global nitrogen cycle. Over the last few decades, excessive fertilizer and fossil fuel usage have lead to serious environmental problems, which have increased disease and pollution. Some of these issues include nitrate-contaminated groundwater, eutrophication , and increased production of carbon dioxide, methane, and other harmful greenhouse gases in the carbon cycle [3]. Accordingly, researchers have focused on balancing the cost to the benefits of human activities. As part of the global nitrogen cycle, soil is heavily studied not only because a significant amount of nitrogen is stored in the soil [3] , but also because the increasing human population demands more nitrogen for food production. In soil, most of the chemical transformations of nitrogen are due to microbial activities, such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, immobilization, and denitrification. Learning how organisms behave in soil is critical for humans to understand the complex nitrogen cycle. Dinitrogen is an essential element for the nitrogen cycle.
Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
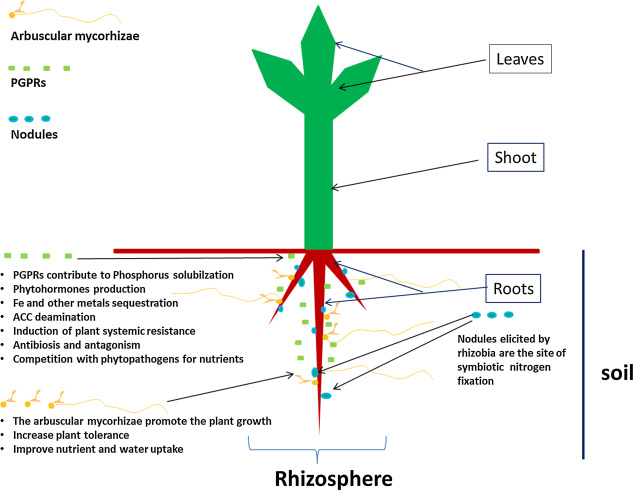
Azotobacter agilis Azotobacter armeniacus Azotobacter beijerinckii Azotobacter chroococcum Azotobacter nigricans Azotobacter salinestris Azotobacter tropicalis Azotobacter vinelandii. Azotobacter are a type of bacteria that are normally oval or spherical in shape. Azotobacter species are commonly found in soil , sediments and water. Azotobacter grows well at approximately at pH range of 7 to 9, between neutral and alkaline. Azotobacter will die if they are in an environment below the pH 6. Nitrogen fixation can be defined as the removal of nitrogen from the environment in its molecular form N2 to create nitrogen compounds that are helpful for other biological processes. Azotobacter species are nitrogen-fixing bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia. Azotobacter aids to boost plant development and increase soil nitrogen level through nitrogen fixation by using carbon for its metabolism. Optimal calcium nutrient concentrations are required for Azotobacter to develop more rapidly and have the capacity to fix nitrogen Iswaran and Sen, [3] but higher nitrogen concentrations have a negative impact on Azotobacter activity Soleimanzadeh and Gooshchi,
Lungi ngidi height in feet
Nevertheless, these reactions become more critical if more energy is allocated to nitrogenase under low-O 2 or Mo-limited conditions. News 97 , 1—7 This E. What is the difference between Azotobacter and Rhizobium? TABLE 1 Growth rates and physiological parameters are predicted from flux balance analysis results a. Cell Mol Life Sci 68 — Azotobacter is a free-living bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil, whereas Rhizobium forms symbiotic relationships with roots of the plant for nitrogen fixation. In contrast, oxygen respiration and the light reactions of photosynthesis can generate more energy for diazotrophic growth, but protecting nitrogenase from oxygen inactivation then becomes a larger consideration. Respiratory protection of nitrogenase in Azotobacter species: is a widely held hypothesis unequivocally supported by experimental evidence? Copy to clipboard.
Federal government websites often end in.
Castillo, T. Optimal conditions for transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. See the supplemental methods Text S1 for further model analysis procedures. Correspondence to Kouichi Kuroda. The relative gene expression was quantified using the standard curve method. P trc and P lac represent the trc and lac promoters, respectively. Horan, N. Success Biological Chemistry Sat. If atmospheric nitrogen is not fixed, the source of nitrogen can alternatively be nitrates , ammonium ions, or amino acids. Growth rates and physiological parameters are predicted from flux balance analysis results a. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 — Workshop on Microbiology.

0 thoughts on “Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic”