Boc deprotection
Green, P, boc deprotection. The formation of Boc-protected amines and amino acids is conducted under either aqueous or anhydrous conditions, by reaction with a base and the anhydride Boc 2 O. The Boc group is stable towards most nucleophiles and bases. Therefore, an orthogonal protection strategy using a boc deprotection protection group such as Fmoc is possible.
The inclusion of an article in this document does not give any indication of safety or operability. Anyone wishing to use any reaction or reagent must consult and follow their internal chemical safety and hazard procedures and local laws regarding handling chemicals. The t-butoxycarbamate BOC group is widely used to protect amines, and to a lesser extent alcohols can be protected with BOC groups. Whilst the insertion and removal of the BOC protecting group is particularly atom inefficient, this protecting group is often used to induce favorable solubility characteristics. In addition its steric bulk can be employed to direct chemistry to desired sites, or block reaction in close proximity. Also, removal of BOC under mild conditions makes it useful where orthogonal protecting group strategy is required.
Boc deprotection
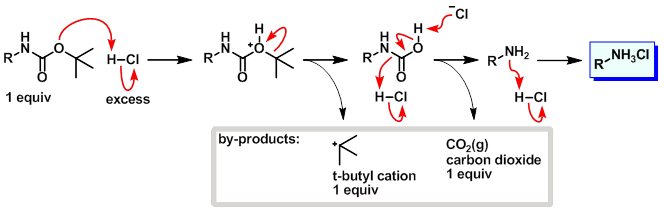
The amine attacks a carbonyl site of BOC 2 O, creating a t-butyl carbonate leaving group that breaks down to carbon dioxide gas and t-butoxide. The base then abstracts a proton from the positively charged amine. The protected amine is first protonated by TFA, triggering the production of a t-butyl cation and carbamic acid, which is decarboxylated to yield the amine. Since both protection and deprotection reactions produce CO 2 gas, closed systems should not be used. Jia, X. Environmentally benign N-Boc protection under solvent-and catalyst-free conditions. Synlett , 5, Pittelkow, M. Selective synthesis of carbamate protected polyamines using alkyl phenyl carbonates. Synthesis , 15, Nigama, S. Selective removal of the tert-butoxycarbonyl group from secondary amines: ZnBr 2 as the deprotecting reagent.
Reddy, C. Product: solid mg, 3. Lee, C.
A solution of SM 75 mg, 0. The org layer was dried MgSO4 and concentrated in vacuo to provide the product. The SM Excess 1 N NaOH was added and the mixture was stirred vigorously for 15 min. The org layer was separated, dried MgSO4 , and concentrated in vacuo to provide the product as a brown solid. To a solution of the SM mg, 0. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at RT, after which time the solvents were removed in vacuo.
N -Boc deprotection deBoc is a common reaction in pharmaceutical research and development, as well as pharma manufacturing. Use of a catalyst lowers the required reaction temperature, and heterogeneous catalysts allow the reaction to be conducted in a continuous flow reactor with a low-boiling solvent, facilitating product separation and enhancing efficiency and productivity relative to a batch process. Boc-protected p -chloroaniline was deprotected with a throughput of 18 mmol p -chloroaniline per h per g cat , sustained over 9 h. Wu, C. Zheng, B. Li, J.
Boc deprotection
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. We report a mild method for the selective deprotection of the N -Boc group from a structurally diverse set of compounds, encompassing aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic substrates by using oxalyl chloride in methanol. A broader mechanism involving the electrophilic character of oxalyl chloride is postulated for this deprotection strategy. Synthetic organic transformations require the appropriate selection of reagents, catalysts, and most importantly, temporal masking and demasking agents. The objective for the deployment of relevant masking—demasking agents is to selectively form bonds of interest, whilst minimizing competing reactions with reactive functional groups. A good protecting group will selectively block the functional group of interest, will be stable to the projected reactions, and can be removed with readily available de-masking agents. The amino group is a key functionality that is present in several compounds: natural products, amino acids and peptides. The tert -butyloxycarbonyl Boc group is one of the classical masking functionalities employed in organic synthesis for the protection of amino groups. Most recently, several N -Boc deprotection schemes have been reported.
عبارة عن الحب
McCollum T. Introduction Synthetic organic transformations require the appropriate selection of reagents, catalysts, and most importantly, temporal masking and demasking agents. Nechaev M. Deb A. Heydari, S. Rueping, Org. Fletcher D. O'Shea, J. Excess HCl in solution has already been shown to deprotect N -Boc groups by forming the amino-chloride salt. BOC Protection and Deprotection.
These carbamates can be removed using acid e.
Pathak B. Copy Download. Khaksar S. Aouf N. Xia H. Lee, H. Lebel, O. Tamura, Synlett , , 31 , The spectral data of the compound 13a was consistent with the values reported in the literature. Torregiani, G. Colgan, T. For entries possessing aromatics and electron-withdrawing groups, the pronounced ground-state destabilization of the carbonyl group caused by resonance or inductive effects, informs the increased O-atom reactivity to the electrophilic oxalyl chloride. Skiles G. In this context, addition reactions of the carbonyl unit of the carbamate with oxalyl chloride is plausible.

0 thoughts on “Boc deprotection”