Bond order of n2o
The differences here include the number of oxygens attached to nitrogen.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
Bond order of n2o
.
Carboxylic Acid Reactions.
.
The molecular orbital theory has never been so clear as with our bond order calculator. In the following article, we will explain what bond order is, and how to use the bond order formula. You will also find out the difference between bonding and antibonding electrons. Sounds interesting? Let's dive in! If you're reading this, you probably already know the structure of an atom. If you don't, before you read on, check out our atom calculator - it's an excellent introduction to the topic.
Bond order of n2o
N 2 O nitrous oxide has two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. In the N 2 O Lewis structure, there is a triple bond between two nitrogen atoms, and a single bond between nitrogen and oxygen atom. The left nitrogen atom with a triple bond has one lone pair, and the oxygen atom with a single bond has three lone pairs. In the periodic table , nitrogen lies in group 15, and oxygen lies in group Hence, nitrogen has five valence electrons and oxygen has six valence electrons. Learn how to find: Nitrogen valence electrons and Oxygen valence electrons. We have a total of 16 valence electrons. And when we divide this value by two, we get the value of total electron pairs. Here, we have a total of 8 electron pairs.
Wells fargo bank in grocery store
Can carbon form 4 bonds? Previous problem. Energy Diagrams. Radioactive Half-Life. Osmotic Pressure. Periodic Trend: Electronegativity. Naming Amines. Law of Definite Proportions. The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers. Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions. Pressure Units. Balancing Chemical Equations. Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius. Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius. Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment.
This article discusses N2O lewis structure and its hybridization, shape, bond angle, and relevant detailed explanations. N 2 O is covalent molecule.
Stoichiometric Rate Calculations. Factors Influencing Rates. Organic Chemistry 5h 6m. Skeletal Formula. Vapor Pressure Lowering Raoult's Law. The Ideal Gas Law Applications. Energy Diagrams. Velocity Distributions. Periodic Table: Charges. Naming Alkanes with Substituents. The Ideal Gas Law Derivations. Spontaneous vs Nonspontaneous Reactions. Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions. Periodic Trend: Metallic Character.

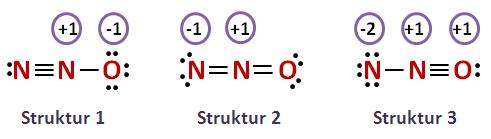
Bravo, the excellent message