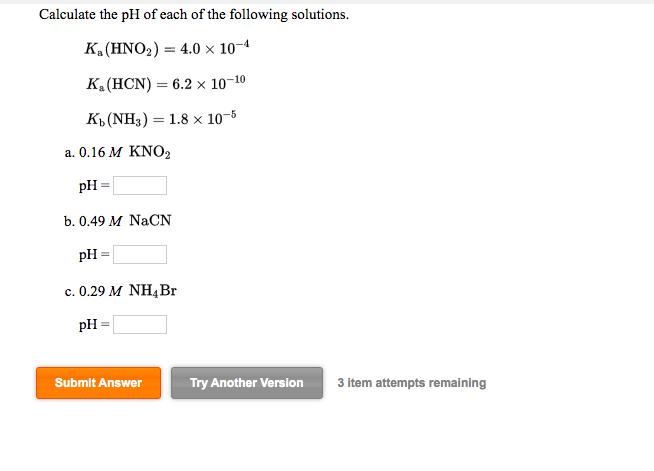
Calculate the ph of each of the following solutions
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter.
Interpretation: The pH value for each of the given solutions to be calculated. Concept introduction: The pH of a solution is defined as a figure that expresses the acidity of the alkalinity of a given solution. The value of K w is calculated by the formula,. To determine: The pH value for each of the given solution of 0. The pH of the given solution of 0.
Calculate the ph of each of the following solutions
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs. Extensive Properties. Scientific Notation. Metric Prefixes. Significant Figures. Significant Figures: Precision in Measurements.
Intermolecular Forces.
Determine the pH of each of the following solutions. If a solution has a pH of 8. Is the solution acidic or basic? What is the molarity of hydronium ion in the solution? Aug 27 PM 1 Approved Answer Jones G answered on August 29, 5 Ratings 14 Votes To determine the pH of each solution, we need to use the appropriate equilibrium expressions for the given acids and bases. Ask your question!
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Introduction to acids and bases. About About this video Transcript. Created by Jay. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted.
Calculate the ph of each of the following solutions
The pH scale runs from 0 to 14—a value of seven is considered neutral, less than seven acidic, and greater than seven basic. To calculate it, take the log of a given hydrogen ion concentration and reverse the sign. See more information about the pH formula below. Here's a more in-depth review of how to calculate pH and what pH means with respect to hydrogen ion concentration, acids, and bases. There are several ways to define acids and bases, but pH specifically only refers to hydrogen ion concentration and is applied to aqueous water-based solutions. When water dissociates, it yields a hydrogen ion and a hydroxide. See this chemical equation below.
Stifel financial advisor
The resultantmixture is then evaporated in The Ideal Gas Law Applications. Lattice Energy. Structural Formula. Periodic Trend: Successive Ionization Energies. Problem 40E: Write the dissociation reaction and the corresponding Ka equilibrium expression for each of the Millikan Oil Drop Experiment. A clean metal surface is irradiated with light of three different wavelengths? Speed of Light. Which is the stronger acid, HCl or Problem E: Zinc hydroxide is an amphoteric substance. Gases 3h 54m.
The pH of an aqueous solution is the measure of how acidic or basic it is.
It is intended primarily for allied health majors and for students needing to fulfill a Equilibrium Constant K. Exam Duration: 3 hours Reading Time: 15 minutes This paper has 25 pages The Ideal Gas Law. Standard Temperature and Pressure. Vapor Pressure Lowering Raoult's Law. Conversion Factors. Problem CP: Calculate the mass of sodium hydroxide that must be added to 1. Nitrogen Family Reactions. Reger, Scott R. Alcohol Reactions: Substitution Reactions. Constant-Volume Calorimetry. The K a value is 2. Collision Theory. Hess's Law.

Where I can read about it?