Carbon dioxide lewis dot
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is Carbon dioxide lewis dot double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure.
The Lewis structure is an image of atoms and atomic bond structures in a molecule that indicate the presence of lone pairs of electrons, named after the American physical chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. Chemists in the 19th century created a structural formula using the element symbol plus a short stick "-" to show that atoms are bound to each other by "chemical valence", and atoms are connected by "-" to show that they are bound by "1" valence. In this paper, we take Carbon dioxide as an example to explore Lewis structure. Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a colorless, odorless gas present throughout the atmosphere and is an essential compound for life on Earth.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
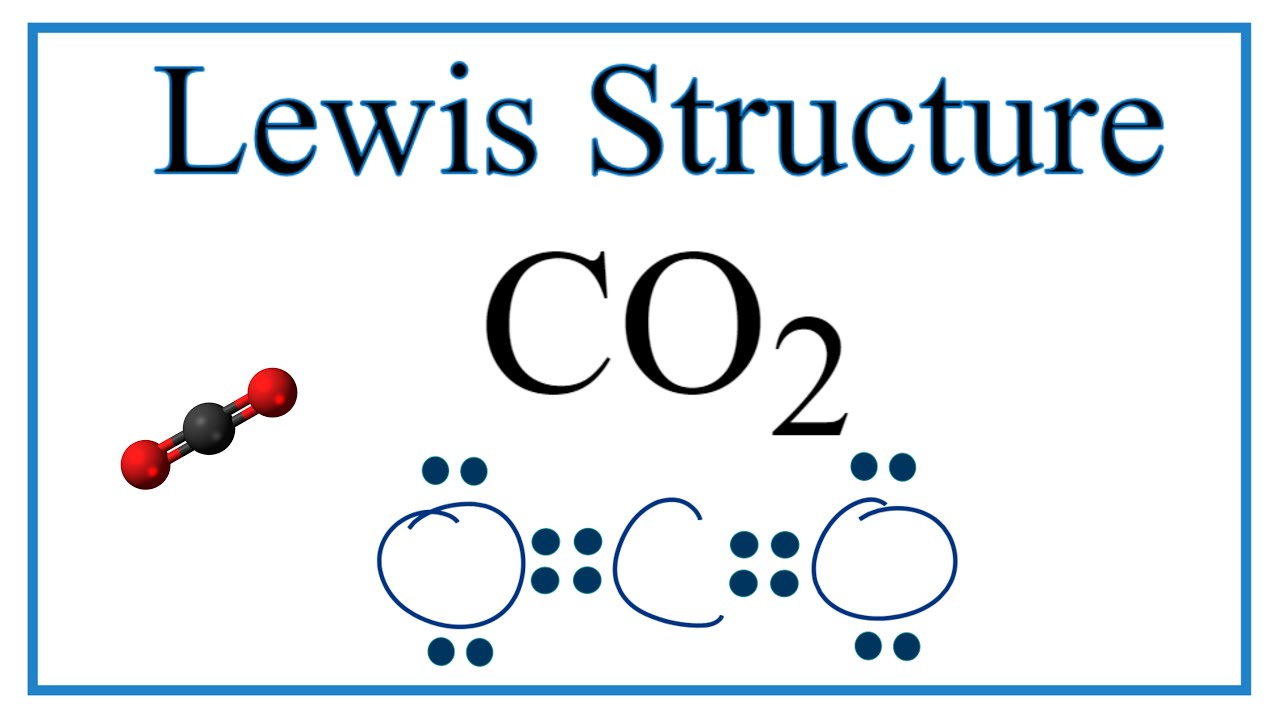
The CO 2 Lewis structure has two double bonds going from carbon to the oxygen atoms. According to the octet rule , each oxygen atom needs to bond twice and the carbon atom needs to bond four times. Carbon has four valence electrons that form a total of four bonds. So carbon is shown with four dots around it. Oxygen needs just two bonds, represented as the lone dots to the left and right of the O atoms. The first thing about the CO 2 Lewis structure is to put carbon in the center. Make both O atoms connect to C. As a rule, carbon is always going to be in the center, and the other atoms connect to it. Second, connect the lone dots on each O to the C in the center. Each O needs to bond twice. And carbon needs four bonds.
You may like Is argon flammable?
.
Carbon dioxide CO 2 lewis structure has two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. There are two double bonds around carbon atom in the CO 2. No lone pairs on carbon atom and each oxygen atom has two lone pairs on their valence shells. Shape of CO 2 is linear. Steps of drawing the lewis structure of CO 2 are explained in detail in this tutorial.
Carbon dioxide lewis dot
Ionic bonding typically occurs when it is easy for one atom to lose one or more electrons, and for another atom to gain one or more electrons. However, some atoms will not give up or gain electrons easily. Yet they still participate in compound formation. There is another mechanism for obtaining a complete valence shell: sharing electrons. When electrons are shared between two atoms, they form a covalent bond. Let us illustrate a covalent bond by using H atoms, with the understanding that H atoms need only two electrons to fill the 1 s subshell. Each H atom starts with a single electron in its valence shell:. We can use circles to show that each H atom has two electrons around the nucleus, completely filling each atom's valence shell:.
Colombianas culonas
There are no lone pairs in the carbon atom. So it works out that C bonds with each O twice. Use and Mechanism of Carbon dioxide Dec 9, Carbon dioxide CO2 is a naturally occurring colorless and odorless gas. Sign in Account Toggle child menu Expand. Carbon has four valence electrons that form a total of four bonds. As a result, the carbon atom takes on a linear molecular shape with symmetric charge distribution. Start Quiz. Your result is as below. Did not receive OTP? Total electron pairs are calculated by dividing the total valence electron count by two. Self Paced Toggle child menu Expand. Oxygen needs just two bonds, represented as the lone dots to the left and right of the O atoms. Lesser known, atmospheric CO 2 also absorbs into oceans, where it can form carbonic acid, which can interfere with animals that produce calcium carbonate shells. Second, connect the lone dots on each O to the C in the center.
One of the postulates of the Lewis Dot Structure for representing molecules is that a bond is the result of a pair of electrons being shared between two different nuclei, and as such, can be represented as a line between the two nuclei the letters that represent the elements involved. But what if the electrons are shared between more than two nuclei? When this happens, there is no one Lewis Dot Structure that accurately describes the molecule.
What is Lewis structure? What is it used for? Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom. Is CO 2 polar or non-polar? Generally, small symmetric molecules are nonpolar. The two oxygen atoms have equal electronegativity, so they pull electron density from carbon at an angle of degrees from either direction. One On One Toggle child menu Expand. Each oxygen atom in the CO 2 molecule has two lone pairs of electrons. CO2 Double Bond. In particular, all these two double bonds are located around carbon atoms. The Lewis structure of CO 2 is shown below:. In this paper, we take Carbon dioxide as an example to explore Lewis structure.

0 thoughts on “Carbon dioxide lewis dot”