Catalytic site atlas
Present addresses: Gemma L. Julius O. Nicholas Furnham, Gemma L.
Our objectives with M-CSA are to provide an open data resource for the community to browse known enzyme reaction mechanisms and catalytic sites, and to use the dataset to understand enzyme function and evolution. We are releasing M-CSA as a new website and underlying database architecture. At the moment, M-CSA contains entries, of these with detailed mechanism information, and with information on the catalytic site residues only. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. NAR Journals.
Catalytic site atlas
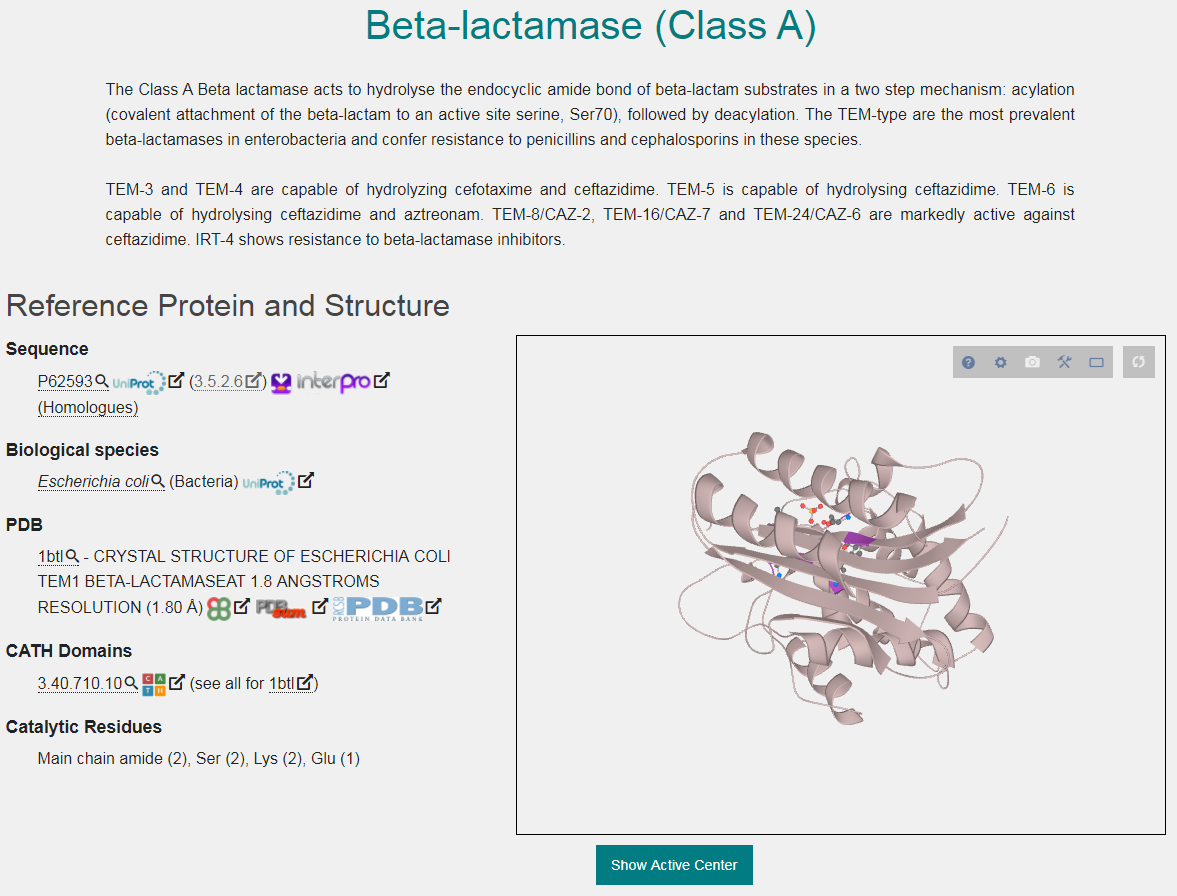
M-CSA is a database of enzyme reaction mechanisms. It provides annotation on the protein, catalytic residues, cofactors, and the reaction mechanisms of hundreds of enzymes. There are two kinds of entries in M-CSA. Glutamate racemase is responsible for the synthesis of D-glutamate, an essential building block of peptidoglycan, found in bacterial cell walls where it provides structural integrity. Due to its uniqueness to bacteria, peptidoglycan, and enzymes involved in its biosynthesis, are targets for designing new antibacterial drugs. Peptidoglycan is formed from a repeating unit of a disaccharide, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to which a small group of amino acids L-alanine, D-alanine, D-glutamate and either lysine or diaminopimelic acid are covalently attached. The presence of D-amino acids protects the cell wall from proteases which can only recognise the L-isomer. As of 25th February , M-CSA contains hand-curated entries, of them with detailed mechanistic description. Glutamate racemase. Last updates Summer - More entries with mechanism details The number of entries with a detailed mechanism description has been extended from to thanks to Amelia Brasnett, Morwenna Hall, Charity Hornby, and James Willey who have worked as interns in the Thornton group over the Summer. The new website facilitates the data entry process and supports different mechanism proposals, among others improvements. DOI: PMID:
Related Databases Citing. Permissions Icon Permissions. CSA 2.
Understanding which are the catalytic residues in an enzyme and what function they perform is crucial to many biology studies, particularly those leading to new therapeutics and enzyme design. The curated entries are used, along with the variation in residue type from the sequence comparison, to generate 3D templates of the catalytic sites, which in turn can be used to find catalytic sites in new structures. The CSA database schema has been re-designed and both the CSA data and search capabilities are presented in a new modern web interface. The database consists of two types of annotated site: an original hand-annotated set containing information extracted from the primary literature, using defined criteria to assign catalytic residues, and an additional homologous set, containing annotations inferred by PSI-BLAST and sequence alignment to one of the original set. CSA Version 1. The CSA will be updated on a monthly basis to include homologous sites found in new PDBs, and new hand-annotated enzymes as and when their annotation is completed.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Understanding which are the catalytic residues in an enzyme and what function they perform is crucial to many biology studies, particularly those leading to new therapeutics and enzyme design. The curated entries are used, along with the variation in residue type from the sequence comparison, to generate 3D templates of the catalytic sites, which in turn can be used to find catalytic sites in new structures. The CSA database schema has been re-designed and both the CSA data and search capabilities are presented in a new modern web interface. As biological catalysts they facilitate the many metabolic processes and pathways that are critical for life to exist and have been the focus of studies by biologists and chemists for over years. They are also some of the principal targets in pharmaceutical drug development, with many approved drugs acting to modify the action of enzymes implicated in disease processes.
Catalytic site atlas
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. The database consists of two types of annotated site: an original hand-annotated set containing information extracted from the primary literature, using defined criteria to assign catalytic residues, and an additional homologous set, containing annotations inferred by PSI-BLAST and sequence alignment to one of the original set. CSA Version 1. The CSA will be updated on a monthly basis to include homologous sites found in new PDBs, and new hand-annotated enzymes as and when their annotatation is completed. Enzymes are amongst the most studied biological molecules and are vital for all processes of life. The catalytic activity of an enzyme is performed by a small, highly conserved constellation of residues within the active site.
Movie shows in vr punjab
Open in new tab Download slide. The new website facilitates the data entry process and supports different mechanism proposals, among others improvements. The template made from each curated entry can be accessed from relevant the CSA entry page as well as collectively being made available for download. The presence of D-amino acids protects the cell wall from proteases which can only recognise the L-isomer. To consolidate much of this information, two databases were developed: MACiE which stands for M echanism, A nnotation and C lassification i n E nzymes is a database of enzyme reaction mechanisms. D Shows the annotations held for each catalytic residues in each catalytic site. George RA et al. A number of people have contributed to the CSA over the years as annotators and developers. The Catalytic Site Atlas CSA 2 was established to provide curated annotations of the small number of highly conserved residues that are directly involved in undertaking the catalytic activity in enzymes whose structures have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank PDB 3. A free-text report of the overall reaction and mechanism are provided C with a reaction diagram marked up with groups conserved across the reaction and bond changes.
Our objectives with M-CSA are to provide an open data resource for the community to browse known enzyme reaction mechanisms and catalytic sites, and to use the dataset to understand enzyme function and evolution.
The CSA underwent several annotation cycles which extended both coverage and the level of annotation data captured. Each E. Sign In or Create an Account. Science and Mathematics. Julius O. CSA 2. More from Oxford Academic. Additionally, the CSA 2. To date, approximately a third of the entries have had this review completed. All the data in the CSA is downloadable and freely available to the academic community. They are also some of the principal targets in pharmaceutical drug development, with many approved drugs acting to modify the action of enzymes implicated in disease processes. More metrics information. Authoring Open access Purchasing Institutional account management Rights and permissions. Using a library of structural templates to recognise catalytic sites and explore their evolution in homologous families. Pearson, Janet M.

Bravo, remarkable idea