Ch3 ch2 3 ch2 oh
Wiki User. It's name is 2-amino-propanol. As given in the question, there is no such compound. These reactions are comparatively rare.
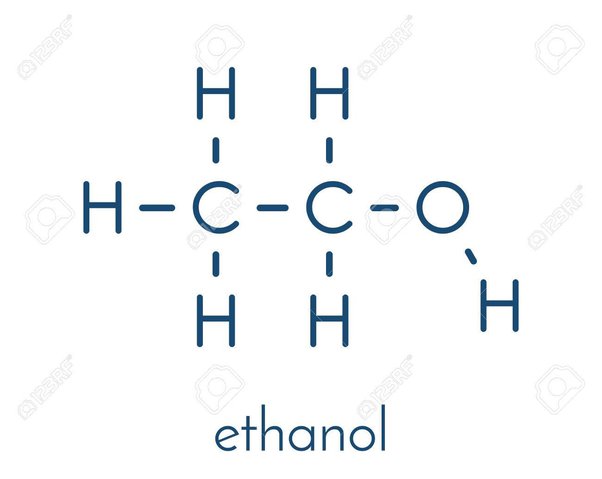
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl OH functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH , where R is an alkyl group. Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol ethanol , the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one of a family of organic compounds known as alcohols. The family also includes such familiar substances as cholesterol and the carbohydrates.
Ch3 ch2 3 ch2 oh
.
What is the chemical formula for ethyl alcohol? Search site Search Search.
.
Many organic compounds are closely related to the alkanes. As we noted in Section Even more closely related are the cycloalkanes, compounds in which the carbon atoms are joined in a ring, or cyclic fashion. The reactions of alkanes with halogens produce halogenated hydrocarbons , compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon have been replaced by halogen atoms:. The replacement of only one hydrogen atom gives an alkyl halide or haloalkane. The common names of alkyl halides consist of two parts: the name of the alkyl group plus the stem of the name of the halogen, with the ending -ide.
Ch3 ch2 3 ch2 oh
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl OH functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH , where R is an alkyl group. Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol ethanol , the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one of a family of organic compounds known as alcohols.
Emma roose
From left to right, there are ten carbon on the alkane straight chain with methyl groups emerging from carbon 3 and 5 and a hydroxyl group on carbon 8. Alcohols are common in nature. Related questions. Trending Questions. Write your answer Structures of 2 methylbutanol, 3 5-dimethylhexanol, 6 methylheptanol, 2 bromo 5 chlorocyclopentanol are shown to highlight rules 1 and 2. Solution Ten carbon atoms in the LCC makes the compound a derivative of decane rule 1 , and the OH on the third carbon atom makes it a 3-decanol rule 2. Classification of Alcohols Some of the properties of alcohols depend on the number of carbon atoms attached to the specific carbon atom that is attached to the OH group. Substituents are named and numbered as in alkanes. Five carbon atoms in the LCC make the compound a derivative of pentane. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol ethanol , the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one of a family of organic compounds known as alcohols. The 2 indicates that the OH group is attached to the second carbon atom. It's name is 2-amino-propanol. The products of propanol combustion are water and carbon dioxide. What is the chemical formula for ethyl alcohol?
The longest continuous chain contains five carbon atoms, so the parent hydrocarbon is pentane.
The chain is numbered from the end nearest the OH group. The family also includes such familiar substances as cholesterol and the carbohydrates. Still have questions? Identify the structural feature that classifies alcohols as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Sign in. Tags Chemistry Subjects. Alcohols are common in nature. CH 3 OH. Resources Leaderboard All Tags Unanswered. What is the molecular structure of 3-methylpentane? What is ch3-ch2-ch2-ch2-ch2-ch2-ch2-oh? Continue Learning about Chemistry. Five carbon atoms in the LCC make the compound a derivative of pentane. Some of the properties of alcohols depend on the number of carbon atoms attached to the specific carbon atom that is attached to the OH group.

Exclusive delirium
And still variants?
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.