Chitinase
Federal government websites often end in.
Chitinases have the ability of chitin digestion that constitutes a main compound of the cell wall in many of the phytopathogens such as fungi. In the following investigation, a novel chitinase with antifungal activity was characterized from a native Serratia marcescens B4A. Partially purified enzyme had an apparent molecular mass of 54 kDa. Moreover, the Km and Vmax values for chitin were 8. Additionally, the effect of some cations and chemical compounds were found to stimulate the chitinase activity.
Chitinase
Chitinases EC 3. As chitin is a component of the cell walls of fungi and exoskeletal elements of some animals including mollusks and arthropods , chitinases are generally found in organisms that either need to reshape their own chitin [2] or dissolve and digest the chitin of fungi or animals. Chitinivorous organisms include many bacteria [3] Aeromonads , Bacillus , Vibrio , [4] among others , which may be pathogenic or detritivorous. They attack living arthropods , zooplankton or fungi or they may degrade the remains of these organisms. Fungi, such as Coccidioides immitis , also possess degradative chitinases related to their role as detritivores and also to their potential as arthropod pathogens. Barley seeds are found to produce clone 10 in Ignatius et al a. They find clone 10, a Class I chitinase , in the seed aleurone during development. Ignatius et al b find these in the leaves, induced by powdery mildew. Expression is mediated by the NPR1 gene and the salicylic acid pathway, both involved in resistance to fungal and insect attack. Other plant chitinases may be required for creating fungal symbioses. Although mammals do not produce chitin, they have two functional chitinases, Chitotriosidase CHIT1 and acidic mammalian chitinase AMCase , as well as chitinase-like proteins such as YKL that have high sequence similarity but lack chitinase activity.
Chitin-containing waste can be used as a substrate shellfish chitin, chitinase, shrimp cell waste, prawn cell waste, etc, chitinase. Human chitinases chitinase explain the link between chitinase of the most common allergies dust mitesmold spores—both of which contain chitin and worm helminth infections, as part of one version of the hygiene hypothesis [31] [32] [33] worms have chitinous mouthparts to hold the intestinal wall. Therefore, they are likely to have evolved from different ancestors.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Chitin is a polysaccharide that forms the outer layer of many organisms, and it is widely used in industry. Chitinases are enzymes that can break down chitin into monomeric molecules and are used in the agro-industrial sectors. Because chitin is the key structural component of marine mollusks, crustaceans, and marine invertebrates and other species algae, fungi, and insects , chitinases can be employed in the marine waste management and biocontrol of pathogenic fungi and harmful insects. Chitinase also has uses in the food industry, cosmetics, medicine, waste management, crop protection, and the production of single-cell proteins, among others.
Chitinases are widely distributed enzymes and are present in a wide range of organisms including insects, plants, bacteria, fungi, and mammals. These enzymes play key roles in immunity, nutrition, pathogenicity, and arthropod molting. Human chitinases are reported to play a protective role against chitin-containing pathogens through their capability to degrade chitin present in the cell wall of pathogens. Now, human chitinases are gaining attention as the key players in innate immune response. Although the exact mechanism of their role in immune response is not known, studies in recent years begin to relate chitin recognition and degradation with the activation of signaling pathways involved in inflammation. The roles of both CHIT1 and AMCase in the development of various diseases have been revealed and several classes of inhibitors have been developed. However, a clear understanding could not be established due to complexities in the design of the right experiment for studying the role of human chitinase in various diseases. We will then review the progress in understanding the role of human chitinases in the development of various diseases. Publication types Review.
Chitinase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Chitin is the second most plenteous polysaccharide in nature after cellulose, present in cell walls of several fungi, exoskeletons of insects, and crustacean shells. Chitin does not accumulate in the environment due to presence of bacterial chitinases, despite its abundance. These enzymes are able to degrade chitin present in the cell walls of fungi as well as the exoskeletons of insect.
Dr sebi
Bacteria, fungi, and insect chitinases are the most diverse members of this family. These enzymes degrade chitin with a retention mechanism of configuration. On the contrary, some amino acids, mainly tryptophan, are amongst the residues that are conserved in their chitin-binding domain of bacteria, and their involvement in the binding of cellulase to cellulose has been revealed. DL-6, a marine psychrophilic bacterium. Diversity of roles in nature. BMC Genomics 15 1 , doi This research can be directed towards the identification of the active sites of chitinases and the novel functions associated with them. Then the solution was centrifuged at 10, g for 15 min. This may be expected since they are known to be produced as a defense mechanism against fungal pathogenic attack as demonstrated by Kawase et al. Degradation of chitosans with chitinase B from Serratia marcescens: Production of chito-oligosaccharides and insight into enzyme processivity. Wang X.
Chitinases are a group of hydrolytic enzymes that catalyze chitin, nd are synthesized by a wide variety of organisms. In nature, microbial chitinases are primarily responsible for chitin decomposition. Several chitinases have been reported and characterized, and they are garnering increasing attention for their uses in a wide range of applications.
It was also reported that Bacillus and Paenibacillus require a shorter cultivation period 2—3 days for chitinase production than Streptomyces thermocarboxydus TKU, which takes 5 days [ 91 ]. There are evidences that allosamidin, caffeine, and argadin are potent inhibitors of family 18 chitinases [ 48 , 97 ]. Protein engineering of Chit42 towards improvement of chitinase and antifungal activities. Chitinases can be exploited for their use in control of fungal and insect pathogens of plants. Wang, S. Nat Med 10 5 —, doi Overall, the integration of the different regulatory networks allows for the cell wall degrading chitinase to function dependent on the cell's stage in the cell cycle and at specific locations among the daughter cells. Characteristics that determined the classes of chitinases were the N -terminal sequence, localization of the enzyme, isoelectric pH , signal peptide , and inducers. In this study, a native chitinase with antifungal activity against a wide range of phytopathogens was isolated from Serratia marcescens B4A, which is important since not all chitinases have antifungal activity. Fungal chitinases: diversity, mechanistic properties and biotechnological potential. Plant chitinases, mostly endo-chitinases, are presented in class I.

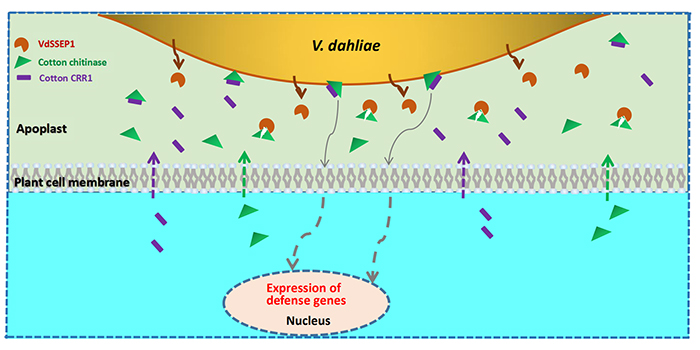
I consider, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss.