Clin var
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. ClinVar accessions submissions reporting human variation, interpretations of the relationship of that variation to human health and the evidence supporting each interpretation, clin var.
Interpretations of the clinical significance of variants are submitted by clinical testing laboratories, research laboratories, expert panels and other groups. ClinVar aggregates data by variant-disease pairs, and by variant or set of variants. Data aggregated by variant are accessible on the website, in an improved set of variant call format files and as a new comprehensive XML report. ClinVar recently started accepting submissions that are focused primarily on providing phenotypic information for individuals who have had genetic testing. ClinVar continues to make improvements to its search and retrieval functions.
Clin var
Genome Medicine volume 15 , Article number: 51 Cite this article. Metrics details. Curated databases of genetic variants assist clinicians and researchers in interpreting genetic variation. Yet, these databases contain some misclassified variants. It is unclear whether variant misclassification is abating as these databases rapidly grow and implement new guidelines. Using archives of ClinVar and HGMD, we investigated how variant misclassification has changed over 6 years, across different ancestry groups. We considered inborn errors of metabolism IEMs screened in newborns as a model system because these disorders are often highly penetrant with neonatal phenotypes. We used samples from the Genomes Project 1KGP to identify individuals with genotypes that were classified by the databases as pathogenic. We observed that African ancestry individuals have a significantly increased chance of being incorrectly indicated to be affected by a screened IEM when HGMD variants are used. However, this bias affecting genomes of African ancestry was no longer significant once common variants were removed in accordance with recent variant classification guidelines. Considering misclassified variants that have since been reclassified reveals our increasing understanding of rare genetic variation. We found that variant classification guidelines and allele frequency databases comprising genetically diverse samples are important factors in reclassification. We also discovered that ClinVar variants common in European and South Asian individuals were more likely to be reclassified to a lower confidence category, perhaps due to an increased chance of these variants being classified by multiple submitters. We discuss features for variant classification databases that would support their continued improvement.
Long-term economic impacts of exome sequencing for suspected monogenic disorders: diagnosis, management, and reproductive outcomes. The alteration in the record is archived, however, and will be able to be retrieved from the web clin var as record histories soon.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Automated variant filtering is an essential part of diagnostic genome-wide sequencing but may generate false negative results. We sought to investigate whether some previously identified pathogenic variants may be being routinely excluded by standard variant filtering pipelines. We evaluated variants that were previously classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic in ClinVar in known developmental disorder genes using exome sequence data from the Deciphering Developmental Disorders DDD study.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. Go to the search box in the gray area at the top of the page. Just type your search term and click on the Search button to the right of the search box. ClinVar can be searched with terms like:. In other words, when you enter a term or phrase of interest in the query box, that term or phrase will be processed to retrieve records that contain or have some relationship to the word s you entered.
Clin var
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Shower b&q
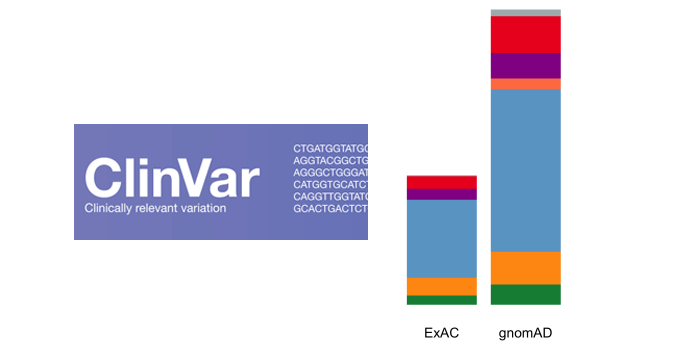
This work has several limitations. Scope ClinVar accepts submissions for variations identified through clinical testing, research and literature curation. Brenner Genome Medicine Rare disorders have many faces: in silico characterization of rare disorder spectrum Simona D. The site is secure. Please check for further notifications by email. The database is tightly coupled with dbSNP and dbVar, which maintain information about the location of variation on human assemblies. Certainly, 1KGP individuals are not expected to be enriched for disease, yet these studies found that the implied rates of disease were higher in 1KGP than the known disease prevalence. Abstract Purpose Automated variant filtering is an essential part of diagnostic genome-wide sequencing but may generate false negative results. Automated variant filtering is an essential part of diagnostic genome-wide sequencing but may generate false negative results. Historically, large-scale exome and genome sequencing projects from which MAF is often derived have undersampled non-European individuals [ 63 , 64 ].
.
Using orthogonal methods, researchers have identified variant features that are associated with the correct classification. We examined the responsible ClinVar variant and found this variant could not be ruled out as disease-causing. However, because the 1KGP hemizygous South Asian ancestry male NA has not yet reached the maximal age of onset, a pathogenic classification cannot be ruled out. We thank the members of the Brenner Lab for their suggestions to improve the project. Revision received:. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60, humans. Additional file 2: Table S2. HGMD rarely provides explanations for variant reclassification, so it is difficult to directly investigate why certain variants were reclassified. However, this bias affecting genomes of African ancestry was no longer significant once common variants were removed in accordance with recent variant classification guidelines. ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. It also meant that ClinVar variants that were not yet registered in dbSNP were excluded from the file. In this article, we describe recent improvements to ClinVar to make variant-centric data more accessible to enrich the phenotypic content of the database and to make searching the database easier. Advance article alerts.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - I am late for a meeting. I will return - I will necessarily express the opinion on this question.