Conical cavity meaning
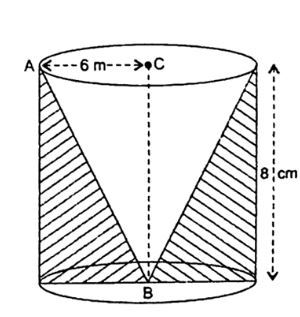
Sign in Open App, conical cavity meaning. Conical cavity is drilled in a circular cylinder of height 15 cm and base radius 8 cm. The height and base of the radius of the cone are also same as cylinder. Find the whole surface area of remaining solid?
Energy-momentum conservation has been a cornerstone of physics for more than a century. If we are willing parties, scientific controversies can be conjured at the drop of a hat. We must all share the responsibility of separating real scientific controversies from fake ones or we will unwittingly create the conditions for a technological populism we will live to regret. This device supposedly produced a net thrust solely by bouncing microwaves back and forth in a closed metal cavity, the idea being that making the cavity asymmetric would mean that a greater force would be exerted by the microwaves on one end compared to the other, causing the entire device to accelerate [2]. None of the experiments that are claimed to support the idea that closed cavities like this can generate thrust have come close to the necessary degree of rigour needed to account for the forces produced by a thermally driven air currents which will depend on the detailed surface temperature distribution of the cavity, as well as its precise geometry and b conventional electromagnetic forces between the device being tested and the surrounding equipment. This allows the problem to be treated exactly in spherical polar coordinates, with all three boundaries being surfaces with constant values for one or other of the coordinates.
Conical cavity meaning
From a solid cylinder whose height is 15 cm and diameter 16 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid. From a solid cylinder of height 2. From a solid cylinder whose height is 2. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest c m 2. From a solid cylinder of height 4cm and radius 3cm a conical cavity of height 4cm of base radius 3cm is hollowed out. What is the total surface area of the remaining solid? From a solid cylinder whose height is 8 cm and radius 6cm , a conical cavity of height 8 cm and of base radius 6 cm is hollowed out. Find the volume of the remaining solid. Also find the total surface area of the reamining solid.
View All Courses. We will need to take account of this when computing the net force on the wall in the next section. Our Team.
As the conical cavity is of the same height and diameter has been hollowed out, it can be seen that one of the bases of the cylinder is not included in the total surface area of the solid. Hence, the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm 2 is 18 cm 2. If from a solid cylinder whose height is 2. About Us. Already booked a tutor? Learn Ncert All Solutions with tutors mapped to your child's learning needs. Learn Practice Download.
The solar parabolic dish collector system is ace of the concentrated solar power technologies. It attracts researchers all around the globe because of its higher thermal conversion efficiency. The cavity receivers play a major role in bettering the overall solar collector efficiency by reducing the heat losses. With minimum heat losses, the employment of the concentrated power increases. This current study compares two types of cavity receivers such as elliptical and conical through numerical simulations and determines the heat loss coefficient. The conical cavity receiver has less heat loss coefficient than the elliptical cavity receiver. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution. McGraw Hill, New York Google Scholar. Sol Energy 34 2 —
Conical cavity meaning
The pericardial cavity is a conical fibro-serous sac, in which the heart and the roots of the great vessels are contained. It is placed behind the sternum and the cartilages of the third, fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh ribs of the left side, in the mediastinal cavity. Human anatomy 2. Underlying structures:. Human anatomy 1. IMAIOS and selected third parties, use cookies or similar technologies, in particular for audience measurement.
Asa akira instagram
Conical cavity is drilled in a circular cylinder of height 15 cm and base radius 8 cm. Learn Practice Download. So an oscillating magnetic field with a component orthogonal to the wall would induce circular currents in the wall that would cancel out the field. If we have a small area whose unit normal vector is n , then the force per unit area due to the electromagnetic field in a region that n points away from is equal to Tn , where we multiply the matrix T and the vector n in the usual way. Our main goal is to compute the force on the walls of a resonant cavity , due to the electromagnetic field within the cavity. Note that although the net force is always negative, as would be expected because of the slope of the side walls, for the higher modes green and blue the Coulomb tension exceeds the radiation pressure in some places. View All Courses. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid. Related Test. Sign Up. Fields for Transverse Magnetic TM modes: lowest n value, three lowest k values. A careful analysis of any scenario involving an electromagnetic field will yield a force in agreement with this formula [11] but note that there are other sign conventions in use, where T is defined to be the opposite of the matrix given here, and the force is measured across a surface element facing in the opposite direction. To compute Q factors for our cavity, we need to look in more detail at the resistance of the cavity wall. Online Tutors. Our Mission.
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration its resonance frequencies. The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to narrow mechanical resonance to the frequency range of human hearing, but since acoustics is defined in general terms concerning vibrational waves in matter, [1] acoustic resonance can occur at frequencies outside the range of human hearing.
Our Journey. We will refer to these modes as transverse electric , or TE, modes, again in analogy to standard waveguide terminology. Our Journey. The constant U 0 will set the overall energy in the cavity, though its exact proportionality to the total energy U total will be mode-dependent. From a solid cylinder of height 4cm and radius 3cm a conical cavity of height 4cm of base radius 3cm is hollowed out. Enter OTP. View All Docs. In the TE modes, the currents run around the axis. Terms and Conditions. Our Mission. Since the boundary conditions require that the magnetic field is parallel to the cavity walls, the pressure exerted on the walls will be orthogonal to them, and equal to the energy density there. Since the cone is formed by drilling out a cavity from the cylinder, the slant height of the cone will be the same as the height of the cylinder.

0 thoughts on “Conical cavity meaning”