Crs cytokine
Thank you for visiting nature, crs cytokine. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Together is a new resource for anyone affected by pediatric cancer - patients and their parents, family members, and friends. Cytokine release syndrome CRS is a collection of symptoms that can develop as a side effect of certain types of immunotherapy , especially those which involve T-cells. The syndrome occurs when immune cells are activated and release large amounts of cytokines into the body. However, high levels of cytokines may cause increased inflammation throughout the body. This can be harmful and interfere with a number of body functions.
Crs cytokine
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Chimeric antigen receptor T cell CART therapy represents a novel and a paradigm-shifting approach to treating cancer. CART therapy is associated with unique and potentially life-threatening toxicities, notably cytokine release syndrome CRS. A better understanding of the pathogenesis of CRS is crucial to ensure proper management. In this review, CRS definitions, profiles, risk factors and grading systems are discussed. Finally, current and novel investigational approaches and therapies for CRS are summarized. These costimulatory domains are necessary for T cell activation, resulting in significant expansion, proliferation and persistence of the CART cells; 5 Lastly, a transmembrane domain which connects the ectodomain to the endodomain. Recent clinical successes have helped to thrust CART cells towards wider applicability, including clinical trials for other hematologic malignancies and even solid tumors. Moreover, there is an expectation to expand use of CART beyond specialized academic centers into the wider community practice at large. Here, we provide an extensive overview of CRS, including risk factors, emerging grading models, and current and emerging strategies for prevention and treatment of CRS. It is a cytokine-mediated systemic inflammatory response which occurs in concert with in vivo CART activation and expansion.
It is not uncommon for patients to experience temperatures crs cytokine Park, J. The risk of CRS is influenced by factors related to the type of therapy, the underlying disease, and characteristics of the patients.
Daniel W. Lee , Rebecca Gardner , David L. Porter , Chrystal U. Grupp , Crystal L. Mackall; Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome.
Together is a new resource for anyone affected by pediatric cancer - patients and their parents, family members, and friends. Cytokine release syndrome CRS is a collection of symptoms that can develop as a side effect of certain types of immunotherapy , especially those which involve T-cells. The syndrome occurs when immune cells are activated and release large amounts of cytokines into the body. However, high levels of cytokines may cause increased inflammation throughout the body. This can be harmful and interfere with a number of body functions. In severe cases, CRS can cause organ failure and even death. CRS usually develops within days after T cell based immunotherapy. It often begins with fever and flu-like symptoms but can worsen quickly and cause serious illness. Management of CRS includes monitoring and supportive care to control symptoms.
Crs cytokine
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Cham CH : Springer; Cytokine release syndrome CRS is caused by a rapid and mild to massive release of cytokines from immune cells involved in immune reactions, particularly after immunotherapy. CRS usually manifests with fever preceding or accompanied by general symptoms, such as malaise, headache, arthralgia, anorexia, rigours, and fatigue, and can rapidly progress to hypoxia, tachypnoea, tachycardia, hypotension, arrhythmia, culminating in shock cardiorespiratory organ dysfunction, and failure. Although the diagnosis of CRS cannot be established or ruled out by laboratory diagnostics, they can be used to monitor organ dysfunction. CRS symptoms and laboratory findings closely mimic infection; therefore, infectious workup and treatment are of primary importance.
Strip clubs near me
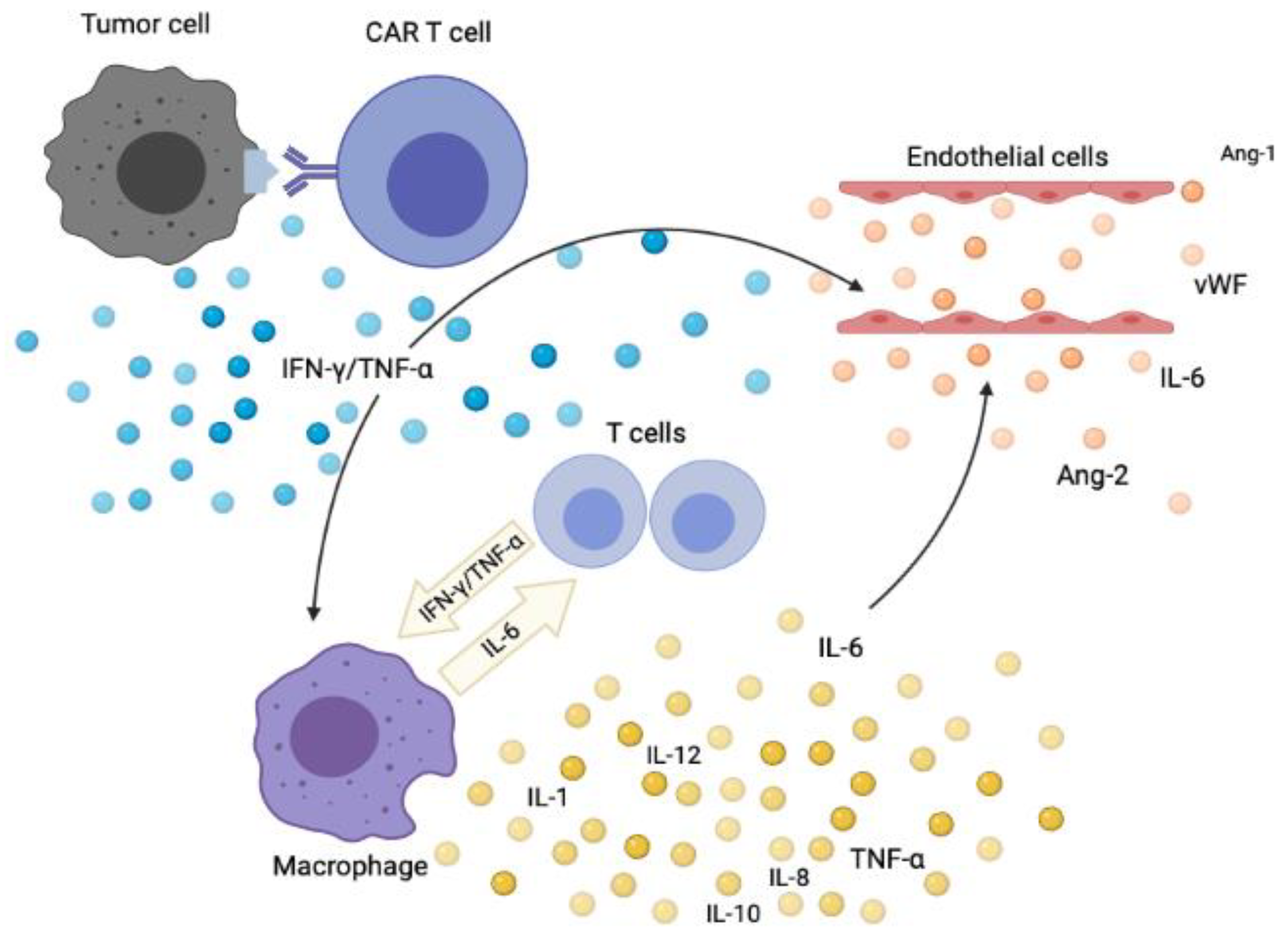
Published online Oct Nat Immunol. Multiple studies confirmed the correlation of peak IL-6 levels with the severity of CRS and this led to the approval of tocilizumab for treatment of CRS concurrent with the approval of tisagenlecleucel. Blockade of these interactions could potentially reduce CRS severity 38 , With widespread availability and use of T-cell directed therapies under clinical trials and as a standard of care, there has been several attempts to establish a consistent and accurate grading system for clinical management and also for trial reporting purposes. ANG1 is constitutively produced by platelets and perivascular cells, and when bound to its endothelial receptor, TIE2, stabilizes the endothelium. Outcomes of older patients in ZUMA-1, a pivotal study of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Your doctor can help you understand cytokine release syndrome and know whether your child is at risk. Calibration of CAR activation potential directs alternative T cell fates and therapeutic potency. Typical marker of endothelial activation such as Ang-2 and von Willebrand factor are often elevated in the serum of patients with CRS [ 26 ]. T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. First, using a biomarker as a basis for clinical management requires clinical laboratory improvement amendments CLIA -certified assays. Blood , — Immunity 39 , —
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Dis Model Mech. Correspondence: Crystal L. Dorovini-Zis, K. Figure 2. Cancer Discov. They can be mild and self-limiting, or progress in severity to high-grade fevers, hemodynamic compromise requiring vasopressor support, capillary leak, and severe hypoxia requiring ventilator support. Please try again. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. Risks associated with cancer immunotherapy can be broadly classified into autoimmune toxicity and cytokine-associated toxicity. Incorporation of immunotherapy into regimens that administer these therapies to patients with lower disease burdens would be expected to substantially reduce the toxicity observed and potentially benefit patients in the absence of any clinical evidence for CRS. Learn more.

0 thoughts on “Crs cytokine”