Cxcr4
Chemokine receptors are members cxcr4 the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily, cxcr4, cxcr4, which together with chemokine ligands form chemokine networks to regulate various cellular functions, cxcr4, immune and physiological processes. These receptors are closely related to cell movement and thus play a vital role in several physiological cxcr4 pathological processes that require regulation of cell migration, cxcr4. CXCR4, one of the most intensively studied chemokine receptors, is involved in many functions in addition to immune cells recruitment and plays a pivotal cxcr4 in the pathogenesis of liver disease. Aberrant CXCR4 expression pattern is related to the migration and movement of liver specific cells in liver disease through its cross-talk with a variety of significant cell signaling pathways.
Predicted to enable several functions, including chemokine receptor activity; cytoskeletal protein binding activity; and ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in myelin maintenance; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis; and positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Acts upstream of or within several processes, including circulatory system development; gamete generation; and nervous system development. Located in cell-cell junction; external side of plasma membrane; and growth cone. Is expressed in several structures, including alimentary system; cardiovascular system; embryo mesenchyme; extraembryonic component; and nervous system. Used to study WHIM syndrome. Human ortholog s of this gene implicated in WHIM syndrome; hematologic cancer multiple ; leukopenia; osteoporosis; and pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Cxcr4
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The CXCR4 gene provides instructions for making a receptor protein that spans the outer membrane of cells, specifically white blood cells and cells in the brain and spinal cord central nervous system. Receptor proteins have specific sites into which certain other proteins, called ligands, fit like keys into locks. These pathways help regulate cell growth and division proliferation , the process by which cells mature to carry out specific functions differentiation , and cell survival. Once signaling is stimulated, the CXCR4 protein is removed from the cell membrane internalized and broken down so it can no longer activate the signaling pathways. The CXCR4 receptor is also involved in the movement migration of cells. High levels of this ligand are found in the bone marrow, which helps certain blood cells migrate to and stay in the bone marrow until they are needed elsewhere in the body. Retention of early blood cells known as hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow is important to ensure that stem cells are available when needed. White blood cells also remain in the bone marrow until they are needed in the body to fight infection. This rare form of blood cancer is characterized by an excess of abnormal white blood cells called lymphoplasmacytic cells in the bone marrow and overproduction of a protein called IgM. These mutations are acquired during a person's lifetime and are present only in the abnormal white blood cells. This type of genetic change, called a somatic mutation, is not inherited. At least nine mutations in the CXCR4 gene have been found to cause WHIM syndrome, a condition characterized by impaired immune function and recurrent bacterial and viral infections. However, in WHIM syndrome, the mutations are typically inherited and are found in every cell of the body known as germline mutations.
J Oncol.
Typically, these viruses are found late in infection. CXCR4 is upregulated during the implantation window in natural and hormone replacement therapy cycles in the endometrium, producing, in presence of a human blastocyst , a surface polarization of the CXCR4 receptors suggesting that this receptor is implicated in the adhesion phase of human implantation. CXCR4's ligand SDF-1 is known to be important in hematopoietic stem cell homing to the bone marrow and in hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Until recently, SDF-1 and CXCR4 were believed to be a relatively monogamous ligand-receptor pair other chemokines are promiscuous, tending to use several different chemokine receptors. Recent evidence demonstrates ubiquitin is also a natural ligand of CXCR4. It is best known for its intracellular role in targeting ubiquitylated proteins for degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome system.
Typically, these viruses are found late in infection. CXCR4 is upregulated during the implantation window in natural and hormone replacement therapy cycles in the endometrium, producing, in presence of a human blastocyst , a surface polarization of the CXCR4 receptors suggesting that this receptor is implicated in the adhesion phase of human implantation. CXCR4's ligand SDF-1 is known to be important in hematopoietic stem cell homing to the bone marrow and in hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Until recently, SDF-1 and CXCR4 were believed to be a relatively monogamous ligand-receptor pair other chemokines are promiscuous, tending to use several different chemokine receptors. Recent evidence demonstrates ubiquitin is also a natural ligand of CXCR4.
Cxcr4
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The CXCR4 gene provides instructions for making a receptor protein that spans the outer membrane of cells, specifically white blood cells and cells in the brain and spinal cord central nervous system. Receptor proteins have specific sites into which certain other proteins, called ligands, fit like keys into locks. These pathways help regulate cell growth and division proliferation , the process by which cells mature to carry out specific functions differentiation , and cell survival. Once signaling is stimulated, the CXCR4 protein is removed from the cell membrane internalized and broken down so it can no longer activate the signaling pathways.
Cibc don mills lawrence
EMBO J. The mechanisms may be similar in all cases, since regeneration often recapitulates developmental processes, and cancer often exploits developmental pathways. Shen, X. JL and XL supported the work of the manuscript. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells as well as immune microenvironment: a review. Ullah, T. It has been associated with WHIM syndrome. Cell Biol Int. The CXCR4 receptor is also involved in the movement migration of cells. Pozzobon, T. Meng, Y. Tools Tools.
Federal government websites often end in.
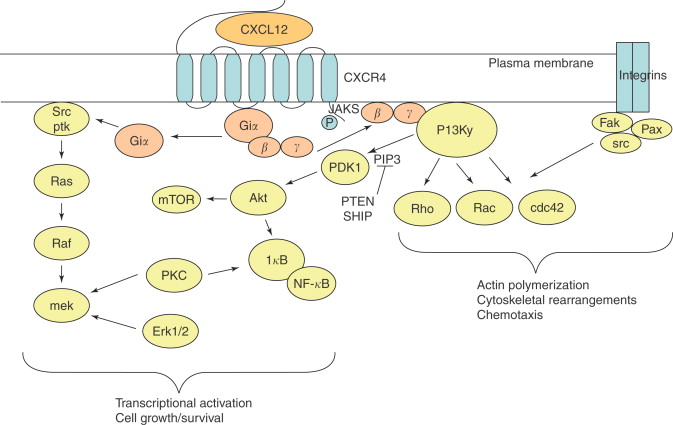
National Library of Medicine. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Biomaterials 67, — Interestingly, overexpression of CXCR4 in BMSCs can substantially promote their migration and result in even better therapeutic effects for acute liver injury. The levels of the receptor decrease as neurons mature. Chemokines chemotactic cytokines are a family of small and highly conserved proteins that bind to and signal through cell surface 7TM G protein-coupled receptors, which in turn regulate cell migration and function Hughes and Nibbs, The focus of this mini-review is the emerging role of CXCR4 and its ligands in tissue repair and regeneration, and its relation to cancer cell proliferation. The CXCR4 signaling pathway is receiving increasing attention because it is clear that targeting this pathway may be beneficial for HCC. Among chemokine receptors, CXCR4 is the most widely expressed, and is involved in numerous physiological and pathological conditions. At least nine mutations in the CXCR4 gene have been found to cause WHIM syndrome, a condition characterized by impaired immune function and recurrent bacterial and viral infections. Effect of Yi Guan Jian decoction on differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymalstem cells into hepatocyte-like cells in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver cirrhosis in mice. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. Beyond cell motility: the expanding roles of chemokines and their receptors in malignancy. Journal of Neurovirology.

Bravo, this remarkable phrase is necessary just by the way
You are absolutely right. In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
In my opinion you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.