Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
Read till the end to know more.
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon where electrons are emitted from the metal surface when light of sufficient frequency is incident upon it. The concept of the photoelectric effect was first documented in by Heinrich Hertz and later by Lenard in Hertz who had proved the wave theory himself did not pursue the matter as he felt sure that it could be explained by the wave theory. However, the concept failed in the following accounts:. Electrons emitted from underneath the metal surface lose some kinetic energy during the collision. But the surface electrons carry all the kinetic energy imparted by the photon and have the maximum kinetic energy.
Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
Albert Einstein, a German physicist, is considered one of the greatest scientists of all times. He has contributed to the fields of general relativity , black holes, photoelectric effect, to name a few. In , Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of the photoelectric effect. Einstein's idea about light was revolutionary and magnificent. He gave an efficient method of irradiation. Light has some tiny group of particles known as photons. These particles consist of higher energy, which is also called the quantum of radiation. Therefore, light is made up of packets of energy or quantum of energy. Photons carry momentum and energy from the source of light by which they are emitted. The discovery of the photoelectric effect was one of the greatest achievements of Einstein's life, for which he received the Nobel Prize. Einstein was the first to suggest that light is both a wave and a particle. This is called the wave-particle duality of light. The wave-particle duality is the fundamental concept behind quantum mechanics and the reason for the development of solar cells and electron microscopes. According to the Photoelectric effect, when a metal surface is irradiated with light of sufficient energy, it causes the electrons of the metal to eject out.
What is the threshold frequency? Below this frequency, there is no electron emission. Light is a collection of photons.
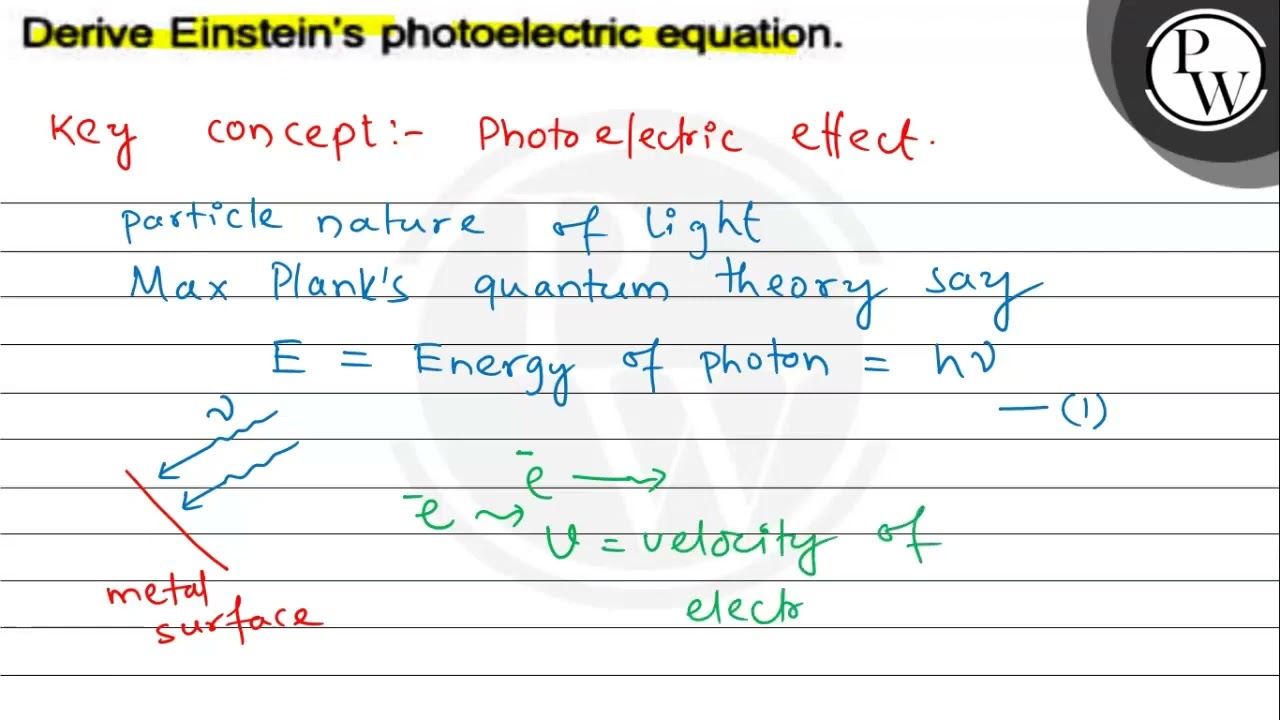
Einsteins photoelectric equation is. Write Einstein's photoelectric equation. What is photoelectric effect? Mention the Einstein's photoelectric equation. Explain the laws of photoelectric effect from the Einstein photoelectric equation.
Albert Einstein, a German physicist, is considered one of the greatest scientists of all times. He has contributed to the fields of general relativity , black holes, photoelectric effect, to name a few. In , Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of the photoelectric effect. Einstein's idea about light was revolutionary and magnificent. He gave an efficient method of irradiation.
Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Einstein's Photoelectric Equation. About About this video Transcript. Explaining the photoelectric effect using wave-particle duality, the work function of a metal, and how to calculate the velocity of a photoelectron. Created by Jay. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted.
Book cover keyboard
Einstein Photoelectric Equation: In , Albert Einstein explained the various laws of photoelectric emission on the basis of Planck. Einstein was the first to suggest that light is both a wave and a particle. Learn more. Table of Content. Zener diode Learn about the basics, applications, working, and basics of the zener diode. Define Uniform Circular Motion. When electrons are imparted with a threshold frequency v0 , they acquire enough energy to eject out of the surface. A metallic strip, when exposed to light or sun, will not be able to produce the Photoelectric effect unless the frequency is greater than the threshold value. On quantum of light radiation is called a photon which travels with the speed of light. Because increasing the intensity of low-intensity light will only increase the number of low-energy photons, no single photon with sufficient electron output will be produced. Trending Topics. From the experiments of the Photoelectric effect, it is found that no electron emission occurs if the incident radiation has a frequency less than the threshold frequency. The wave theory says that light of any frequency must eject electrons.
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which electrons are ejected from the surface of a metal when light is incident on it. These ejected electrons are called photoelectrons. The process through which photoelectrons are ejected from the surface of the metal due to the action of light is commonly referred to as photoemission.
Watch Now. What is threshold frequency in connecting with photoelectric effect? According to Einstein:. Who discovered electron? Since the middle of the nineteenth century, the spectrum of light emitted by atoms of gas has been thoroughly studied. Photoelectric current does not occur if the frequency of the incident radiation is below the threshold frequency. Learn more. The vacuum also facilitates electron microscopy by preventing gasses from interfering with electron passage between electrodes. In addition, emissions occur as soon as the light strikes; there is no apparent delay. Unit Of Mobility. However, the emission of electrons only happened for frequencies greater than that of a threshold frequency v0.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
You are absolutely right. In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
Yes well!