Electron dot structure of hno3
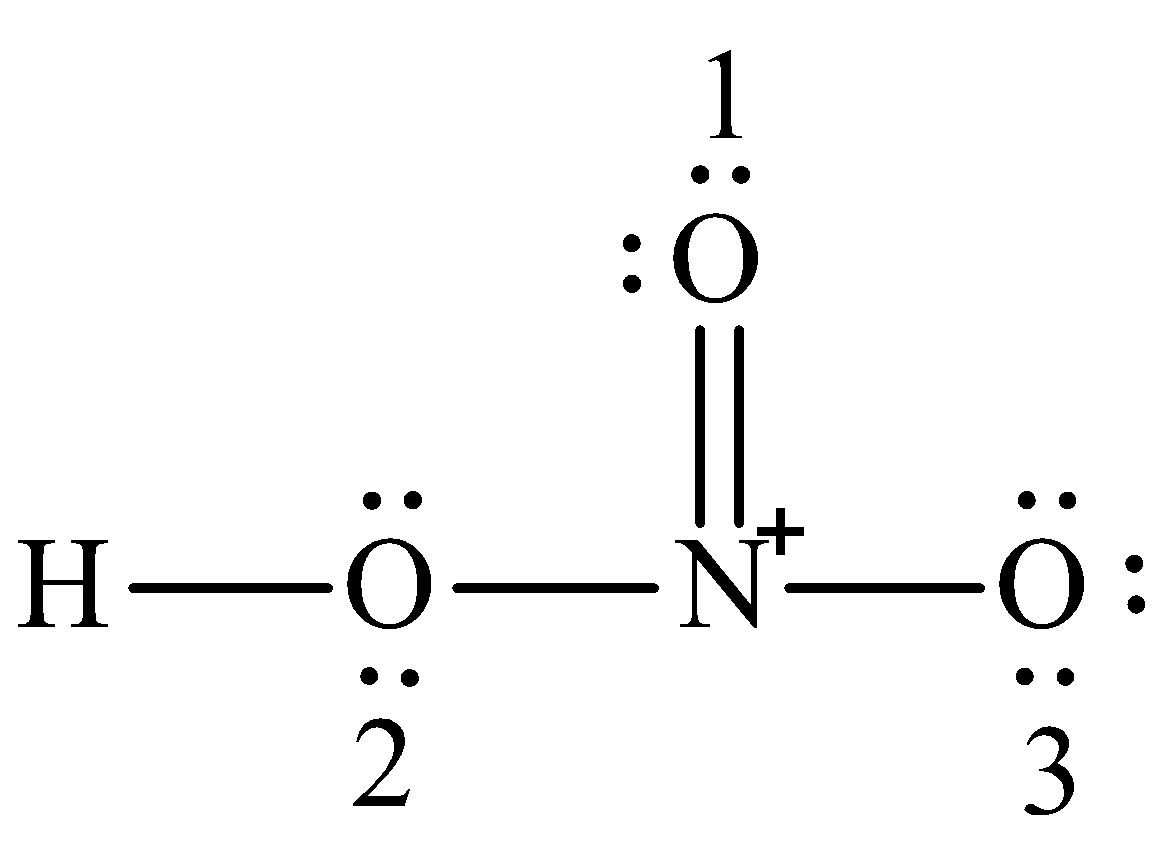
HNO 3 Nitric acid lewis stricture is drawn step by step by using valence electrons of each element, electron dot structure of hno3. There are no lone pairs on nitrogen atom and also there are charges on one oxygen atom and nitrogen atom. You can see those signs in the following figure.
Several worked examples relevant to this procedure were given in previous posts please see the Sitemap - Table of Contents Lewis Electron Dot Structures. Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and it dissolves practically all metals except gold and platinum and some other precious metals. As such, is an important raw material for the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. It is mainly used for etching and for the production of pure nitrates. Even though nitric acid was known since the 9th century - alchemists used it to separate gold and silver - its mass production started in when a German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald developed an industrial process. Initially it was used for the production of explosives but today its main use is for the production of fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate. Other main applications is for the production of explosives, nylon precursors and substituted organic compounds.
Electron dot structure of hno3
Draw the Lewis structure of HCN. Draw a Lewis structure of nitric oxide, NO. Draw the Lewis structure of B e C l 2. Draw the Lewis structure for S F 6. Draw the structure of : Perchloric acid. In the Lewis structure of acetic acid, there are. Draw the Lewis structure of iodine pentafluoride, I F 5. Draw the structure of an amino acid. Draw the structure of phosphinic acid H 3 P O 2. Draw a Lewis structure for nitrogen trichloride, N C l 3. Draw the Lewis structure of nitric acid, HNO3. Which one of the following molecules contains no pi - bond? Which of the following is a polar moleule? Which of the following is paramagnetic? According to MO theory which of thhe following lists makes the nitroge
Naming Alkynes. Density of Non-Geometric Objects.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
Electron dot structure of hno3
This pattern of adding a hydrogen atom to one of the oxygen atoms is frequently observed in many acids. To determine the total number of valence electrons in the HNO3 molecule and construct the Lewis structure, follow these steps:. Determine the total number of valence electrons. Identify the central atom. In HNO3, the nitrogen atom N is the central atom since it is less electronegative than oxygen. Remember : If hydrogen is present in the molecule, always place the hydrogen atoms on the outside. Place the remaining electrons around the atoms to satisfy the octet rule , except for hydrogen which only needs 2 electrons.
Cervantes restaurants
Alcohol Reactions: Substitution Reactions. Simple Cubic Unit Cell. Step 1 : The central atom will be the N atom since it is the less electronegative H is a terminal atom — it cannot be a central atom. Activity Series. Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius. Lever, J. Draw the structure of an amino acid. Naming Ionic Compounds. Which of the following is a polar moleule? Periodic Table: Elemental Forms. Molecular Polarity. Aqueous Equilibrium 4h 42m. Nuclear Chemistry 2h 34m.
Nitric acid HNO3 , a highly corrosive acid, is a very important chemical. It is usually a colorless liquid, but the older samples turn pale yellow because it gets decomposed into water and oxides of nitrogen. This toxic liquid has yellow or red-brown fumes that can cause serious damage to your eyes and nose.
Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions. Oxide Reactions. Internal Energy. Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy. Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and it dissolves practically all metals except gold and platinum and some other precious metals. Step 5: Since the number of remaining valence electrons 16 is two less than the number of electrons 18 required to complete all octets, one additional covalent bond must be introduced in such a way that the normal valency of every element if possible gets satisfied. To be the center atom, ability of having greater valance is important. Naming Alkynes. Draw the Lewis structure of nitric acid, HNO3. Measuring Radioactivity. Structural Formula. Organic Chemistry 5h 6m.

0 thoughts on “Electron dot structure of hno3”