Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions, enzymes byjus. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete. These enzymes are enzymes byjus produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. Lets look at some of its applications below.
The human body is composed of different types of cells, tissues and other complex organs. For efficient functioning, our body releases some chemicals to accelerate biological processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion and a few other metabolic activities to sustain a healthy life. Hence, enzymes are pivotal in all living entities which govern all the biological processes. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes.
Enzymes byjus
Education Business Technology. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Production of enzymes. Production of enzymes Adarsh Patil. Immobilization of enzymes. Immobilization of enzymes kamblesai Enzyme Immobilization and Applications. Enzyme Immobilization and Applications Madhukar Vedantham. Protein engineering. Protein engineering Pulipati Sowjanya.
Test your Knowledge on Enzymes!
Stay tuned for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory. Flashcards 1. A2-Level flashcards.
To live, grow, and reproduce, microorganisms undergo a variety of chemical changes. They alter nutrients so they can enter the cell and they change them once they enter in order to synthesize cell parts and obtain energy. Metabolism refers to all of the organized chemical reactions in a cell. Reactions in which chemical compounds are broken down are called catabolic reactions while reactions in which chemical compounds are synthesized are termed anabolic reactions. All of these reactions are under the control of enzymes. Enzymes are substances present in the cell in small amounts that function to speed up or catalyze chemical reactions.
Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. Lets look at some of its applications below. Enzymes are generally made of protein molecules except ribozymes. Enzyme molecules are highly specific to the substrates and convert them into products. They are active only in certain range of temperature and pH.
Lana paws
Welcome onboard. Your result is as below. Almost all enzymes are extremely sensitive to pH change. Hibiscus Flower Parts. Initially, substrates associate themselves by noncovalent interactions to the enzymes which include ionic, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Hashim khan July 8, at pm. Megha sajeevan August 18, at pm. Effect of Temperature and pH on enzyme activity clairebloom. Watch Now. An enzyme and its cofactor together constitute the holoenzyme.
Enzymes help with specific functions that are vital to the operation and overall health of the body. They help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function, and more.
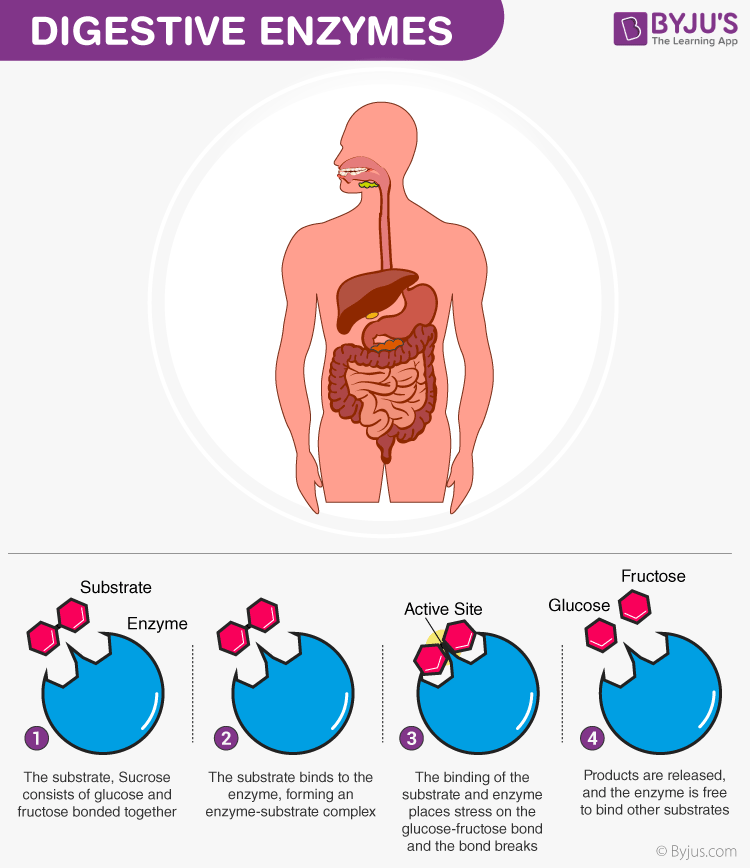
Oxaloacetate is formed within the enzyme EQ and gets released Q. Subham Panja. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. Protein engineering saurav. Another key characteristic of the ping-pong mechanism is that one product is formed and released before the second substrate binds. Effect of Temperature and pH on enzyme activity clairebloom. In cases where there is no activation energy provided, a catalyst plays an important role to reduce the activation energy and carried forward the reaction. Share Share Share Call Us. Customize your course in 30 seconds Which class are you in? Often, the active site is a cleft or a pocket produced by the amino acids which take part in catalysis and substrate binding. Also Read: Digestive Enzymes. Biology Applications of Enzymes. A-Level specific 1.

You are absolutely right. In it something is also thought good, I support.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will talk.