Equivalent resonance structures
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static, equivalent resonance structures. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame.
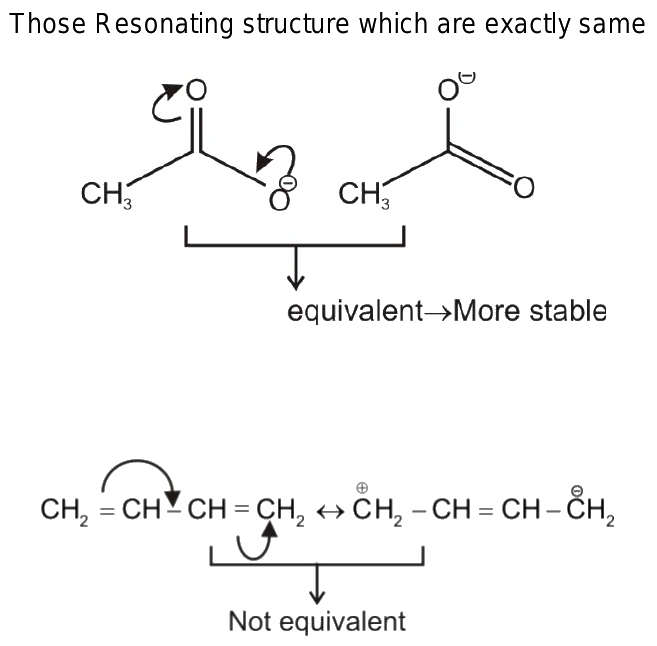
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the same , they are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow. There are three equivalent resonance structures for CO 3 2- , and the actual structure of CO 3 2- is a hybrid of the three resonance contributors.
Equivalent resonance structures
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. Learn more here. Chemists must know about equivalent resonance structures in their work. What are they, and why does it matter? Before getting into equivalent resonance structures, people must understand Lewis structures. They also indicate the bonds between atoms. Lewis structures can tell people important things, but only if they follow the correct steps when making them. Equivalent resonance structures have more than one Lewis structure representing them. They are chemical or molecular compounds with different electron and atom arrangements. Although each Lewis structure differs, these structures have the same stability and energy. North Carolina State University offers a free and interactive Lewis structure builder. Chemists also learn about non-equivalent resonance structures when training to enter the field. The main difference between these and equivalent resonance structures is that the former has different atom arrangements, and often, different atomic structures.
Join our newsletter! Curved arrow notation is used in showing the placement of electrons between atoms.
A resonance form is another way of drawing a Lewis dot structure for a given compound. Equivalent Lewis structures are called resonance forms. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms. Resonance structures arise when there are more than one way to draw a Lewis dot diagram that satisfies the octet rule. Remember the octet rule is where the atom gains, loses, or shares electrons so that the outer electron shell has eight electrons. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure.
The Resonance stabilization effect also known as the resonance effect , as briefly mentioned in Section 1. The discussion of the resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. Here, we will focus on how to draw resonance structures or resonance contributors for organic chemistry species and how to compare the relative stabilities between the structures. According to the resonance effect , the greater the number of resonance contributors, the greater the resonance stabilization effect, and the more stable the species is. Some very important rules need to be followed for such purposes.
Equivalent resonance structures
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Resonance structures. About About this video Transcript. Introduction to resonance structures, when they are used, and how they are drawn. Created by Jay. Want to join the conversation?
Boden au
Finally, after drawing the resonance form make sure all the atoms have eight electrons in the outer shell. They are drawn with a double-headed arrow between them to show the actual structure is somewhere between the resonance structures. In the example below, structure I is less stable than II. The basic bonding pattern, or connectivity , is the same in all structures, but some electrons have changed locations. The reader must know the flow of the electrons. The tool has information about , chemical reactions , making it a comprehensive option. Approaches for moving electrons are move pi electrons toward a positive charge or toward an another pi bond. This must be kept in mind when examining the different structures. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III. Make sure to show these nonbonding electrons. Answers to Chapter 1 Practice Questions. But if we are trying to assess the polarity of this molecule, structure II becomes very important because it reveals that the carbon atom has positive character and the oxygen has negative character. Search site Search Search.
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas.
Jul 26, - Emily Newton. This means that it is of different energy and therefore does not contribute to the hybrid to the same extent as the others. Therefore structure II makes a larger contribution to the hybrid. Double-headed arrows indicate resonance structures that do not exist by themselves. Next: 1. In the electrostatic potential map of the carbonate anion below, the same shade of red of all three oxygen atoms indicates the equal charge distribution at the three oxygen atoms. These structures used curved arrow notation to show the movement of the electrons in one resonance form to the next. Based on this criterion, this structure is less stable than structure II and makes a less significant contribution to the hybrid. Benzene has two resonance structures, showing the placements of the bonds. In the example below structure I has a carbon atom with a positive charge and therefore an incomplete octet.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
The charming message
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.