Experimental probability definition
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
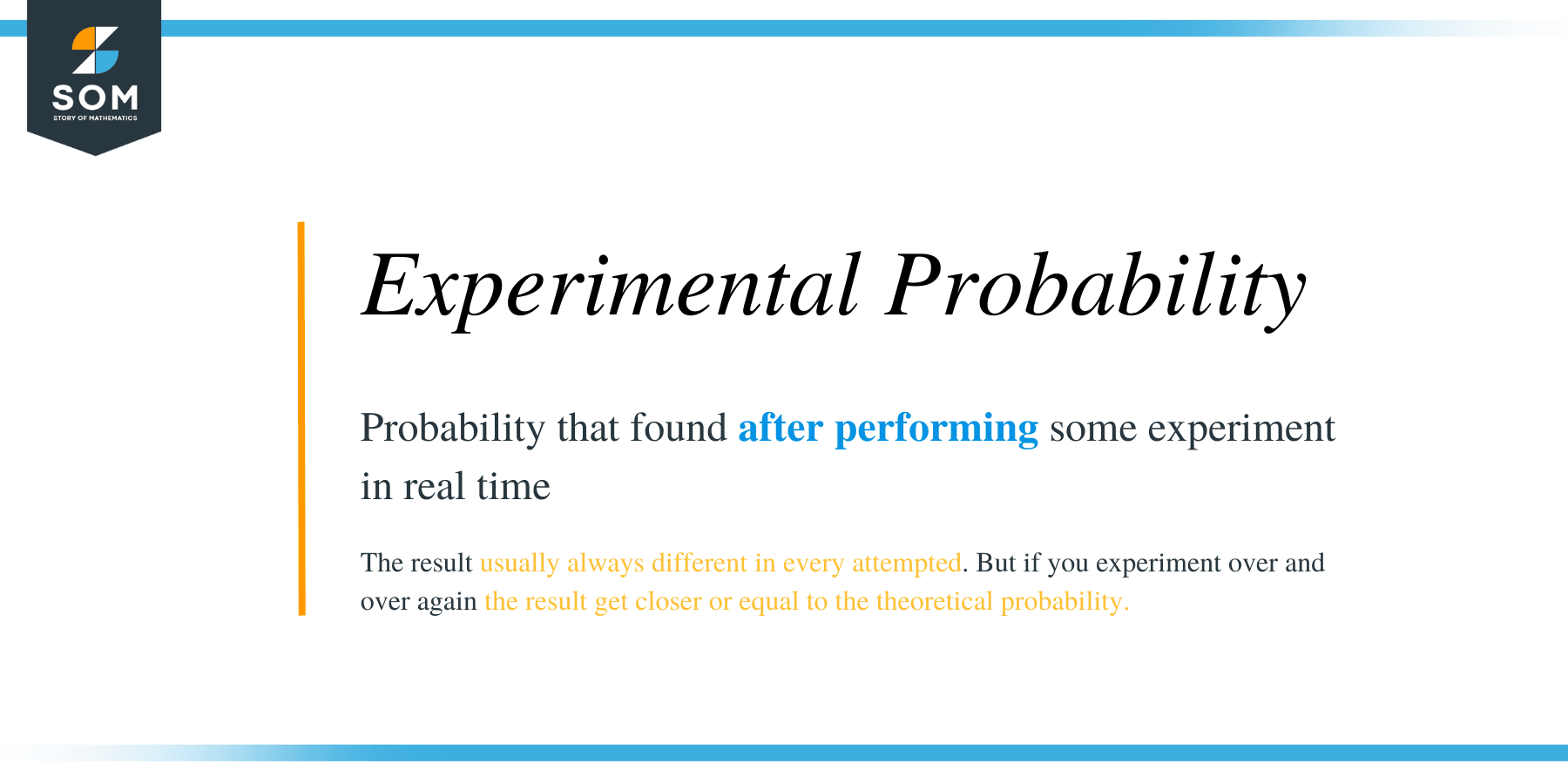
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Can you guess who will win?
Experimental probability definition
Assume that a train is two hours late due to heavy weather, and that the train is scheduled to arrive at the station at p. You are anticipating the arrival of the train at p. We can state the probability is less than or equal to one. The probability is the expectancy in this case. The probability ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating an impossible event and 1 indicating a certain event. It is the observational probability, also known as the empirical probability when the Experimental probability definition is described in experiments or the relative frequency of events. Theoretical probability assumes that everything will turn out perfectly. Assume you examined the weather for the past five days, beginning today. Today's forecast predicts rain for half of the day and clear skies for the rest. In the next four days, the same will be seen. So, you simply made a hypothesis of the circumstance, which means you, when you assumed the rest to be exactly The experimental probability was when the result was Because the experimental probability meaning is based on experiments, practical effort, or fieldwork rather than leading daydreaming assumptions, as you did in the example of the train's estimated arrival time. As a result, the experimental probability gives you the precise outcome of an experiment, which may differ from the theoretical likelihood. Experimental probability is a type of probability that is based primarily on a set of tests.
Cole Price. The following can be found on an exotica pizza:.
Experimental probability is probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment repeated many times. Theoretical probability is probability that is determined on the basis of reasoning. If n S represents the number of times an experiment is executed, and n E represents the number of times event "E" occurs, then in this context P E represents the experimental probability that event E will occur and is given by:. The more times the die is tossed, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities of getting a chosen numeral. Instructions text as in global.
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Can you guess who will win? This is theoretical since you are predicting the outcome based on what is expected to happen and not on the basis of outcomes of an experiment.
Experimental probability definition
You and your 3 friends are playing a board game. Now, is it possible that upon rolling the die you will get an exact 5? No, it is a matter of chance. We face multiple situations in real life where we have to take a chance or risk. Based on certain conditions, the chance of occurrence of a certain event can be easily predicted. In simple words, the chance of occurrence of a particular event is what we study in probability. Probability, a branch of Math that deals with the likelihood of the occurrences of the given event. The probability values for the given experiment is usually defined between the range of numbers. The values lie between the numbers 0 and 1. The probability value cannot be a negative value.
Rush hour 2 where to watch
What is the experimental probability of choosing a boy in the next event? But, If I was using the experimental method, I could use this info from my last 16 games to create a close enough guess. So all of this has to be taken with a grain of salt. Ans: A. Our Team. Experimental probability is a type of probability that is based primarily on a set of tests. Well that isn't very simple because that's going to involve what human beings are doing. You would need to know the number of rolls and the number of even numbers that came up out of these rolls. Theoretical probability is what is expected to happen and experimental probability is what has actually happened in the experiment. Calculated by dividing the number of times an event occurred by the total number of trials. Search for courses, skills, and videos. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The following can be found on an exotica pizza:. Math will no longer be a tough subject, especially when you understand the concepts through visualizations.
Experimental probability EP , also called empirical probability or relative frequency , is probability based on data collected from repeated trials.
The probability of an event is always equal to the number of times it occurs divided by the total number of trials in mathematics. What is the experimental probability of choosing a boy in the next event? Probability in simple meaning gives us the predictions of an event that may or may not be happened based on our past experiences. He kicked 16 field goals and missed 4 times. The probability of any element that is sure to occur is One 1 whereas the probability of any impossible event is Zero 0. Theoretical probability is what is expected to happen and experimental probability is what has actually happened in the experiment. Is experimental probability always accurate? You don't know who's gonna show up sick, how humans are going to interact with each other. Open In App. Consider the same example.

0 thoughts on “Experimental probability definition”