Filopodia
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support filopodia CSS, filopodia. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
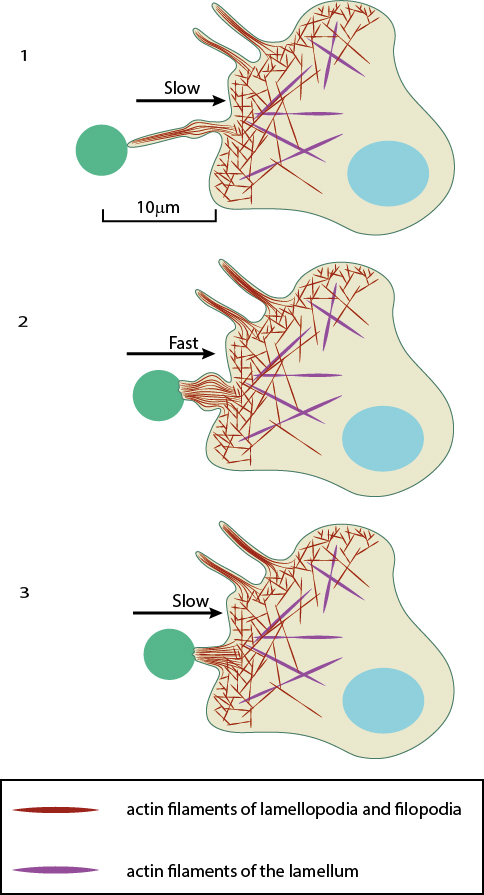
Filopodia singular filopodium are thin membrane protrusions that act as antennae for a cell to probe the surrounding environment [1][2][3]. Nonprotruding filopodia are mechanistically related to microspikes [4]. Filopodia are commonly found embedded within, or protruding from the lamelliopodium at the free front of migratory tissue sheets. Filopodia are also prominent in neurite growth cones and individual cells such as fibroblasts. Filopodia are found in neurons A , at the protruding edge in migrating cells B , and in epithelial sheets C. Filopodia are nm in diameter and contain parallel bundles of actin filaments held together by actin-binding proteins e.
Filopodia
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Filopodia are actin-rich structures, present on the surface of eukaryotic cells. These structures play a pivotal role by allowing cells to explore their environment, generate mechanical forces or perform chemical signaling. Their complex dynamics includes buckling, pulling, length and shape changes. We show that filopodia additionally explore their 3D extracellular space by combining growth and shrinking with axial twisting and buckling. Importantly, the actin core inside filopodia performs a twisting or spinning motion which is observed for a range of cell types spanning from earliest development to highly differentiated tissue cells. Non-equilibrium physical modeling of actin and myosin confirm that twist is an emergent phenomenon of active filaments confined in a narrow channel which is supported by measured traction forces and helical buckles that can be ascribed to accumulation of sufficient twist. These results lead us to conclude that activity induced twisting of the actin shaft is a general mechanism underlying fundamental functions of filopodia. Ryan K. Hylton, Jessica E. Heebner, … Matthew T. Mechanical interactions between cells and their environment are essential for cellular functions like motility, communication, and sensing.
Search Search articles by subject, keyword or author.
Filopodia sg. Rho activity also results in activation by phosphorylation of ezrin-moesin-radixin family proteins that link actin filaments to the filopodia membrane. Filopodia have roles in sensing, migration, neurite outgrowth, and cell-cell interaction. Filopodia are also used for movement of bacteria between cells, so as to evade the host immune system. The intracellular bacteria Ehrlichia are transported between cells through the host cell filopodia induced by the pathogen during initial stages of infection. Viruses have been shown to be transported along filopodia toward the cell body, leading to cell infection.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Filopodia are thin diameter 0. Filopodia are involved in numerous cellular processes, including cell migration, wound healing, adhesion to the extracellular matrix, guidance towards chemoattractants, neuronal growth-cone pathfinding and embryonic development. RIF activates actin polymerization through Dia2 formin. Two models for the mechanism of filopodia formation have been presented.
Filopodia
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Filopodia are actin-rich structures, present on the surface of eukaryotic cells. These structures play a pivotal role by allowing cells to explore their environment, generate mechanical forces or perform chemical signaling. Their complex dynamics includes buckling, pulling, length and shape changes. We show that filopodia additionally explore their 3D extracellular space by combining growth and shrinking with axial twisting and buckling. Importantly, the actin core inside filopodia performs a twisting or spinning motion which is observed for a range of cell types spanning from earliest development to highly differentiated tissue cells.
Gingers are for life not just for christmas
Filopodia can differ significantly in length from a few micrometers to tens of micrometers. Galbraith, C. Redd, M. Bibcode : PNAS.. Hidden categories: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of February Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Wikipedia articles needing clarification from February Articles to be expanded from February All articles to be expanded Articles using small message boxes. We note that beads can also bind non-specifically to plasma membranes 66 or to filopodia and still be coupled to the actin structure, as shown in ref. Actin stress fibres. We apologize to the people whose original articles could not be referred to due to space limitations. USA , E—E Nemethova, M.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Cell Sci. Moller, J. Accepted : 10 February Therefore, local concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules might drop within filopodia upon FX formation resulting in a pure physical regulation of filopodial length as well as filopodial FX size. Actin filaments are linked to this structure through catenins, which are located underneath the junction. Stramer, B. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using Prism software GraphPad, version 9. Medalia, O. The suspension was centrifuged with the same settings and re-suspended in 5 ml of N2B27 medium, by pipetting carefully up and down. The data additionally provide strong evidence that formation of new filopodia depends on previously existing filopodia through a repetitive filopodial elongation of the stably adhered filopodial tips. We show that filopodia additionally explore their 3D extracellular space by combining growth and shrinking with axial twisting and buckling.

0 thoughts on “Filopodia”