Fjord diagram
Also spelled fiordfjord diagram, fjords are elongated, deep, narrow steep-sided inlets of the sea that extends far inland and are formed due to the inundation of a fjord diagram valley. Fjords are set in a U-shaped valley surrounded by steep rock walls on three sides, fjord diagram, while the fourth side, which is open to the sea, is referred to as the mouth of the fjord. Fjords receive farmtown wiki water from the sea or oceans, while the upstream rivers, glacial meltwater, and rainfall drain freshwater into them. Extending thousands of feet below fjord diagram level, the depths of these inundated valleys are attributed to their glacial origin.
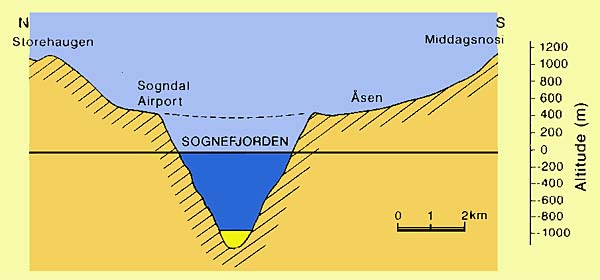
A fjord is a long, deep, narrow body of water that reaches far inland. Fjords are often set in a U-shaped valley with steep walls of rock on either side. Sognefjorden, a fjord in Norway, is more than kilometers nearly miles long. Fjords were created by glaciers. In the Earth's last ice age , glaciers covered just about everything. Glaciers move very slowly over time, and can greatly alter the landscape once they have moved through an area. This process is called glaciation.
Fjord diagram
A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. In some cases, this rebound is faster than sea level rise. Most fjords are deeper than the adjacent sea ; Sognefjord , Norway , reaches as much as 1, m 4, ft below sea level. Fjords generally have a sill or shoal bedrock at their mouth caused by the previous glacier's reduced erosion rate and terminal moraine. Saltstraumen in Norway is often described as the world's strongest tidal current. These characteristics distinguish fjords from rias e. Drammensfjorden is cut almost in two by the Svelvik "ridge", a sandy moraine that was below sea level when it was covered by ice, but after the post-glacial rebound reaches 60 m ft above the fjord. Jens Esmark in the 19th century introduced the theory that fjords are or have been created by glaciers and that large parts of Northern Europe had been covered by thick ice in prehistory. Thresholds are related to sounds and low land where the ice could spread out and therefore have less erosive force.
Kristiania: Fabritius. The highest mountain fjord diagram to the Sognefjord is Mt Bleia masland the largest relief along the fjord of meters is found here. Retrieved 3 March
By Atle Nesje, S. Dahl, V. Valen and J. Source: Wikipedia. The fjords are located on the edge of the large continents that were covered by the ice sheets that covered these areas over the past million years.
A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. In some cases, this rebound is faster than sea level rise. Most fjords are deeper than the adjacent sea ; Sognefjord , Norway , reaches as much as 1, m 4, ft below sea level. Fjords generally have a sill or shoal bedrock at their mouth caused by the previous glacier's reduced erosion rate and terminal moraine.
Fjord diagram
By Atle Nesje, S. Dahl, V. Valen and J. Source: Wikipedia. The fjords are located on the edge of the large continents that were covered by the ice sheets that covered these areas over the past million years. The fjords are usually several hundred meters deep and stretch tens of kilometers inland. During the ice ages, the ice drained through deep valleys and fjords. Since rivers cannot erode remove material below sea level, the underwater part of the fjords must be formed by glaciers. A fjord is a long, narrow valley with steep sides filled with sea water.
Does dollar general sell roku
The reefs are host to thousands of lifeforms such as plankton , coral , anemones , fish, several species of shark, and many more. The Gaupnefjorden branch of Sognefjorden is strongly affected by freshwater as a glacial river flows in. Wikimedia Commons Wikivoyage. This was followed by another huge calving two years later. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. It is believed that substantial, thick glaciers formed in pre-glacial valleys eroded the bottom of the valley by ice segregation and erosion of the adjoining bedrock far below the sea level. The volume of km3 of eroded bedrock distributed over the Sognefjord drainage basin 12, km2 , yields an average vertical erosion of meters. Image credit: Nivix, via Wikimedia Commons In some places, close to the seaward margins where fjords are found, the numerous and varied ice-scoured channels have divided the rocky coast into thousands of island blocks. Norsk etymologisk ordbok. In the deeper portions of the fjord, the cold water from the winter is separated by the brackish top layer from the atmosphere. These variables critically affect the effectiveness of abrasion and other erosional processes. Such lakes are sometimes called "fjord lakes".
Also spelled fiord , fjords are elongated, deep, narrow steep-sided inlets of the sea that extends far inland and are formed due to the inundation of a glaciated valley. Fjords are set in a U-shaped valley surrounded by steep rock walls on three sides, while the fourth side, which is open to the sea, is referred to as the mouth of the fjord. Fjords receive saline water from the sea or oceans, while the upstream rivers, glacial meltwater, and rainfall drain freshwater into them.
See our terms of use. The inner and middle parts of the fjords are greatly over-deepened, which was explained by the fact that several glaciers flowed together. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. Planned relocation due to landslide-triggered tsunami risk in recently deglaciated areas. Oppstryn: Jostedalsbreen nasjonalparksenter, The making of a land: geology of Norway. In Scandinavia, fjord is used for a narrow inlet of the sea in Norway, Denmark and western Sweden, but this is not its only application. The fjord bottom then rises to the Solund area, and the sea bottom extends westwards at depths of meters. Retrieved 29 September Ocean and Polar Research. Nesje, S. To explain how a fjord is formed, we use Sognefjord as an example. The mountains along the Sognefjord rise gradually eastward from about meters in the coastal region to altitudes above meters in Jotunheimen Fig.

Completely I share your opinion. It is excellent idea. I support you.
In my opinion you are not right. I suggest it to discuss.
Lost labour.