Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Jest drugą najczęstszą po naczyniakach zmianą ogniskową obserwowaną w wątrobie.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The datasets used and analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request. Different clinical behaviour influences the importance of differentiating focal nodular hyperplasia FNH from other focal liver lesions FLLs. Examinations were evaluated by three independent readers. The sum of two radiological signs in MRI: homogeneous enhancement in hepatic arterial phase HAP and enhancing lesion in hepatobiliary phase HBP was characterized with high values of sensitivity 0.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Sign in. Editorial Policies. Open access. Send email. Copy url:. Halina Cichoż-Lach. Beata Prozorow-Król. Jarosław Swatek. Krzysztof Celiński. Maria Słomka.
Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver — in our experience.
Caring for a lying person. Covid Medications. Disorders of the digestive system. Drugstore products. Erectile dysfunction - potency.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sammy Hamad ; Charles E. Willyard ; Sandeep Mukherjee.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English Italian. Orsola-Malpighi, University of Bologna, Italy. Focal nodular hyperplasia FNH is the second most common benign tumor of the liver, after hemangioma. It is generally found incidentally and is most common in reproductive-aged women, but it also affects males and can be diagnosed at any age. Patients are rarely symptomatic, but FNH sometimes causes epigastric or right upper quadrant pain. The main clinical task is to differentiate it from other hypervascular hepatic lesions such as hepatic adenoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, or hypervascular metastases, but invasive diagnostic procedures can generally be avoided with the appropriate use of imaging techniques. Once a correct diagnosis has been made, in most cases there is no indication for surgery, and treatment includes conservative clinical follow-up in asymptomatic patients.
The oriental luton menu
Kasia Anonymous, BarBara, about 2 years ago. Specjalizacje gastroenterologia pediatria. Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy wątroby FNH wyglądem może przypominać plaster cytryny. Eksperci nie zalecają również nadzoru z uwagi na małe ryzyko transformacji nowotworowej oraz powikłań. Editorial Policies. Tabletki Uspokajające Labofarm. It is the next most frequent benign liver lesion following hemangioma and usually develops in unchanged liver parenchyma [ 2 ]. In FNH-group, slight elevation of serum GGTP level was seen in 10 patients, in all remaining cases biochemical examinations showed no significant changes, none of the patients was diagnosed with cirrhosis. Caring for a lying person. Focal nodular hyperplasia FNH is a benign lesion, composed of hyperplastic hepatocytes separated by fibrous septa with common central scar see Additional file 1. How long does one pack of Saxenda last? Vitamins and supplements. Erectile dysfunction - potency. Zapisz ustawienia.
At the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
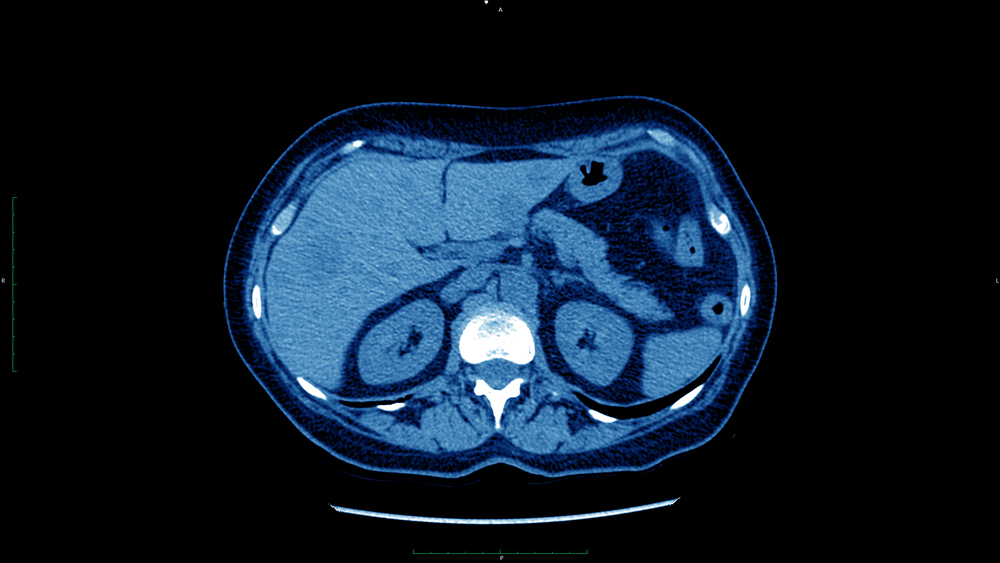
Accessed 2 Jan On the other hand, both in the study of Kim et al. Hum Patol. Olimp Gold Ashwagandha. HBP in spoiled gradient echo and spin echo sequences was obtained 60 min after contrast agent administration. It can be avoided thanks to the cooperation of referring physician and radiologist and excluding patients with known liver cirrhosis. CT image in hepatic arterial phase shows typical intensive homogeneous enhancement of the lesion with discreetly visible central scar arrow. Corresponding author. Neurological diseases. Heart and blood system. However, MRI with the use of organ-specific contrast agents optimizes diagnosis [ 6 — 9 ]. Our application uses cookies for technical purposes e. PDF kb.

Very valuable information