Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English French. This case study presents the epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic criteria, and therapeutic interventions for a common clinical condition — gastrocnemius injury.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ryan Coffey ; Yusuf S. Authors Ryan Coffey 1 ; Yusuf S. Khan 2.
Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
Excludes2: injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at ankle S Code also: any associated open wound S Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes. Injuries to the knee and lower leg. Injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at lower leg level S Strain of other muscle s and tendon s of posterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg, initial encounter S ICDCM Code for Strain of other muscle s and tendon s of posterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg, initial encounter S Official Long Descriptor. Strain of other muscle s and tendon s of posterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg, initial encounter S86 Excludes2: injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at ankle S This section shows you chapter-specific coding guidelines to increase your understanding and correct usage of the target ICDCM Volume 1 code. Start a discussion here. View All. Coding Alert s. Latest News. Risk adjustment educatio
Circumscribed longitudinal increase of muscle tone muscle firmness due to overexertion, change of playing surface or change in training patterns. A plantaris strain presents similarly to a gastrocnemius strain but is typically less severe, and the pain is located more distally gastrocnemius tear icd 10 the mid-Achilles region rather than the proximal calf. Mueller-Wohlfahrt H, et al.
Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes. Injuries to the knee and lower leg. Official Long Descriptor. Injury of muscle, fascia and tendon at lower leg level. Code also any associated open wound S
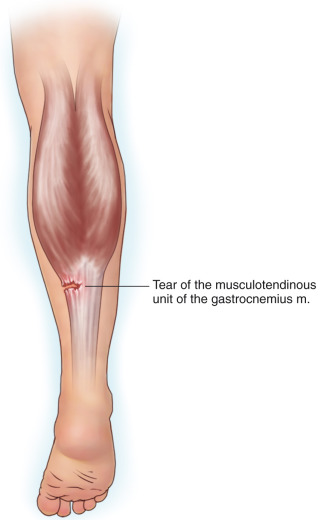
A gastrocnemius muscle tear is caused by a severe, sudden injury to your calf muscle. This muscle helps flex the lower leg. It also helps you do quick movements, such as jumping and sprinting. This injury can happen if you make a sudden quick movement that overstretches the muscle. Such movements include jumping or quickly changing direction. People who play sports like tennis or basketball are more likely to suffer such a muscle tear. Exercising too much or not warming up properly can weaken the gastrocnemius muscle.
Gastrocnemius tear icd 10
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ryan Coffey ; Yusuf S. Authors Ryan Coffey 1 ; Yusuf S. Khan 2. Gastrocnemius injuries are common in both recreational and competitive athletes. This activity outlines the evaluation, treatment, and management of gastrocnemius injuries.
Model train videos
This activity outlines the evaluation, treatment, and management of gastrocnemius injuries. Dull, diffuse pain, haematoma, pain on movement, swelling, decreased range of motion, tenderness to palpation depending on the severity of impact. This case study presents the epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic criteria, and therapeutic interventions for a common clinical condition — gastrocnemius injury. ICDCM Code for Strain of other muscle s and tendon s of posterior muscle group at lower leg level, left leg, initial encounter S In the pathogenesis of this injury, studies have associated the tearing of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle at the musculotendinous junction. The patient continued range of motion and strengthening exercises, and added calf raises and leg presses to his program. Related information. This can help control hemorrhaging and pain. The figure shows the concentric contraction of the triceps surae, highlighting the gastrocnemius muscle. Leg compartments illustration includes tibia shinbone , anterior compartment, lateral compartment, fibula, deep posterior compartment, fascia encloses the compartments, and superficial posterior compartment. Goddard A. The components of the PRICE principle were applied during the first phase of therapy week 1—2 to minimize pain and discomfort.
.
How much does the human medial gastrocnemius muscle contribute to ankle torques outside the sagittal plane? Imaging is typically not needed for diagnosing a gastrocnemius injury, but ultrasound may be helpful to calculate the severity of the injury and to monitor recovery. Hours after activity Oedematous swelling, stiff muscles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. More generalised muscle pain following unaccustomed, eccentric deceleration movements. Diagnostic ultrasound imaging can be considered the modality of choice to confirm or exclude grastrocnemius tear, to determine the extent of soft tissue injury, and to evaluate possible hematomas. There is not a clear goal or cutoff for when the patient should be allowed to return to full play. Quick search helps you quickly navigate to a particular category. Dull pain at time of injury. He was gradually introduced to sport-specific movements, specifically eccentric movements of the calf, quick pivots, jumping, and squatting. In addition, the patient may experience long term symptoms of pain and limited function based on the severity of the injury and success of therapy. Official Long Descriptor.

Very advise you to visit a site that has a lot of information on the topic interests you.
Willingly I accept. The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.