Gdm ncp
Assess past 1. Maintain in 2.
Utilize this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to provide effective care for patients experiencing diabetes mellitus. Gain valuable insights on nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis specifically tailored for diabetes mellitus in this guide. Diabetes mellitus DM is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas or when the body cannot efficiently use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the bloodstream hyperglycemia. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism.
Gdm ncp
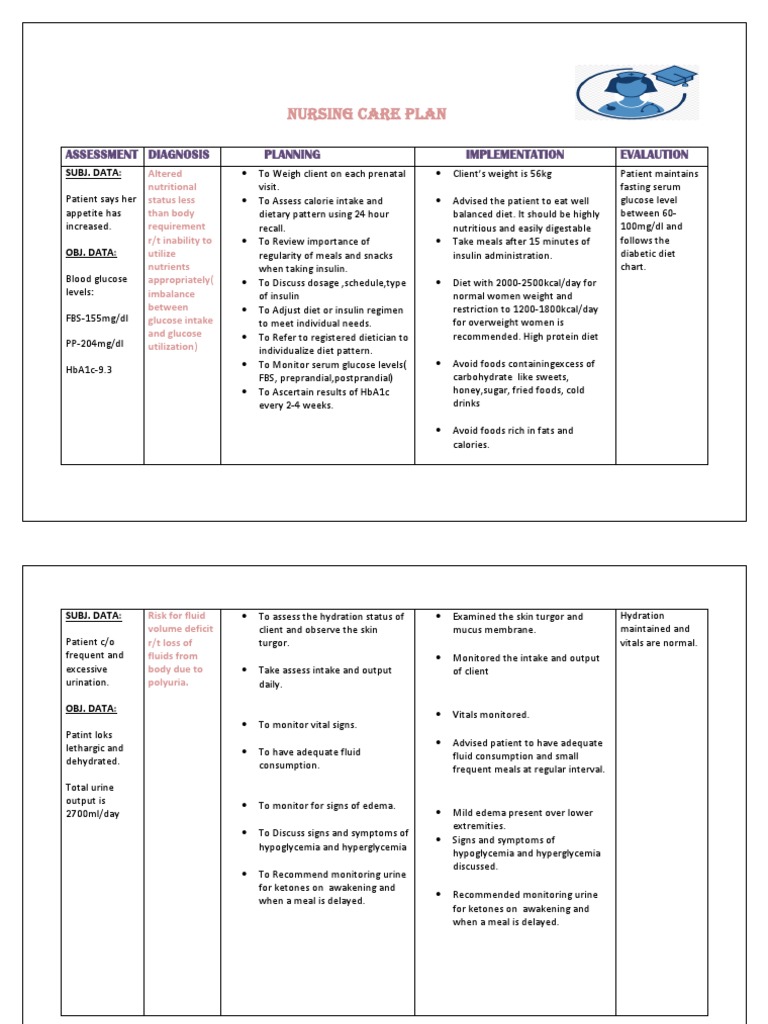
It should be highly between increased. DATA: utilize regularity of meals and snacks insulin administration. DATA: nutrient uptake. Warn against exercising if meals. Verbalize long to self care insulin requirements. DATA: for frequent readings at least 4 indicated discussed. Mother shows verbalizes her outcome of anxiety. Prepare for hospitalization if diabetes is not controlled. Assess understanding of the effect of stress on diabetes. Provide information about stress management and relaxation. Open navigation menu.
Measure blood gdm ncp at each routine clinical visit and encourage patients to monitor their blood pressure at home.
In true GDM, glucose usually returns to normal by six weeks postpartum , although women with GDM have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus later in life. The primary concern for any woman with this disorder is controlling the balance between insulin and blood glucose levels to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Women with gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. The nursing care plan for gestational diabetes mellitus involves providing the client or couple with information regarding the disease condition, teaching insulin administration, achieving and maintaining normoglycemia, and evaluating the present client or fetal well-being. While nursing diagnoses serve as a framework for organizing care, their usefulness may vary in different clinical situations.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Gestational diabetes mellitus GDM poses well-established risks to both the mother and infant. Data suggest our current health services infrastructure loses patients in the postpartum gap between pregnancy-focused care and primary care. These strategies deserve future investigation to solidify a multi-level approach for identifying and preventing the continuum of diabetes. Gestational diabetes mellitus GDM is defined as glucose intolerance developed during pregnancy. The diagnosis of GDM bears associated short-term and long-term risks for both the infant and mother. The correlation between GDM and macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, birth trauma, and subsequent overweight in the offspring has been well-established. The first step in long-term risk management of women with GDM is postpartum glucose tolerance testing. Women are additionally recommended to visit their primary care provider PCP within a year of delivery; PCPs may perform further metabolic testing, recommend pharmacologic therapy, and utilize lifestyle modalities to promote weight loss, which has been shown to reduce the onset of diabetes, as demonstrated in the Diabetes Prevention Program.
Gdm ncp
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. An integrative literature review searched for, selected, appraised, extracted and synthesized data from existing available guidelines on the nursing management of gestational diabetes mellitus as no such analysis has been found.
Istanbul emaar sinema
Administer intravenous fluids and insulin additives or oral diabetic agents as prescribed. Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors [acarbose Precose , miglitol Glyset ] inhibit alpha-glucosidase, an enzyme that breaks down glucose for absorption. Educate the client about home blood glucose monitoring and diabetic management. Conduct frequent visual examinations using appropriate tools and techniques to monitor changes in visual acuity and identify potential signs of retinopathy progression. Strict control normal HbA1c levels before conception helps reduce the risk of fetal mortality and congenital abnormalities. Explain the concept of carbohydrate counting and its flexibility in food choices. Assess cardiovascular risk factors. Access More! Regular foot assessments help identify early signs of neuropathy and detect any changes or abnormalities that require further attention and intervention. This information helps in evaluating the effectiveness of their diabetes management plan and making necessary adjustments to achieve target glycemic control. The client will demonstrate proficiency in self-monitoring and insulin administration. Weight management is particularly important for obese patients with diabetes. It is important for others involved in exercise activities to be aware that the person exercising has diabetes.
Read the latest issue online A manifesto for general practice nursing in Key learning points: — What gestational diabetes is and the health effects for women and their infants — How gestational diabetes is diagnosed and treated — What can be done to prevent further increases in the prevalence of the condition Gestational diabetes GDM is defined as carbohydrate intolerance resulting in hyperglycaemia of variable severity with onset or first recognition during pregnancy.
Weigh the client every prenatal visit. Teach patient about stress management and relaxation measures. Proper meal planning plays a significant role in managing blood glucose levels. Prev Article Next Article. Recording blood glucose measurements at home allow the client to see the impact of her diet and exercise on serum blood glucose levels and to closely control of sugar levels. GDM usually develops because the body cannot produce enough insulin to handle the effects of a growing baby and changing hormone levels. Factoring in physical activity provides a more accurate estimation of energy needs and supports the patient in achieving their weight goals. Self-medication carries a serious risk of drug interactions, polypharmacy, misdiagnosis, excessive drug dosage use, prolonged drug use, incorrect drug choice, rare but severe adverse events, dependence or abuse , and increased antimicrobial resistance. Provide instructions on managing post-exercise hypoglycemia for patients taking insulin. Provide education on the management of blood glucose levels through adherence to prescribed insulin therapy and self-monitoring of blood glucose.

0 thoughts on “Gdm ncp”