Glycogen phosphorylase
Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxalphosphate and phosphate PDB entry 1ygp.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis. The main role of PYGM is providing sufficient energy for muscle contraction. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Initially it was believed that phosphorylase was responsible for both glycogen breakdown and synthesis in the living cell. Rather, glycogen synthesis was attributable solely to the activity of glycogen synthase, subsequent to the transport of glucose into the cell. However, the well-established observation that phosphorylase was inactivated i. Such data indicate that phosphorylase inactivation may be the most important mechanism for glycogen accumulation under defined conditions. These results support the initial belief that phosphorylase plays a quantitative role in glycogen formation in the living cell. However, the mechanism is not via activation of phosphorylase, but rather via inactivation of the enzyme. Glycogen is a branched, glucose polymer and the storage form of glucose, particularly in skeletal muscle and liver. The importance of glycogen as an energy substrate during many, if not most, forms of physical exercise is well established. The reaction is catalyzed by glycogen phosphorylase, which, together with debranching enzyme, results in full degradation of the glucose polymer. Phosphorylase is rate-limiting for glycogenolysis, and the reaction is considered to be irreversible in the cell.
Acta Diabetol.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The PYGL gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called liver glycogen phosphorylase. This enzyme breaks down a complex sugar called glycogen. Liver glycogen phosphorylase is one of three related enzymes that break down glycogen in cells; the other glycogen phosphorylases are found in the brain and in muscles.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis. The main role of PYGM is providing sufficient energy for muscle contraction. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood. PYGM is important not only in glycogen metabolism, but also in such diverse processes as the insulin and glucagon signaling pathway, insulin resistance, necroptosis, immune response, and phototransduction. PYGM is implicated in several pathological states, such as muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency McArdle disease , schizophrenia, and cancer. Here we attempt to analyze the available data regarding the protein partners of PYGM to shed light on its possible interactions and functions.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glucose is the main energy fuel for the human brain. Maintenance of glucose homeostasis is therefore, crucial to meet cellular energy demands in both - normal physiological states and during stress or increased demands. Glucose is stored as glycogen primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle with a small amount stored in the brain. Liver glycogen primarily maintains blood glucose levels, while skeletal muscle glycogen is utilized during high-intensity exertion, and brain glycogen is an emergency cerebral energy source. Glycogen and glucose transform into one another through glycogen synthesis and degradation pathways. Overall, defects in glycogen metabolism mainly present as GSDs and are a heterogenous group of inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism.
American quarter horse for sale
In order to be used for metabolism , it must be converted to glucosephosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. As a result, PKA can no longer initiate the phosphorylation cascade that ends with formation of active glycogen phosphorylase a. The kinase PHK mediates the neural and hormonal regulation of glycogen breakdown by phosphorylating and thereby activating muscle glycogen phosphorylase. RIPK3 activates glycogen phosphorylase and therefore influences glycogenolysis [ 39 , 40 ]. The relationship between McArdle disease and schizophrenia, if any, is so far elusive. The major mechanism for phosphorylase inactivation i. Copy Download. However, it is expressed in tissues other than muscle, such as the brain, lymphoid tissues, and blood. Evolution of Allosteric Control in Glycogen Phosphorylase.
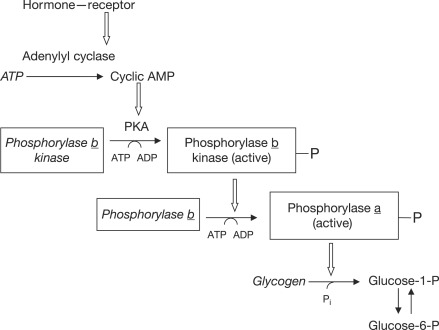
Search Fundamentals of Biochemistry. In the previous section, you learned that glucagon signaling down-regulates glycogen synthesis. Now let's look at glycogen breakdown, called glycogenolysis, and its control by two hormones, glucagon, and epinephrine.
The search for the MEN1 gene. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Ingestion of a carbohydrate rich diet after prior glycogen depletion has proven to be an effective approach. Identification of a mutation in liver glycogen phosphorylase in glycogen storage disease type VI. PYGM plays a role in insulin and glucagon signaling, and insulin resistance pathways involving regulation of the glycogen level. The authors clearly demonstrated a marked accumulation of glycogen solely in the leg that underwent prior depletion during cycling. Toggle limited content width. Research on animal models of human diseases has led to the development of effective therapies and treatment in many cases. Exercise and glycogen depletion: effects on ability to activate muscle phosphorylase. About Molecule of the Month. Increased temperature accelerates glycogen synthesis and delays fatigue in isolated mouse muscle during repeated contractions. Glycogen storage site.

In my opinion you are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I not absolutely understand, what you mean?
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can prove it.