Glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 GSK3 may be the busiest kinase in most cells, with over sit to stand vtech substrates to deal with. Glycogen synthase does GSK3 maintain control to selectively phosphorylate each substrate, and why was it evolutionarily favorable for GSK3 to assume such a large responsibility? GSK3 must be particularly adaptable for incorporating new substrates into its repertoire, and we discuss the distinct properties of GSK3 that may contribute to its capacity to fulfill its roles in multiple signaling pathways. The mechanisms regulating GSK3 glycogen synthase post-translational modifications, glycogen synthase priming, cellular trafficking, protein complexes have been reviewed previously, so here we focus on newly identified complexities in these mechanisms, how each of these regulatory mechanism contributes to the ability of GSK3 to select which substrates to phosphorylate, glycogen synthase, and how these mechanisms may have contributed to its adaptability as new substrates evolved, glycogen synthase.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen is the major glucose reserve in eukaryotes, and defects in glycogen metabolism and structure lead to disease. Glycogenesis involves interaction of glycogenin GN with glycogen synthase GS , where GS is activated by glucosephosphate G6P and inactivated by phosphorylation. We describe the 2.
Glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis , the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase EC 2. Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase , the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation. The crystal structure of glycogen synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens , however, has been determined at 2. This structural property, among others, is shared with related enzymes, such as glycogen phosphorylase and other glycosyltransferases of the GT-B superfamily. Since the structure of eukaryotic glycogen synthase is highly conserved among species, glycogen synthase likely forms a tetramer in humans as well. Glycogen synthase can be classified in two general protein families. The first family GT3 , which is from mammals and yeast, is approximately 80 kDa, uses UDP-glucose as a sugar donor, and is regulated by phosphorylation and ligand binding. Although the catalytic mechanisms used by glycogen synthase are not well known, structural similarities to glycogen phosphorylase at the catalytic and substrate binding site suggest that the mechanism for synthesis is similar in glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase. However, since glycogen synthase requires an oligosaccharide primer as a glucose acceptor, it relies on glycogenin to initiate de novo glycogen synthesis.
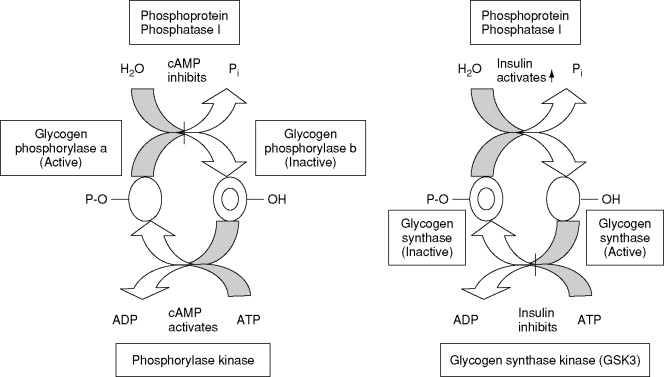
Regulation of GS by insulin is multifactorial, and insulin activates GS by inducing glycogen-associated form of protein phosphatase 1 PP1 that dephosphorylates the residues phosphorylated by GSK3 Suzuki, glycogen synthase al.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen synthase GYS1 is the central enzyme in muscle glycogen biosynthesis. GYS1 activity is inhibited by phosphorylation of its amino N and carboxyl C termini, which is relieved by allosteric activation of glucosephosphate Glc6P. We present cryo-EM structures at 3.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Salah A.
Glycogen synthase
Although glucose is the primary fuel for cells, it is not an efficient molecule for long-term storage in complex i. Therefore, in both plants and animals, the glucose molecules are linked together to form polysaccharides known as glucans. The average size of a glycogen unit is a cytoplasmic granule containing over glucose molecules. The addition of a glucosephosphate to another or to a glycogen chain is energetically unfavorable, so it must be coupled with a sufficiently exergonic reaction to proceed. The phosphoanhydride exchange reaction catalyzed by UDP-glucose phosphorylase is minimally exergonic. However, the pyrophosphate released is quickly hydrolyzed by inorganic pyrophosphatase, a ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme, in a highly exergonic reaction. This pyrophosphate hydrolysis is a mechanism utilized in many biosynthetic pathways to provide energy for otherwise endergonic reactions.
Farm life simulator codes
We modelled a single phosphorylated site 3a Ser Fig. However, despite this the two are not functionally redundant as demonstrated by the gene knockout studies. To gain a higher resolution structure for the human GS, we applied D2 symmetry and achieved a global resolution of 2. Mahalingan, K. Crystal structure of glycogen synthase: homologous enzymes catalyze glycogen synthesis and degradation. Expression and purification of functional human glycogen synthase-1 hGYS1 in insect cells. Download citation. Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase , the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation. Crystal structure of glycogen synthase: homologous enzymes catalyze glycogen synthesis and degradation. WR had a severely reduced ability to bind maltoheptaose, with an apparent AC 50 of Long-term use of lithium the well studied GSK3 inhibitor for bipolar disorder has not been shown to be associated with an increased risk of cancer. Turnbull, J.
Thank you for visiting nature.
Density corresponding to the GN 34 C-terminal region is shown in green. Short-term in vitro inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 potentiates insulin signaling in type I skeletal muscle of Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats. Kinases phosphorylating GSK3 at this site are not well characterized Hughes et al. Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 in insulin signalling. Nature , — Thomas J. Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome. We also thank B. Comparisons between human, C. Inhibition of GSK-3 selectively reduces glucosephosphatase and phosphatase and phosphoenolypyruvate carboxykinase gene expression. Importantly, as most of the inhibitors are targeted to the ATP-binding site, achieving selectivity over other related kinases is challenging and is one of the key issues that need to be addressed. Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose that functions as the primary energy store in eukaryotes. Diabetes 60 , — Emsley, P. Curr Mol Med.

I consider, that you commit an error. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Interestingly :)