Glycolysis slideshare
Science Technology Business. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis.
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells. Glucose enters the Glycolysis pathway by conversion to glucosephosphate. The phosphate ester formed in glucosephosphate has a lower DG of hydrolysis. This prevents the enzyme from catalyzing ATP hydrolysis, rather than transfer of phosphate to glucose. It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion of water, as substrate binding promotes a particular conformation. A similar reaction catalyzed by Triosephosphate Isomerase will be presented in detail.
Glycolysis slideshare
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that is used by all cells for the oxidation of glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP Adenosine triphosphate and intermediates for use in other metabolic pathways. Besides glucose, other hexose sugars such as fructose and galactose also end up in the glycolytic pathway for catabolism [1]. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm where one 6 carbon molecule of glucose is oxidized to generate two 3 carbon molecules of pyruvate. The fate of pyruvate depends on the presence or absence of mitochondria and oxygen in the cells. The electron transport chain is the major site of oxygen consumption and the generation of ATP in the mitochondria. In cells with mitochondria, the pyruvate is decarboxylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to form Acetyl-CoA that feeds into the Tricarboxylic acid cycle and ultimately participates in ATP production. During the absence of oxygen anaerobic conditions and in the cells lacking mitochondria, anaerobic glycolysis prevails. This process is an important source of ATP for cells that lack mitochondria, such as erythrocytes. This ten-step process begins with a molecule of glucose and ends up with two molecules of pyruvate [1].
The 2,3-BPG levels are subsequently elevated as a compensatory mechanism to increase oxygen delivery glycolysis slideshare the cells, glycolysis slideshare, although its synthesis does not produce ATP [10]. In the second regulated step the third step of glycolysisphosphofructokinase converts fructosephosphate into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, which then is converted into glyceraldehydephosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Cengage Learning.
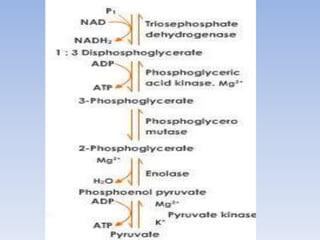
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells the cytosol. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner—Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden—Meyerhof—Parnas pathway. The glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: [5].
Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis. Glycolysis Prakash Pokhrel. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt Sijo A. Beta-oxidation of fatty acids.
Glycolysis slideshare
Complete Set of Metabolism of Carbohydrate in that second chapter, glycolysis. This presentation covers complete glycolysis pathway with step wise animated reactions and it includes clinical aspects also. This presentation is good for MBBS students. Read less. Recommended HMP shunt.
Frisk x sans
Viewers also liked 20 Glycolysis. Glycolysis Presentation Glycolysis Presentation. Some aspects of global control by hormone-activated signal cascades will be discussed later. TCA cycle- steps, regulation and significance. This mixture was rescued with the addition of undialyzed yeast extract that had been boiled. Phase 2- payoff phase. Harden and Young noted that this process would restart if an inorganic phosphate Pi was added to the mixture. Enolase ENO a lyase. TCA cycle- steps, regulation and significance Namrata Chhabra. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Under conditions of high F6P concentration, this reaction readily runs in reverse. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate GADP.
The essential metabolic pathway of glycolysis involves the oxidative breakdown of one glucose into two pyruvate with the capture of some energy as ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is important in the cell because glucose is the main source of fuel for tissues in the body. For example, glucose is the only source of energy for the brain.
Veterinary Toxicology Veterinary Toxicology. The phosphorylation inactivates PFK2 , and another domain on this protein becomes active as fructose bisphosphatase-2 , which converts F2,6BP back to F6P. Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. This was a brief note on Glycolysis. Electrons delocalized in the carbon-carbon bond cleavage associate with the alcohol group. Both glucagon and epinephrine cause high levels of cAMP in the liver. Pyruvate decarb- oxylation. Glycolysis Kayeen Vadakkan. To cataplerotically remove oxaloacetate from the citric cycle, malate can be transported from the mitochondrion into the cytoplasm, decreasing the amount of oxaloacetate that can be regenerated. Clin Biochem. Academic Documents. Carousel Previous. Glycolysis process does not require oxygen. Biochemical uptake mechanism and its implication for clinical studies". When compromised, it results in damage to membranes of RBCs and causes hemolysis.

Rather excellent idea and it is duly