Guttation diagram
Use app Login. What is guttation?
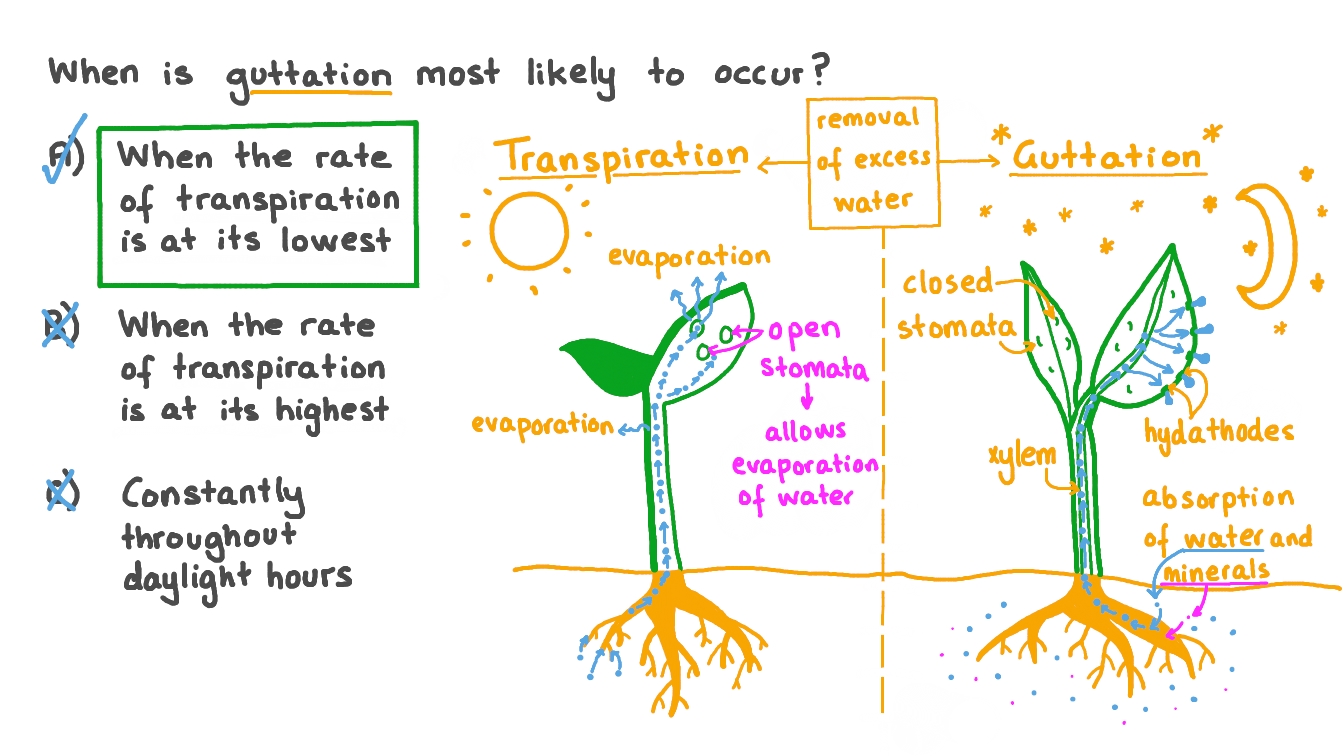
Guttation is a process by which plants release excess water from leaves as droplets. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. In this article, we will read about the demonstration, its mechanism, and demonstration , the role of hydathodes in guttation , the composition of water released during guttation , the difference between guttation and transpiration , and the importance of guttation. Guttation is a process that occurs in the case of vascular plants, in which excess water is removed from the leaf tips. Pores similar to stomata called hydathodes are present on the leaf tips that aid in this process.
Guttation diagram
.
This solution contains water, minerals, and various organic compounds.
.
Guttation is how plants expel excess water or nutrients through tiny openings on leaves and stems. Name — guttation Common name — crying plant, weeping leaves, teary plant, dewdrop Type — plant physiological process. This biological process enables plants to restore balance between their nutrient intake and needs. Guttation occurs when a plant oozes water and minerals out from perfectly healthy leaves , stems, and sometimes even flower petals. It takes place when roots of a plant absorb more water than the plant actually needs. Tiny, specialized cells on the surface of a leaf or stem are connected to veins and sap channels of the plant. This cluster of cells works as a nozzle. This process where excess pressure is released from inside the plant is called guttation.
Guttation diagram
Hydathodes form natural openings but, unlike stomata, are open permanently and offer little resistance to the flow of fluid out of leaves. The cells of epithem are soft and made of loosely arranged thin-walled parenchyma cells and without chloroplast, and are involved in absorption and secretion. Internally, they are connected by tracheary endings to a large chamber with masses of thin-walled parenchymatous tissue surrounded by a sheath layer.
Why cant michael myers be killed
The water released during guttation consists of a dilute liquid of mineral salts. Add Other Experiences. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. This mechanism enables plants to maintain internal water balance. Suggest Changes. This article is being improved by another user right now. Hire With Us. Influenced by factors such as root pressure , and humidity. Guttation depends on the root pressure. Easy Normal Medium Hard Expert. Last Updated : 23 Jan, Water is lost in the form of liquid droplets. Because of water-conducting xylem elements is a vascular bundle terminate in a hydathode, xylem sap is forced to flow through the hydathodes.
Guttation is the process of liquid exudation from hydathodes situated on the tip, along the margins and adaxial and abaxial surfaces of leaves. Hydathodes, also known as water stomata or water pores, unlike stomata, are always open representing the path of least resistance to the liquid outflow from them. Guttation fluids contain a variety of living and non-living ingredients.
It includes organic compounds as well. We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. Specialized structures known as hydathodes help in the process of guttation. Add Other Experiences. It occurs during the night or early morning when there is high atmospheric humidity and transpiration is less. Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism. Guttation depends on the root pressure. Guttation can be demonstrated via a simple experiment. The composition of the guttation fluid contains essential minerals like potassium, calcium and magnesium. Save Article. Help us improve. Guttation: Definition, Hydathodes and Mechanism. Thank you for your valuable feedback!

0 thoughts on “Guttation diagram”