Haplogroup
Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers haplogroup short tandem repeats STRs and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs. The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation, haplogroup.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Figure S2. The mitogenome sequence data on which this study is based can be obtained from GenBank and the European Nucleotide Archive. The GenBank accession numbers for mitogenome sequences reported in this paper are listed in Table S5. Genetic distances were estimated from these data and projected onto a maximum likelihood rooted phylogenetic tree to analyze clustering and branching dates. Haplogroup J originated approximately
Haplogroup
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Y chromosome contains the largest nonrecombining block in the human genome. By virtue of its many polymorphisms, it is now the most informative haplotyping system, with applications in evolutionary studies, forensics, medical genetics, and genealogical reconstruction. However, the emergence of several unrelated and nonsystematic nomenclatures for Y-chromosomal binary haplogroups is an increasing source of confusion. To resolve this issue, markers were genotyped in a globally representative set of samples, 74 of which were males from the Y Chromosome Consortium cell line repository. A single most parsimonious phylogeny was constructed for the binary haplogroups observed. A simple set of rules was developed to unambiguously label the different clades nested within this tree. This hierarchical nomenclature system supersedes and unifies past nomenclatures and allows the inclusion of additional mutations and haplogroups yet to be discovered. In recent years, an explosion in data from the nonrecombining portion of the Y chromosome NRY in human populations has been witnessed. This explosion has been driven, in part, by the many recently discovered polymorphisms on the NRY. There has been a keen interest in using polymorphisms on the NRY to examine questions about paternal genetic relationships among human populations since the mids Casanova et al. In more recent years, a use has been found for these polymorphisms in DNA forensics Jobling et al. The low level of polymorphism on the NRY hindered research for many years.
American Journal of Human Geneticshaplogroup, 75 6— PLoS One9 8e Haplogroup Journal of Human Genetics96 5—
A haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on the patriline or the matriline. Top-level haplogroups are assigned letters of the alphabet, and deeper refinements consist of additional number and letter combinations. For Y-DNA, a haplogroup may be shown in the long-form nomenclature established by the Y Chromosome Consortium , or it may be expressed in a short-form using a deepest-known single-nucleotide polymorphism SNP. SNPs are locations on the DNA where one nucleotide has "mutated" or "switched" to a different nucleotide. Because a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes , it is possible to predict a haplogroup from the haplotype.
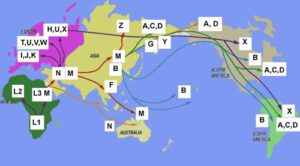
In human genetics , a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. Haplogroups are used to represent the major branch points on the mitochondrial phylogenetic tree. Understanding the evolutionary path of the female lineage has helped population geneticists trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the subsequent spread around the globe. As haplogroups were named in the order of their discovery, the alphabetical ordering does not have any meaning in terms of actual genetic relationships. The hypothetical woman at the root of all these groups meaning just the mitochondrial DNA haplogroups is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor MRCA for all currently living humans. She is commonly called Mitochondrial Eve. The rate at which mitochondrial DNA mutates is known as the mitochondrial molecular clock. It is an area of ongoing research with one study reporting one mutation per years.
Haplogroup
Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats STRs and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs. The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation. Y-chromosomal Adam is estimated to have lived roughly , years ago in Africa [ citation needed ]. By examining other bottlenecks most Eurasian men men from populations outside of Africa are descended from a man who lived in Africa 69, years ago Haplogroup CT. Other major bottlenecks occurred about 50, and 5, years ago and subsequently the ancestry of most Eurasian men can be traced back to four ancestors who lived 50, years ago, who were descendants of African E-M Y-DNA haplogroup nomenclature is changing over time to accommodate the increasing number of SNPs being discovered and tested, and the resulting expansion of the Y-chromosome phylogenetic tree. This change in nomenclature has resulted in inconsistent nomenclature being used in different sources. Haplogroup B. Haplogroup D. Haplogroup E.
The long drive engines
The Y chromosome contains the largest nonrecombining block in the human genome. American Journal of Human Genetics , 75 6 , — A human Y-linked DNA polymorphism and its potential for estimating genetic and evolutionary distance. So, for example, it may mark when a population first migrated out of Africa, or when another group became geographically isolated. Table S1. Firstly, a nomenclature committee comprising some of the current participants in the YCC will receive requests from investigators who wish new binary markers or haplogroups to be incorporated into the nomenclature, and will decide on the changes to be made to the existing system. Both were buried with several Viking artifacts as well as other individuals with mostly Norse ancestry Margaryan et al. Names shown in boxes indicate haplogroup names that require changes from those shown in A. This research was supported by the Research Council of Norway, project number Moore, Richard Ladle. Lineages or markers excluded from a haplogroup are listed within parentheses after the name of the haplogroup or the last derived marker in the case of the mutation-based nomenclature. Mitochondria are thought to be reduced descendants of symbiotic bacteria that were once free living. So in the interest of helping you out, we will walk through an example of a maternal and paternal haplogroup assignment, and explain how knowing your haplogroups can place you in the human family tree and connect you to your ancestry. Haplogroup G M originated some 48, years ago and its most recent common ancestor likely lived 26, years ago in the Middle East. Am J Biol Anthropol.
But what exactly is a haplogroup, and why should you care? So, how do you find your haplogroups?
Haplogroup J. From Namsos to Halden: Myths and realities in the history of norwegian seamen's wages, — Haplogroup A Hg A. In the warmer climates of the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa, earlier subhaplogroups, such as J2 and J1d, tend to be more frequent. Genome Research. Science , , — With respect to the distribution of haplogroup J mtDNAs in Scandinavia, our analysis has provided some insights into the temporal sequence of their arrival in the region. Nature Methods , 9 8 , This section has multiple issues. Part of a series on. To understand the evolution of haplogroup J from a temporal perspective, a phylogenetic tree was constructed from the mitogenome sequences, and the ages for its constituent branches were estimated. Ancient mitochondrial DNA from the northern fringe of the Neolithic farming expansion in Europe sheds light on the dispersion process.

0 thoughts on “Haplogroup”