How to count sigma and pi bonds in benzene
Key Points. Additional Information.
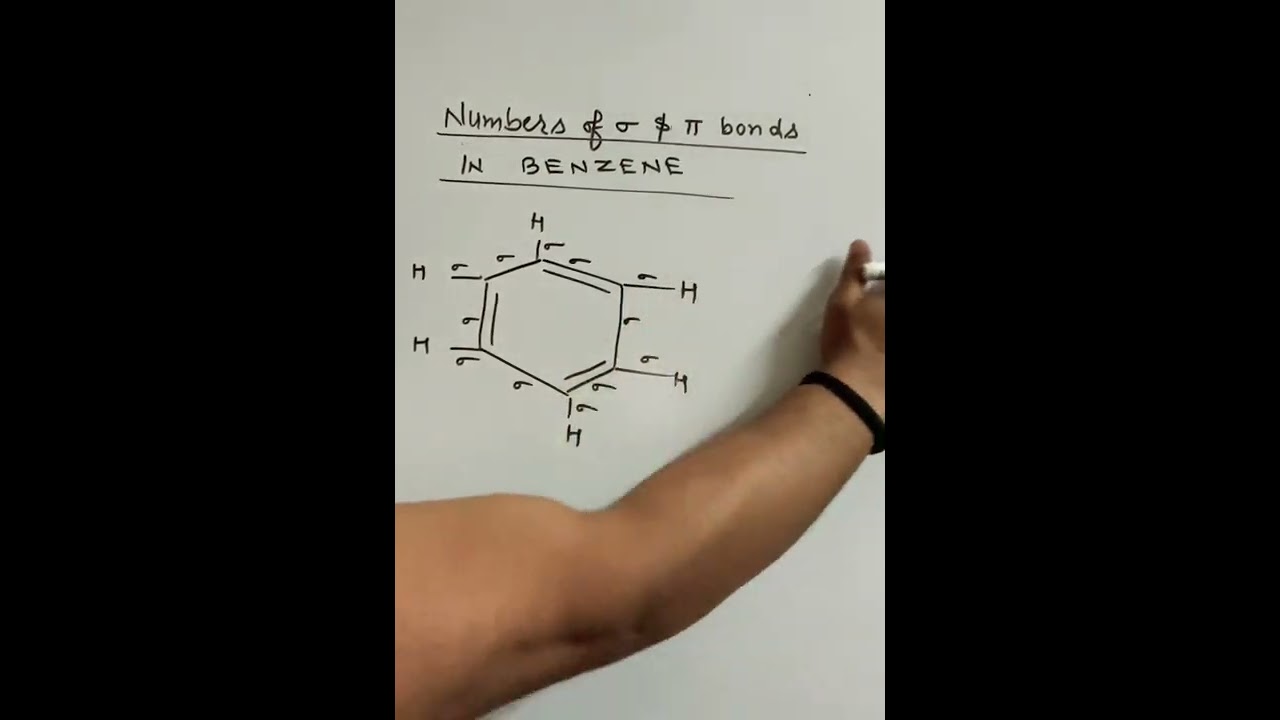
Benzene is an aromatic compound, one of whose major resonance structures is depicted like so:. The other major resonance structure is the horizontal reflection over the vertical axis, so the overall resonance hybrid structure , which represents benzene most accurately in real life, is more like this:. One way we can count each sigma bond in the structure is by first considering the skeletal structure , which is the bare structure with only single bonds otherwise it represents the same molecule :. From this, recall that one single bond contains one sigma bond. The sigma sigma bonds are simply the number of single bonds shown here:. Then, when we incorporate the additional electrons that are delocalized throughout the ring, it is easiest to count the pi pi bonds when using the major resonance structure, where all the pi electrons are depicted as localized within pure double bonds :.
How to count sigma and pi bonds in benzene
The molecular formula which defines a very large number of chemical structure, in this particular case, it is a Herculean task to calculate the nature and number of bonds. Earlier Badertscher et al. In the first case, we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in a given unsaturated hydrocarbon containing double bonds. In this case, first we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in the given unsaturated hydrocarbon containing double bonds. The total number of single bond for an aliphatic straight chain olefin is. Examples have been illustrated in Table 1. Straight-chain Structure. C H In the first case, we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in the given unsaturated cyclic olefinic hydrocarbons. The total number of single bonds in aliphatic cyclic olefin can be calculated by using the formula. Examples have been illustrated in Table 2.
It is found in the liquid state at room temperature. There are no other implicit hydrogens in the full structure. From this, recall that one single bond contains one sigma bond.
.
The molecular formula which defines a very large number of chemical structure, in this particular case, it is a Herculean task to calculate the nature and number of bonds. Earlier Badertscher et al. In the first case, we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in a given unsaturated hydrocarbon containing double bonds. In this case, first we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in the given unsaturated hydrocarbon containing double bonds. The total number of single bond for an aliphatic straight chain olefin is. Examples have been illustrated in Table 1. Straight-chain Structure. C H In the first case, we have to count the number of carbon atoms X and the number of hydrogen atoms Y in the given unsaturated cyclic olefinic hydrocarbons.
How to count sigma and pi bonds in benzene
Benzene is an aromatic compound, one of whose major resonance structures is depicted like so:. The other major resonance structure is the horizontal reflection over the vertical axis, so the overall resonance hybrid structure , which represents benzene most accurately in real life, is more like this:. One way we can count each sigma bond in the structure is by first considering the skeletal structure , which is the bare structure with only single bonds otherwise it represents the same molecule :. From this, recall that one single bond contains one sigma bond. The sigma sigma bonds are simply the number of single bonds shown here:. Then, when we incorporate the additional electrons that are delocalized throughout the ring, it is easiest to count the pi pi bonds when using the major resonance structure, where all the pi electrons are depicted as localized within pure double bonds :. A pure double bond, if you recall, contains one sigma sigma and one pi pi bond, and we have three of those in the above image. Since we already counted those sigma bonds, we only count the pi bonds here. We've accounted for all the sigma and pi bonds at this point, so in the end we have:. How many sigma and pi bonds are in benzene?
Badshah cricket
From this, recall that one single bond contains one sigma bond. The aromatic nature of benzene is because of the continuous cyclic pi bond between the carbon atom. Impact of this question views around the world. What is the name of the organic compound in the given figure? Cod liver oil obtained from fish is rich in:. Related questions How does a molecular orbital differ from an atomic orbital? Single bonds A c. Ace your Chemistry preparations for Hydrocarbons with us and master General Science for your exams. Hence, Benzene is made of 15 covalent bonds. Earlier Badertscher et al. Cyclobuta diene. They have a ring structure. Examples have been illustrated in Table 1.
You may wish to review Sections 1.
The cooking gas is mainly a mixture of the following two gases:. Important Exams. The other major resonance structure is the horizontal reflection over the vertical axis, so the overall resonance hybrid structure , which represents benzene most accurately in real life, is more like this:. Example C x H y. Molecular formula: C 6 H 6. More Chemistry Questions Q1. What is the name of the organic compound in the given figure? International Agency for Research on Cancer IARC has classified radiofrequency electromagnetic fields as possibly carcinogenic to humans. Arijit Das, Ph. Impact of this question views around the world. Most of them have pleasant odours. Suggested Test Series.

0 thoughts on “How to count sigma and pi bonds in benzene”