Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
A patient prescribed spironolactone is demonstrating ECG changes and complaining of muscle weakness.
Use this EKG interpretation cheat sheet that summarizes all heart arrhythmias in an easy-to-understand fashion. An EKG uses electrodes attached to the skin to detect electric currents moving through the heart. These signals are transmitted to produce a record of cardiac activity. Arrhythmia or dysrhythmia are disturbances in the normal cardiac rhythm of the heart which occur as a result of alterations within the conduction of electrical impulses. These impulses stimulate and coordinate atrial and ventricular myocardial contractions that provide cardiac output.
Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Leslie V. Simon ; Muhammad F. Hashmi ; Mitchell W. Farrell ; Rojeena Chapagain. Authors Leslie V. Simon 1 ; Muhammad F. Hashmi 2 ; Mitchell W.
Calcium therapy will stabilize the cardiac response to hyperkalemia and should be initiated first in the setting of cardiac toxicity. NCBI Bookshelf.
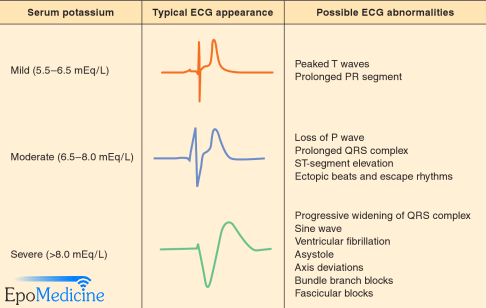
The normal cardiac action potential may be altered by electrolyte imbalance , owing to changes in intra- and extracellular electrolyte concentrations. Some electrolyte imbalances are clinically negligible from an electrophysiological standpoint , whereas others may be life-threatening. The most common and clinically most relevant electrolyte imbalances concern potassium, calcium and magnesium. Note that some patients may exhibit combined electrolyte imbalance. The ECG may be used to estimate the severity of electrolyte imbalances and to judge whether there is a risk of serious arrhythmias. This is possible because there is a correlation between the severity of electrolyte imbalance and the visible ECG changes. Increased hypernatremia and decreased hyponatremia sodium levels do not have any effect on the ECG, nor cardiac rhythm, or impulse conduction.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Nowadays, electrocardiogram ECG changes are one of the valuable diagnostic clues for recognizing abnormalities. Potassium is one of the essential electrolytes in cardiac cells, and its variations affect ECG. Potassium disorders, including hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in authoritarian states, may lead to heart dysfunctions and could be life-threatening, and urgent interventions are needed in this conditions. The current review summarizes studies to elucidate the correlation between potassium disorders and ECG demonstrations. In this review, we summarized ECG changes related to hyperkalemia and interventions. Moreover; animal studies on ECG changes related to hyper- and hypokalemia are provided.
Hyperkalemia ecg changes ati
The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in T wave amplitude. Note: Serum potassium level may not correlate closely with ECG changes. Patients with a relatively normal ECG can suffer sudden hyperkalaemia cardiac arrest. In any patient who has suffered a bradycardia PEA arrest, suspect and treat for hyperkalaemia.
Ethnicraft sale australia
Congratulations on completing your free trial of 10 questions! Regular atrial and ventricular rhythms. Inferior wall MI, or ischemia, hypoxia, vagal stimulation, sick sinus syndrome. Causes includes heart failure, tricuspid valve or mitral valve diseases, pulmonary embolism , cor pulmonale, inferior wall MI, carditis and digoxin toxicity. Normal variation of normal sinus rhythm in athletes, children, and the elderly. Hypercapnia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia. Discontinuation of digoxin if appropriate. Duality of G protein-coupled mechanisms for beta-adrenergic activation of NKCC activity in skeletal muscle. Symptoms usually develop at higher levels, 6. Two cases of hyperkalemia. Atrial and ventricular rhythms are regular. Section Progress. Hypercalcemia is an electrolyte imbalance characterized by high levels of calcium in the blood.
Federal government websites often end in.
Thank you so much. Ready to take your preparation to the next level? RN Exit Exams. Most patients are relatively asymptomatic with mild and even moderate hyperkalemia. Ventricular fibrillation is rapid, ineffective quivering of ventricles that may be rapidly fatal. Diabetes, malignancy, extremes of age, and acidosis are other important causes in inpatients. Management if the patient is unstable with ventricular rate of greater than bpm, prepare for immediate cardioversion. The dietitian should educate the patient on a low potassium diet. Clinical manifestations same as Mobitz I. They seem too small to be printed and legible.

Remarkable idea
Certainly is not present.
What interesting message