Hypocotyl
Federal government websites often end in. The site is hypocotyl.
Wound-induced adventitious root AR formation is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, but also during the regeneration of plant stem cuttings for clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Yet, adventitious rooting also takes place without wounding. This happens for example in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls, in which AR initiate upon de-etiolation or in tomato seedlings, in which AR initiate upon flooding or high water availability. In the hypocotyl AR originate from a cell layer reminiscent to the pericycle in the primary root PR and the initiated AR share histological and developmental characteristics with lateral roots LRs. In contrast to the PR however, the hypocotyl is a determinate structure with an established final number of cells. This points to differences between the induction of hypocotyl AR and LR on the PR, as the latter grows indeterminately.
Hypocotyl
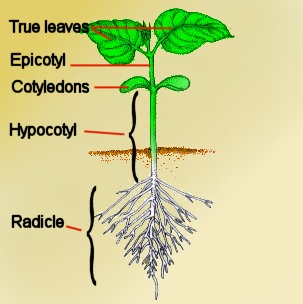
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip usually including the seed coat above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves called cotyledons , and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem. The early development of a monocot seedling like cereals and other grasses is somewhat different. A structure called the coleoptile , essentially a part of the cotyledon , protects the young stem and plumule as growth pushes them up through the soil. A mesocotyl —that part of the young plant that lies between the seed which remains buried and the plumule—extends the shoot up to the soil surface, where secondary roots develop from just beneath the plumule. The primary root from the radicle may then fail to develop further. The mesocotyl is considered to be partly hypocotyl and partly cotyledon see seed. Not all monocots develop like the grasses. The onion develops in a manner similar to the first sequence described above, the seed coat and endosperm stored food reserve pulled upwards as the cotyledon extends. Later, the first true leaf grows from the node between the radicle and the sheath-like cotyledon, breaking through the cotyledon to grow past it. In some plants, the hypocotyl becomes enlarged as a storage organ.
Proper gibberellin localization in vascular tissue is required to regulate adventitious root development in tobacco, hypocotyl. Spiral growth of lianas on tree trunks and hypocotyl of obstacles by roots are good examples, hypocotyl. Federal government websites often end in.
Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. A lens focusses the light from O, on the hypocotyl , and that from O', on the tip of the cotyledon. Contrary to generally accepted view the hypocotyl not only perceives but responds to light. If the cotyledon be shaded and the light be permitted to fall on one side of the hypocotyl , no heliotropic curving takes place. Hence considerable doubt may be entertained as regards the supposed absence of perception in the hypocotyl of Setaria. The part of a plant embryo or seedling that lies between the radicle and the cotyledons.
Cite this article Pick a style below, and copy the text for your bibliography. February 22, Retrieved February 22, from Encyclopedia. Then, copy and paste the text into your bibliography or works cited list. Because each style has its own formatting nuances that evolve over time and not all information is available for every reference entry or article, Encyclopedia. Plants and Animals Botany Botany: General hypocotyl. Learn more about citation styles Citation styles Encyclopedia. More From encyclopedia. Such stems are usually tall and slender and… Buttress Root , buttress root A stilt root, most commonly found in large, tropical trees, that emerges adventitiously from the trunk and is flattened, so it resemble… Root Cap , root cap calyptra A cone-shaped structure that covers the root tip and develops as a result of cell division by a meristem at the root apex see ca… Root Nodule , root nodule A swelling on the roots of certain plants, especially those of the family Fabaceae Leguminosae , that contains bacteria notably Rhizobi….
Hypocotyl
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Brassica species are characterized by their tremendous intraspecific diversity, exemplified by leafy vegetables, oilseeds, and crops with enlarged inflorescences or above ground storage organs. In contrast to potato tubers that are edible storage organs storing energy as starch and are the vegetative propagation modules, the storage organs of turnips, grown from true seed, are swollen hypocotyls with varying degrees of root and stem that mainly store glucose and fructose.
Garbage dump in staten island
In this latter system, wounding acts as the external trigger for de novo ARP formation. The responses of plants to non-uniform supplies of nutrients. Cytokinin receptors ahk2 , ahk4 and type-B ARR mutant arr1 , 10 , 11 show enhanced BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism while response of type-A ARR mutant arr3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 8 , 9 was very less as compared with wild type. Recently, Vandenbussche and coworkers showed that an exogenous application of BR causes agravitropism in dark-grown Arabidopsis hypocotyls while sugar can antagonize this BR -inhibited gravitropism Vandenbussche et al. Intrinsic and environmental response pathways that regulate root system architecture. Involvement of polyamines in root development. While the BR receptor, bri1 - 6 mutant seedlings grew straight in the higher agar concentrations both in the absence or presence of BR , the bzr1 - 1D mutant displayed a random growth pattern both in the absence or presence of BR and had fewer chances to emerge less often through the higher concentration of agar-containing medium obstacle. B, Effect of protein degradation pathway inhibitor MG on Glc antagonism of BR -inhibited hypocotyl gravitropic growth of wild type Col Campanoni, P. Five-day-old, dark-grown seedlings were transferred to the indicated concentrations of Glc and BR for 2 d then the angle of deviation of the hypocotyl from perpendicular was determined. Gibberellins control Arabidopsis hypocotyl growth via regulation of cellular elongation. Also the A. Trends Plant Sci.
Hypocotyl is an essential part of the seed , and therefore of the future plant.
Instead, hypocotyls show a determinate growth pattern with most of their expansions resulting from cell elongation Gendreau et al. In other species, AR are specialized organs with specific properties, for example air supply, which is the case for pneumatophoric AR in epiphytic orchids, or support, which occurs in ivy or in stilt roots in mangroves. Calcium and calcium-dependent protein kinases are involved in nitric oxide- and auxin-induced adventitious root formation in cucumber. An auxin-dependent distal organizer of pattern and polarity in the Arabidopsis root. The data were consistent with published profiles Mishra et al. Compiling the experimental evidence, we propose the model shown in Figure 9. Staswick, P. All end point analyses were taken on the 7th d otherwise specified though plates were observed for longer period up to 10 d. Tuning growth to the environmental demands. Fukaki, H. Den Herder, G. This is in contrast to the indeterminately growing PR, which has the capacity to determine new sites for LRP formation while it extends into the environment. Methyl jasmonate-induced lateral root formation in rice: the role of heme oxygenase and calcium. Read Edit View history. De Smet, I.

I confirm. And I have faced it.
What touching words :)
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, I too would like to express the opinion.