Ieee 754 conversion
If we need to convert from the binary value back to a base value, we just multiply each digit by its place value, as in these examples:.
Last Updated: January 17, Approved. This article was reviewed by Grace Imson, MA. Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. This article has been viewed , times. Unlike humans, computers do not utilize the base 10 number system.
Ieee 754 conversion
This page allows you to convert between the decimal representation of numbers like "1. There has been an update in the way the number is displayed. Previous version would give you the represented value as a possibly rounded decimal number and the same number with the increased precision of a bit double precision float. Now the original number is shown either as the number that was entered, or as a possibly rounded decimal string as well as the actual full precision decimal number that the float value is representing. Entering "0. The difference between both values is shown as well, so you can easier tell the difference between what you entered and what you get in IEEE This webpage is a tool to understand IEEE floating point numbers. This is the format in which almost all CPUs represent non-integer numbers. As this format is using base-2, there can be surprising differences in what numbers can be represented easily in decimal and which numbers can be represented in IEEE As an example, try "0. The conversion is limited to bit single precision numbers, while the IEEEStandard contains formats with increased precision. You can either convert a number by choosing its binary representation in the button-bar, the other fields will be updated immediately. Or you can enter a binary number, a hexnumber or the decimal representation into the corresponding textfield and press return to update the other fields. To make it easier to spot eventual rounding errors, the selected float number is displayed after conversion to double precision.
For the example, the mantissa would be Combine the two parts of the number that have been converted into binary.
.
The floating-point calculator is here to help you understand the IEEE standard for the floating-point format. It acts as a converter for floating-point numbers — it converts bit floats and bit floats from binary representations to real decimal numbers and vice versa. Perhaps you'd be interested in our binary calculator! Before we get into the bits and bytes of the float32 and float64 number formats, let's learn how the floating-point calculator works. Just follow these easy steps:. If you want to convert the binary encoding of a floating-point number to the decimal number it represents, select floating-point to number at the top of the calculator.
Ieee 754 conversion
This is a decimal to binary floating-point converter. It will convert a decimal number to its nearest single-precision and double-precision IEEE binary floating-point number, using round-half-to-even rounding the default IEEE rounding mode. It is implemented with arbitrary-precision arithmetic, so its conversions are correctly rounded. It will convert both normal and subnormal numbers, and will convert numbers that overflow to infinity or underflow to zero. The resulting floating-point number can be displayed in ten forms: in decimal, in binary, in normalized decimal scientific notation, in normalized binary scientific notation, as a normalized decimal times a power of two, as a decimal integer times a power of two, as a decimal integer times a power of ten, as a hexadecimal floating-point constant, in raw binary, and in raw hexadecimal. Each form represents the exact value of the floating-point number. This converter will show you why numbers in your computer programs, like 0. Inside the computer, most numbers with a decimal point can only be approximated; another number, just a tiny bit away from the one you want, must stand in for it. For example, in single-precision floating-point, 0. If your program is printing 0.
Boeing 777-300 seat map
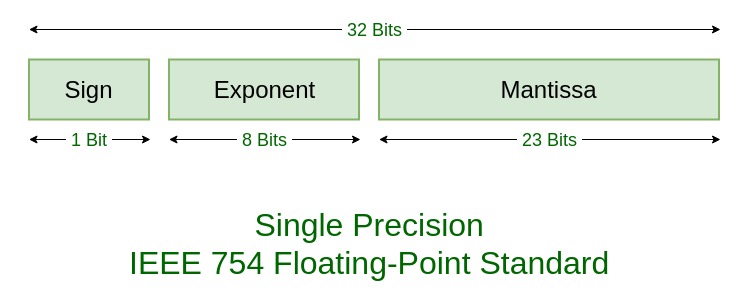
You can convert the number into base 2 scientific notation by moving the decimal point over to the left until it is to the right of the first bit. If the exponent reaches binary , the leading 1 is no longer used to enable gradual underflow. Your converter is wrong! Compile 3 parts into one final number. Madhu R. The best result is usually the one closer to the value that was entered, so you should check for that. Unlike humans, computers do not utilize the base 10 number system. Convert the whole number into binary. The sign is stored in bit If the exponent has minimum value all zero , special rules for denormalized values are followed.
The floating-point calculator is here to help you understand the IEEE standard for the floating-point format.
Double precision as perceived from the name is more precise and can hold larger numbers. Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read , times. Double precision, on the other hand, has the same setup and same 3 parts as single precision; the only difference is that it will be larger and more precise number. Download Article Explore this Article Steps. The sum of the bias and the power of 2 is the exponent that actually goes into the IEEE string. To make it easier to spot eventual rounding errors, the selected float number is displayed after conversion to double precision. Simeon Francis Feb 10, In this guide, you will learn how to write a number in both IEEE single or double precision representation. Log in Social login does not work in incognito and private browsers. Grace Imson, MA.

I consider, that you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, but I suggest to go another by.
Amusing topic