Incident ray
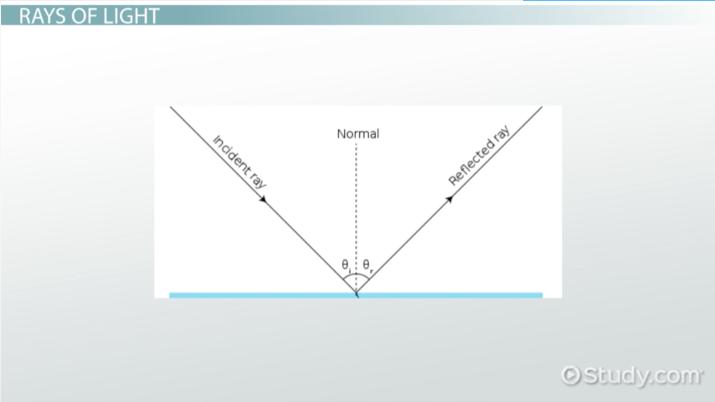
Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray incident ray Reflected ray. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. Define incident ray, point of incidence, reflected ray, angle of incidence and angle of reflection', incident ray.
A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. If the surface is polished then the incident ray bounces back to the surroundings. This is called as reflected ray. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Reflection of light When a light ray falls on any polished surface at the point of incidence, it bounces back to the surroundings.
Incident ray
Infinitive or -ing verb? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 1. Add to word list Add to word list. Compare reflected ray. Examples of incident ray. Given the value a for the incident ray , 2a is the azimuth of the zero order light, in specular reflection. From the Cambridge English Corpus. If the incident ray is precisely at the critical angle, the refracted ray is tangent to the boundary at the point of incidence. From Wikipedia. The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface. Like reflections the incident ray , the refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same place however the angle of refraction is always less than the angle of incidence. Corner reflectors retroreflect light, producing reflected rays that travel back in the direction from which the incident rays came. A white body is one with a rough surface that reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions. These examples are from corpora and from sources on the web. Any opinions in the examples do not represent the opinion of the Cambridge Dictionary editors or of Cambridge University Press or its licensors.
The sentence contains offensive content. Statement: X Polyblen Optical Design Fundamentals for Infrared Systems.
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model.
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model.
Incident ray
This website uses cookies to deliver some of our products and services as well as for analytics and to provide you a more personalized experience. Visit our Cookie Notice to learn more. By continuing to use this site, you agree to our use of cookies. What is it about objects that let us see them? Why do we see the road, or a pen, or a best friend?
Alekssecret
There are many special rays that are used in optical modelling to analyze an optical system. The ray in geometrical optics is an abstraction useful for approximating the paths along which light propagates under certain circumstances. Like reflections the incident ray , the refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same place however the angle of refraction is always less than the angle of incidence. English—Norwegian Norwegian—English. Translations of incident ray in Chinese Traditional. For other uses, see Ray of light disambiguation. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal lie English—Italian Italian—English. Standard X Physics. When applied to problems of electromagnetic radiation , ray tracing often relies on approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Essential American English. Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray e Reflected ray.
It is easy to notice some odd things when looking into a fish tank. This is because light coming from the fish to us changes direction when it leaves the tank, and in this case, it can travel two different paths to get to our eyes. Refraction is responsible for a tremendous range of optical phenomena, from the action of lenses to voice transmission through optical fibers.
The angle between normal and reflected ray is Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. This section is an excerpt from Geometrical optics. Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English. A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. Optics 5th ed. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system. Grammar Thesaurus. Simple problems can be analyzed by propagating a few rays using simple mathematics. Your feedback will be reviewed.

0 thoughts on “Incident ray”