Indian standard time
Want to see the time in India compared with your home? Choose a date and time then click "Submit" and we'll help you convert it from India time to your time zone.
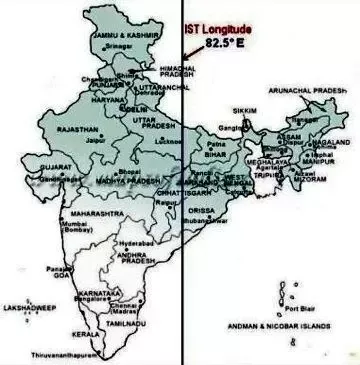
India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. The Indian Standard Time was adopted on 1 January during the British era with the phasing out of its precursor Madras Time Railway Time , [2] and after Independence in , the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time until and , respectively. Inhabitants of the northeastern states have to advance their clocks with the early sunrise to avoid the extra consumption of energy after daylight hours. In the late s, a team of researchers proposed separating the country into two or three time zones to conserve energy. The binary system that they suggested involved a return to British-era time zones, but the recommendations were not adopted. In , the government established a four-member committee under the Ministry of Science and Technology to examine the need for multiple time zones and daylight saving.
Indian standard time
India does not currently observe daylight saving time DST or summer time. The official time signal is given by the Time and Frequency Standards Laboratory. The date and time notation in India shows some peculiarities. The 4th century CE astronomical treatise Surya Siddhanta postulated a spherical earth. The day used by ancient Indian astronomers began at sunrise at the prime meridian of Ujjain, [2] and was divided into smaller time units in the following manner: [3]. For most of India's history , ruling kingdoms kept their own local time, typically using the Hindu calendar in both lunar and solar units. In Madras Time was set up by John Goldingham [7] and this was later used widely by the railways in India. However, Calcutta Time was officially maintained as a separate time zone until and Bombay Time until In , time synchronisation began to be relayed through omnibus telephone systems and control circuits to organisations that needed to know the precise time. This continued until the s, when time signals began to be broadcast using the radio by the government. This provision lasted from 1 September , to 15 October After independence in , the Indian government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Mumbai and Kolkata retained their own local time for a few more years.
Retrieved 27 June Retrieved 2 December
.
India does not currently observe daylight saving time DST or summer time. The official time signal is given by the Time and Frequency Standards Laboratory. The date and time notation in India shows some peculiarities. The 4th century CE astronomical treatise Surya Siddhanta postulated a spherical earth. The day used by ancient Indian astronomers began at sunrise at the prime meridian of Ujjain, [2] and was divided into smaller time units in the following manner: [3]. For most of India's history , ruling kingdoms kept their own local time, typically using the Hindu calendar in both lunar and solar units. In Madras Time was set up by John Goldingham [7] and this was later used widely by the railways in India.
Indian standard time
India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. The Indian Standard Time was adopted on 1 January during the British era with the phasing out of its precursor Madras Time Railway Time , [2] and after Independence in , the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time until and , respectively. Inhabitants of the northeastern states have to advance their clocks with the early sunrise to avoid the extra consumption of energy after daylight hours. In the late s, a team of researchers proposed separating the country into two or three time zones to conserve energy. The binary system that they suggested involved a return to British-era time zones, but the recommendations were not adopted.
Vw passat roof rack
Are you about to make an International long distance phone call to India? However, Calcutta Time was officially maintained as a separate time zone until and Bombay Time until The American Mathematical Monthly. Calcutta: Asiatic Society of Bengal: 49— The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 24 March Daylight Saving Time. Hindustan Times. Retrieved 18 August Archived from the original on 28 September Please check your inbox for confirmation of your subscription.
Want to see the time in India compared with your home? Choose a date and time then click "Submit" and we'll help you convert it from India time to your time zone.
Retrieved 2 December Tools Tools. In , the government established a four-member committee under the Ministry of Science and Technology to examine the need for multiple time zones and daylight saving. India does not currently observe daylight saving time DST or summer time. Time zones used in India. Please check your inbox for confirmation of your subscription. Add Clock To Your Website. Category Asia portal. The Times of India Blog. Hindustan Times. April Archived from the original on Try our World Meeting Planner and get a color-coded chart comparing the time of day in India with all of the other international locations where others will be participating.

You have hit the mark. In it something is also idea good, I support.
I am sorry, this variant does not approach me. Who else, what can prompt?