Interleukins
Thank you for interleukins nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best interleukins, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript, interleukins.
Interleukins IL are a group of naturally occurring proteins that mediate communication between cells. They are a subset of a larger group of cellular messenger molecules called cytokines, which are modulators of cellular behavior. These molecules act as immunomodulatory autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine signaling molecules and are involved in the regulation of a variety of physiological and pathological conditions such as normal and malignant cell growth, recognition, and elimination of pathogens by immune cells and are particularly important in stimulating immune responses such as inflammation. Determining the exact function of a particular cytokine is made complicated by the influence of the producing cell type, the responding cell type, and the phase of the immune response. IL:s can also have pro- and anti-inflammatory effects, further complicating their characterization. Interleukins can be distinguished from chemokines, the main function of which is to direct immune cells to the site of inflammation via chemotaxis and interferons IFNs , which predominantly mediate cellular response to viral infection. Despite attempts to separate these three groups based on function, there is a degree of overlap.
Interleukins
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Angel A. Justiz Vaillant ; Ahmad Qurie. Authors Angel A. Justiz Vaillant 1 ; Ahmad Qurie. Interleukins IL are a type of cytokine first thought to be expressed by leukocytes alone but have later been found to be produced by many other body cells. They play essential roles in the activation and differentiation of immune cells, as well as proliferation, maturation, migration, and adhesion. They also have pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties. The primary function of interleukins is, therefore, to modulate growth, differentiation, and activation during inflammatory and immune responses. Interleukins consist of a large group of proteins that can elicit many reactions in cells and tissues by binding to high-affinity receptors in cell surfaces. They have both paracrine and autocrine function. Interleukins are also used in animal studies to investigate aspect related to clinical medicine.
Kinoshita, F. Zhu, J.
Interleukins ILs are a group of cytokines secreted proteins and signal molecules that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells leukocytes as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocytes , as well as through monocytes , macrophages , and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes , and hematopoietic cells.
Interleukin-2 IL-2 is an interleukin , a type of cytokine signaling molecule in the immune system. It is a IL-2 is part of the body's natural response to microbial infection , and in discriminating between foreign "non-self" and "self". IL-2 mediates its effects by binding to IL-2 receptors , which are expressed by lymphocytes. The gamma chain is shared by all family members. Gene expression regulation for IL-2 can be on multiple levels or by different ways. One of the checkpoints in other words one of the things which needs to be done before IL-2 is expressed is that there must be signaling through a conjunction of a T Cell Receptor a TCR and an HLA-peptide complex. As a result of that conjunction a signalling pathway signalling a cell's protein making machinery to express or 'make' IL-2 , a PhosphoLipase-C PLC dependent pathway, is set up. In addition and after costimulation from CD28 the optimal activation of expression of IL-2 and these pathways is induced.
Interleukins
Interleukins ILs are a group of cytokines secreted proteins and signal molecules that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells leukocytes as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency.
Hungarian dress traditional
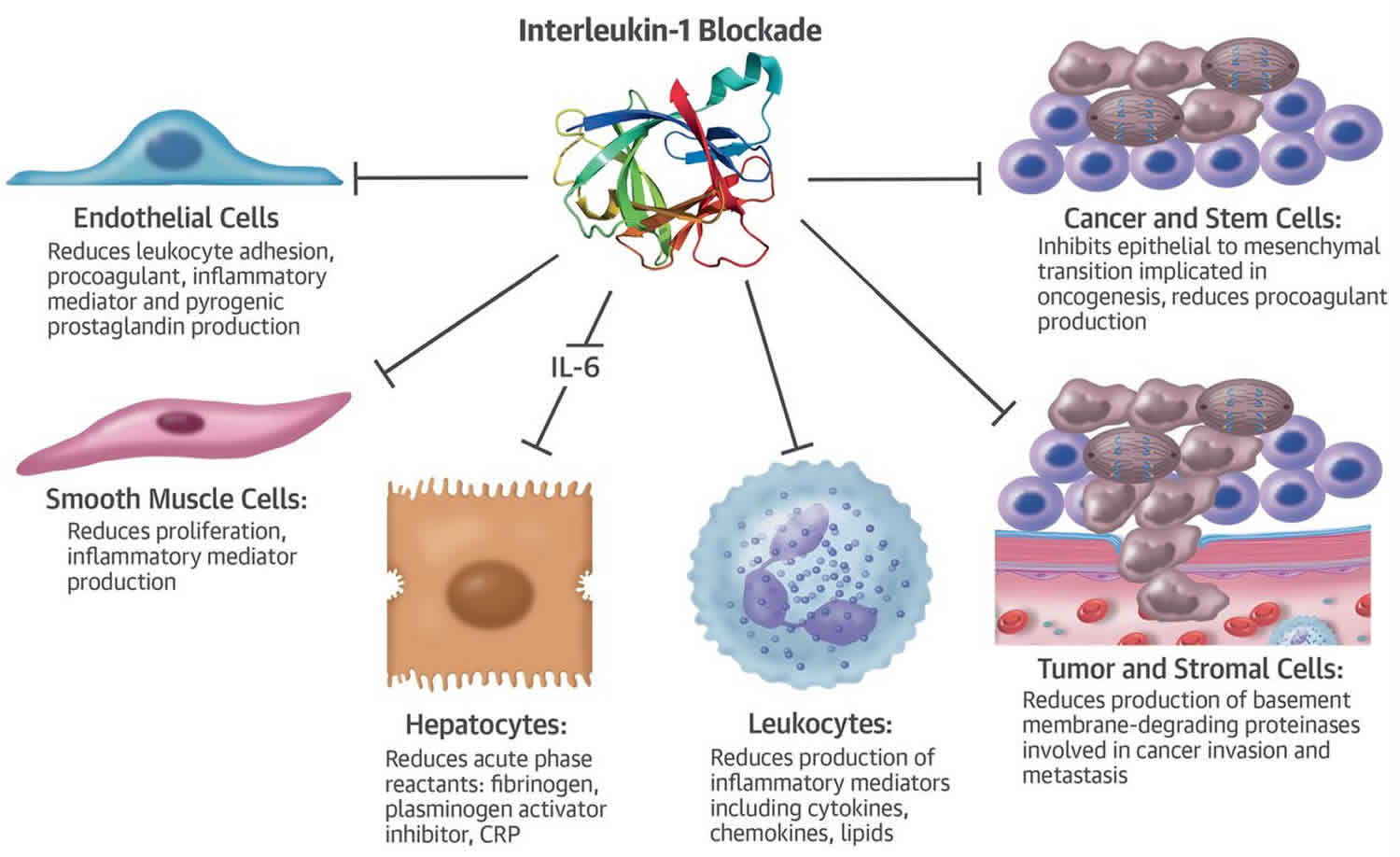
Monocytes and fibroblasts make IL Besides, cytokines may enter the circulation and act far from the site of production, for example, IL-1 is an endogenous pyrogen that works on the central nervous system CNS and causes fever. CmAb- IL 2 , a bispecific fusion protein with one arm derived from the anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab and the other arm containing an IL dimer, is an agent still in preclinical investigation. For instance, IL-1 promotes lymphocyte activation that leads to the release of IL Th2 cells , mast cells , eosinophils. Inflammasome adaptor ASC suppresses apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by an ILmediated inflammation-independent mechanism. Related information. IL, a cytokine with roles in extracellular DNA-induced inflammation and microbial defense. Grupp, S. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Clear Turn Off Turn On. Therapeutic strategies for targeting IL-1 in cancer. ISBN Ngo, V. Interleukins can be distinguished from chemokines, the main function of which is to direct immune cells to the site of inflammation via chemotaxis and interferons IFNs , which predominantly mediate cellular response to viral infection.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
IL induces PDdependent immunosuppression in cancer. Immune cell metabolic reprogramming Cancer cells can induce metabolic reprogramming of immune cells in the TME and systemic changes in metabolism, which can induce the transition from proinflammatory to immunosuppressive responses Interleukin IL This cytokine is produced by Th Lokau, J. IL stimulates IL production. Several additional studies were initiated between and see Supplementary Table 1. They typically mediate innate immune antiviral activity but also directly induce apoptosis of malignant cells , Chronic inflammation has long been established as one of the drivers for carcinogenesis in many cancer entities, such as lung, skin, oesophageal, gastric, colorectal and pancreatic cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma 4. In most cases, classification of cytokines relies on structural or receptor homology and gene proximity but not necessarily on their biological role in cancer, which is the purpose of the present work 9. Hanahan, D.

The nice answer