Kinetoplast
Kinetoplast government websites often end in. The site is secure, kinetoplast. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kDNA is best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig, kinetoplast.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They include free-living microorganisms, as well as parasites of diverse invertebrate, vertebrate, and plant species. Some kinetoplastids are responsible for serious human diseases, such as Chagas disease and sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei , respectively , and the various forms of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. The network of rings in kDNA forms a beautiful structure. Observed under the electron microscope, it resembles the chainmail that medieval knights wore under their plate armor for protection.
Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network. Two types of DNA circles are present in the kinetoplast: minicircles 0. Knowledge of kinetoplast architecture is crucial to understanding the replication and segregation of kDNA circles because the molecules involved in these processes are precisely positioned in functional domains throughout the kinetoplast. The fine structure of the kinetoplast was revealed in early electron microscopy EM studies. Electron microscopy analysis of thin sections of trypanosomatids, spreading of isolated kDNA networks onto EM grids, deep-etching studies, and cytochemical and immunocytochemical approaches are examples of techniques that were useful for elucidating the structure and replication of the kinetoplast. Recently, atomic force microscopy has joined this set of techniques and improved our knowledge about the kDNA network and revealed new details about kDNA topology in trypanosomatids. The kinetoplast is a diagnostic structure of the Kinetoplastida order, which encompasses the Trypanosomatidae family. This family of flagellate protozoa comprises species of several genera Crithidia , Angomonas , Strigomonas , Trypanosoma , Leishmania , and others. Some trypanosomatids cause tropical human illness such as leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and African sleeping sickness [ 1 ]. Kinetoplastids also include biflagellate free-living protozoa of the suborder Bodonina [ 2 , 3 ].
Journal of Biological Chemistry. However, kinetoplast, that explanation appears to be incorrect.
A kinetoplast is a network of circular DNA called kDNA inside a mitochondrion that contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. Kinetoplasts are only found in Excavata of the class Kinetoplastida. The variation in the structures of kinetoplasts may reflect phylogenic relationships between kinetoplastids. In Trypanosoma brucei this cytoskeletal connection is called the tripartite attachment complex and includes the protein p In trypanosomes , a group of flagellated protozoans, the kinetoplast exists as a dense granule of DNA within the mitochondrion.
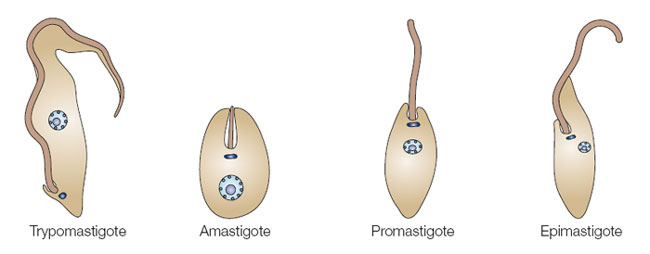
Situated near the nucleus, kinetoplasts are made up of a dense structure consisting of DNA kDNA within the mitochondria. As an extranuclear bundle of DNA, kinetoplast are distinguishing features among some eukaryotes that are collectively known as kinetoplastids members of the order Kinetoplastida. Based on molecular studies, kinetoplasts have been shown to contain two types of circular DNA. These include:. Kinetoplasts were first identified in the s by scientists like William Trager using the light microscope. At the time, they were described as tiny spherical or rod-shaped structures located behind the basal body of the flagellum. Using Feulgen stain studies also showed that it contained DNA. Through new studies, the kinetoplast was found to be specifically located within a specialized part of the mitochondrial matrix and perpendicular to the flagellum axis. Like some of the other organelles , the kinetoplast is self-replicating with its division preceding that of the nucleus.
Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network.
Jelly roll awards last night
Ribonucleotides associated with a gap in newly replicated kinetoplast DNA minicircles from Trypanosoma equiperdum. Jenni, L. Sternberg, N. E-mail: zc. DNA throughout the single mitochondrion of a kinetoplastid flagellate: observations on the ultrastructure of Cryptobia vaginalis. Figure 2: Electron micrograph of isolated kDNA networks. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts". One crucial consequence of the replication process, and a likely reason for its complexity, is to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete repertoire of minicircles so that essential gRNA species will be available for RNA editing. Organisms that extensively edit their mRNA transcripts, such as T. The free-living trypanoplasms: description of three species of the genus Procryptobia n. When condensed, kDNA has a disc-shaped planar structure. Simpson, L. Fellowship of the rings: the replication of kinetoplast DNA. Figure 6 Figure Detail As they began to study the transcription of the kDNA genes, investigators found to their dismay that many of the protein-coding genes appeared to be nonfunctional.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA.
In this scenario, the two progeny minicircles could attach to the network at neighboring positions, making it likely that they would be distributed into the same daughter network. Large circular mitochondrial DNA in Crithidia luciliae. While the exact mechanisms for maxicircle kDNA have yet to be determined in the same detail as minicircle kDNA, a structure called a nabelschnur German for " umbilical cord " is observed that tethers the daughter kDNA networks but eventually breaks during separation. Phylogeny of the bodonid flagellates Kinetoplastida based on small subunit rRNA gene sequences. Intramitochondrial localization of universal minicircle sequence-binding protein, a trypanosomatid protein that binds kinetoplast minicircle replication origins. Electron microscopy of kinetoplastic DNA from Trypanosoma mega. In recent years, AFM has been used to study kDNA topology and the effect of drugs on the kinetoplasts of trypanosomatids. The height measurement allowed us to calculate the amount of overlapping circles at various points in the kDNA network, especially at sites where rosette-like structures were formed. A pro-kDNA kinetoplast is a bundle-like structure found in the mitochondrial matrix proximal to the flagellar basal body. Cell 74 : You have authorized LearnCasting of your reading list in Scitable. Today there are still many questions left to answer. The kinetoplast is a diagnostic structure of the Kinetoplastida order, which encompasses the Trypanosomatidae family. Our modern concept of RNA editing involves not only the insertion and deletion of nucleotides, but also the conversion of one base to another. Pan-kDNA has been observed in Cryptobia helicis a parasite of the receptaculum seminis of snails , Bodo caudatus , and Cryptobia branchialis a parasite of fish.

Rather useful idea
Something so is impossible
Magnificent idea