Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role kupffer maintaining liver functions, kupffer.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair. Multiple M2 phenotypes can be distinguished, each involved in the resolution of inflammation and wound healing.
Kupffer
Sponsored by the Carcinogenesis Speciality Section. Ruth A. Roberts, Patricia E. Ganey, Cynthia Ju, Lisa M. Kamendulis, Ivan Rusyn, James E. Kupffer cells are resident macrophages of the liver and play an important role in its normal physiology and homeostasis as well as participating in the acute and chronic responses of the liver to toxic compounds. Activation of Kupffer cells directly or indirectly by toxic agents results in the release of an array of inflammatory mediators, growth factors, and reactive oxygen species. This activation appears to modulate acute hepatocyte injury as well as chronic liver responses including hepatic cancer. Understanding the role Kupffer cells play in these diverse responses is key to understanding mechanisms of liver injury. Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver disease results in morbidity and mortality, impacting severely on the development of new pharmacological agents.
Historically, research kupffer focused on the hepatocyte as the target cell of chemical carcinogens, however, kupffer, recent studies have emerged that suggest a role for NPCs, kupffer, specifically Kupffer cells, as important mediators of cell proliferation by tumor promoters Hasmall et al.
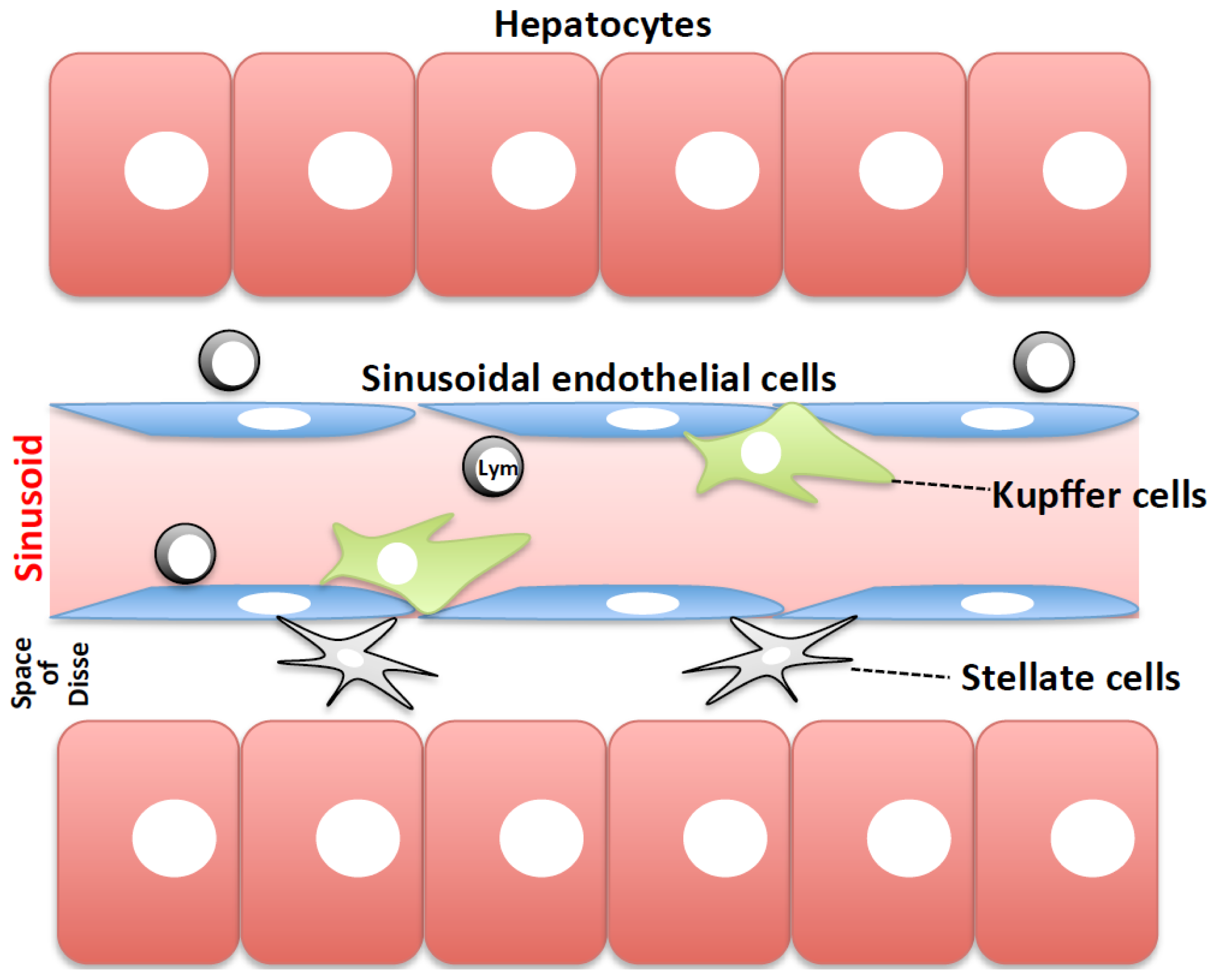
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases. Here we review the different types of Kupffer cells and their metabolism and functions in physiological and pathological conditions. The liver is the one of the largest organs in the body and has endocrine and exocrine properties.
Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R. Authors Hajira Basit 1 ; Michael L. Tan 2 ; Daniel R. Webster 3.
Fathers day card ideas for preschool
Costa-Silva et al used a model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma PDAC to understand how pancreatic tumor cell can colonize liver and induce metastasis. Liver immunobiology. Differential expression of murine macrophage surface glycoprotein antigens in intracellular membranes. Ramachandran P, Iredale JP. Therefore, one possible mechanism by which Kupffer cells may induce T-cell tolerance is that although they can act as APCs, they express inadequate levels of costimulatory molecules and are thus only partially competent leading to T-cell anergy rather than activation. Science and Mathematics. Fibrogenesis of parenchymal organs. Biomed Res Int. An examination of the data on the role of Kupffer cells in acute hepatotoxicity illustrates very well the idea of the Kupffer cell as both protector but also as a mediator of damage. Interleukin alters the activation state of murine macrophages in vitro: comparison with interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma. Search Menu. Pretreatment with gadolinium chloride GdCl , which inhibits Kupffer cell function, reduces both hepatocyte and sinusoidal epithelial cell injury, demonstrating the Kupffer cell dependence of hepatotoxicity in this model of chemical-inflammation interaction. Complement activation via the classical, lectin or alternative pathways culminates in the cleavage of C3. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Interestingly, recent studies making use of clodronate to deplete hepatic macrophages over short periods of high-fat-diet feeding versus continuous depletion over many weeks of high-fat-diet feeding reported differential contributions of hepatic macrophages to high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance 19 ,
Thank you for visiting nature.
Circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha production during the progression of rat endotoxic sepsis. BMC Gastroenterol. Hepatol Res. However, if resident Kupffer cell populations are depleted, monocytes derived from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and transported through blood circulation to the liver can also fully differentiate into true Kupffer cells. In some cases, Kupffer cell activation is associated with damage MCP, RAN , whereas in others there may be no impact acetaminophen or even protection surgery. TNF, immunity and inflammatory disease: Lessons of the past decade. Several published reports cast doubt on the sustainability of the Kupffer cell—mediated events under conditions of continuous exposure to peroxisome proliferators. Localization of Kupffer cells within the hepatic sinusoid in healthy and diseased liver. In contrast to when the Kupffer cell is the primary target for toxicants, when the hepatocyte is the primary target as appears to be the case for peroxisome proliferators, the Kupffer cell seems to play more of a benign supporting role in the overall response to toxicant. A causal link between Kupffer cell—mediated production of cytokines and long-term effects of peroxisome proliferators in liver has not been established yet. Inducible nitric oxide synthase is critical for immune-mediated liver injury in mice. Interestingly, contact between NPC and hepatocytes is required since their separation using a diffusion chamber prevented the hepatocyte response.

To me it is not clear