Lewis structure for c2h4
Most stable structure is taken as the lewis structure of ethene. Hybridization of atoms in ethene molecue can be found from lewis structure.
The bond angle between the orbitals is o with no free rotation about a carbon double bond. C2H4 is the chemical formula of a colourless and flammable gas known as Ethylene. It is said to be a hydrocarbon that has two carbon atoms connected to it with a double bond. It is lighter than air. Here, one 2p orbital does not change, and it will help form a pi bond. Molecular structure defines the arrangement of atoms in a molecule or ion. The bonded pair of hydrogen attached to carbon repels each other, and as a result, the figure thus formed is a trigonal planar.
Lewis structure for c2h4
Hydrocarbons form an essential and inseparable portion of the science of chemistry. Be it petroleum, crude oil, or natural gas, the majority of hydrocarbons are found naturally in these fossil fuels. Apart from this, we can find them in synthetic polymers and other man-made plastic materials. They are organic in nature and as the name suggests, they are formed of only carbon and hydrogen. Sometimes, it also creates compounds with other varieties like sulfur, nitrogen, and so on. Although these are some of the simplest organic compounds we can come across, they have a varied range and differ in several physical and chemical properties. In this article, we will talk about one of the most common and widely used hydrocarbons: Ethylene C2H4. Well, C2H4 is a simple straight-chain hydrocarbon that bears a sweet aroma and has a colorless form. So, it is important for us to learn about C2H4 in detail to understand the nature of straight-chain hydrocarbons in a better manner. Carbon has a covalent nature when it comes to bonding with hydrogen and this leads to the formation of the different types of hydrocarbons that we see. From simplest ones like methane and benzene to some of the complex ones like natural rubber, we deal with several HCs in our daily lives.
Table of Content.
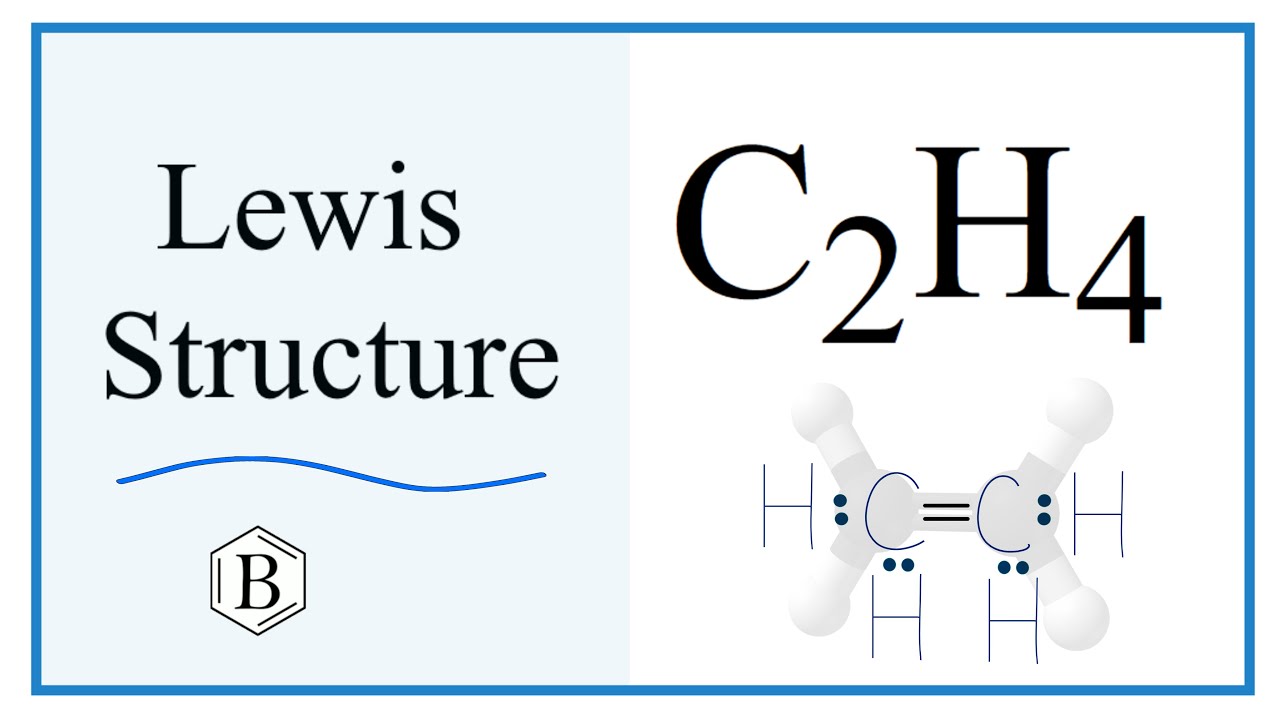
Draw the electron dot structure of ethene, C 2 H 4? Method for calculating electron dot structure:. We can determine the electron dot structure of any given compound by the following steps:. E represents the total number of valence electrons and B. E denotes the number of electrons present in the bond pairs.
Thus far valence bond theory has been able to describe the bonding in molecules containing only single bonds. However, when molecules contain double or triple bonds the model requires more details. Ethylene commonly knows as ethene , CH 2 CH 2 , is the simplest molecule which contains a carbon carbon double bond. The Lewis structure of ethylene indicates that there are one carbon-carbon double bond and four carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Experimentally, the four carbon-hydrogen bonds in the ethylene molecule have been shown to be identical. Because each carbon is surrounded by three electron groups, VSEPR theory says the molecule should have a trigonal planar geometry. Although each carbon has fulfilled its tetravalent requirement, one bond appears different. Clearly, a different type of orbital overlap is involved. The sigma bonds formed in ethene is by the participation of a different kind of hybrid orbital.
Lewis structure for c2h4
Watch the video of Dr. Note that the C 2 H 4 Lewis dot structure involves sharing more than one pair of electrons. Video Transcript: OK, we're going to do one here, this is called ethene. It's C2H4, and we want to write the dot structures for ethene. To do that, we always count our valence electrons up first. Let's take a look: Carbon is in group 4, sometimes written 14, so it has 4 valence electrons. If we come way over here to Hydrogen, it's in group 1: it has 1 valence electron.
Shaving foam walmart
Well, that rhymed. E denotes the number of electrons present in the bond pairs. Also, the free rotation of the two carbon double bonds is restricted. The chemical formula for Ethylene is C2H4 which means it has two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms. However, in Hydrocarbons , we always place the Carbon atoms in the center as shown in the figure. Introduction to Chemical Bonding. In C2H4, if we look into the lewis structure, we will see that there are three bonded pairs of electrons around each carbon and zero lone pair. For the more specific reasons regarding the polarity of C2H4, you must check out the article written on the polarity of C2H4. The molecular orbital theory is a concept of quantum mechanics where atomic linearly combines to form molecular orbitals and we describe the wave nature of atomic particles. It is lighter than air. There are two triangles overlapping each other as we can see in the diagram.
A Lewis structure is a way to show how atoms share electrons when they form a molecule. Lewis structures show all of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell.
And the rest of the 2 electrons from each carbon will be used to make a total of 4 single bonds with 4 hydrogen single atoms. Ethene or C2H4 is a common straight-chain acyclic alkene and an important member of organic hydrocarbons. JEE Examination Scheme. JEE Advanced Syllabus. Here, one 2p orbital does not change, and it will help form a pi bond. Hydrogen atoms are not hybridized because it has only s orbital. Carbon atoms have sp 2 hybridization. The bond angle between the orbitals is o with no free rotation about a carbon double bond. Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. Read full.

I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It agree, rather the helpful information