Lisfranc fracture radiology
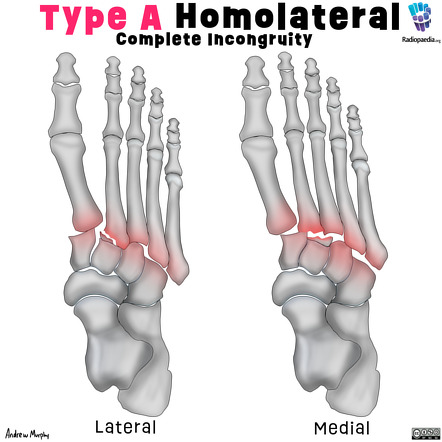
There is lateral displacement of the lesser metatarsals with respect to the first metatarsal with widening of the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal base, lisfranc fracture radiology, with an intra-articular fracture from the medial margin of the base of the 2nd metatarsal. Homolateral Lisfranc fracture dislocation.
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint. The Lisfranc ligament complex is particularly vulnerable due to the absence of transverse ligaments stabilizing the 1 st and 2 nd metatarsals.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy. Chalk Stick Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Updated: Nov 15, Trauma due to falling off a roof. Figure 1. Figure 2. Type B2 Lisfranc injury. B Arrow demonstrates the increase in distance between the first and second metatarsals. The red lines show the misalignment or lateral displacement of the 2nd metatarsal bone over the second cuneiform bone and the preserved alignment of the first metatarsal with the first cuneiform bone. The first cuneiform bone is also fractured and there is lateral shift of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th metatarsals. C Lateral radiograph demonstrates dorsal sub dislocation of the metatarsal base red circle. A Lisfranc Fracture is a relatively rare injury, with an incidence of 1 per 55, persons per year and 0. The trapezoidal shape between these bones, the transverse arch, provides stability. Injury can encompass minor ligamentous lesions and fracture dislocations with more severe trauma, as in this case [2].
Complications of missed or untreated Lisfranc injuries, lisfranc fracture radiology. Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.
Clinical History: A 17 year-old male presents with the history of pain due to a football injury incurred three days prior. What are the findings? What is your diagnosis? Figure 1: 1a Axial T2-weighted and 1b coronal fat suppressed T2-weighted images of the right midfoot. Figure 2: The axial image demonstrates mid substance disruption of the interosseous component of the Lisfranc ligament complex arrow. Figure 3: The coronal image demonstrates mid substance disruption of the dorsal arrowhead and interosseous arrow components of the Lisfranc ligament complex. In the general population, injuries to the Lisfranc ligament complex are uncommon, occurring in approximately 1 in 50, people.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint. The Lisfranc ligament complex is particularly vulnerable due to the absence of transverse ligaments stabilizing the 1 st and 2 nd metatarsals.
Lg dryer stuck on cooling
Two injury mechanisms have been described. On this page:. Published Jun Lisfranc fracture-dislocations: report of two cases. This case was donated to Radiopaedia. Although sprains of the midfoot are not common in the general population, certain athletes suffer a much higher rate of this injury. Rice has made several media appearances as part of his ongoing commitment to public education. Os conundrum: identifying symptomatic sesamoids and accessory ossicles of the foot. Revised : 30 June Rice, MD Nov 10, 6 min read. Radiographic anatomy of the pediatric Lisfranc joint. Yantarat Sripanich, Maxwell W. The M1 joint will be medially dislocated, or any of the M2-M4 joints will be laterally dislocated [2]. Weightbearing computed tomography of the foot and ankle: emerging technology topical review. A Lisfranc Fracture is a relatively rare injury, with an incidence of 1 per 55, persons per year and 0.
A Lisfranc injury or tarsometatarsal injury is a rare, yet extremely important, possible repercussion of trauma to the foot.
Check for errors and try again. These injuries vary from mild sprains typically in an athlete to fracture-dislocations as seen in motor vehicle accidents. Ethics declarations Conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ultrasound appearance of the normal Lisfranc ligament. By System:. The diagnostic accuracy of radiographs in Lisfranc injury and the potential value of a craniocaudal projection. Figure Axial T2 with fat saturation image demonstrating thickening and increased signal of the interosseous component arrow as well as multiple midfoot contusions asterisks three months following a soccer injury. She graduated summa cum laude with a Bachelor of Business Administration degree in Finance and International Business with honors college completion and an international bank management certificate in The first mechanism is plantar flexion and axial load, sometimes with a component of inversion. All Posts. Type C1 demonstrates a divergent pattern in some of the tarsometatarsal joints, and type C2 includes all the tarsometatarsal joints [4]. Rice and Natalie Rice founded Global Radiology CME to provide innovative radiology education at exciting international destinations, with the world's foremost authorities in their field. Figure 7: Axial T2 image demonstrating a normal plantar component of the Lisfranc ligament complex arrowhead. Share Add to. Search Search by keyword or author Search.

I recommend to you to visit a site on which there is a lot of information on a theme interesting you.
I recommend to you to visit a site, with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.