Mandible anatomy radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
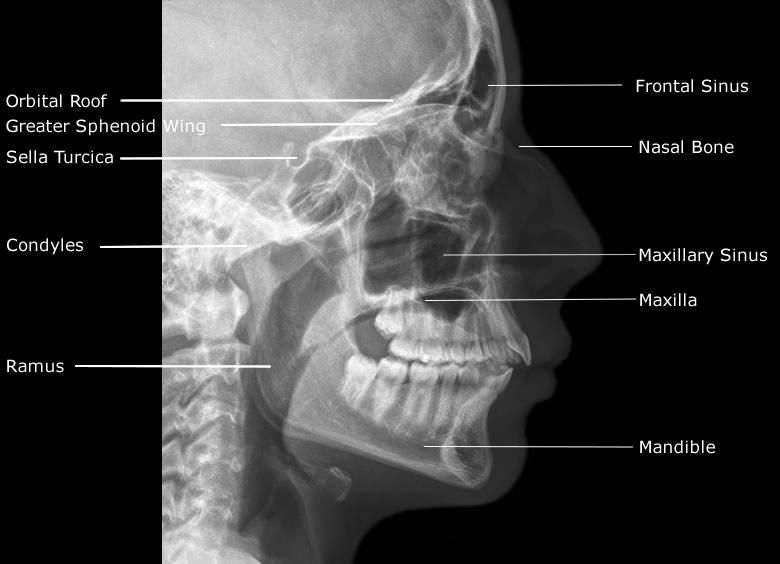
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints TMJ. It bears the lower tooth bearing alveolar process. The body of the mandible is curved, somewhat like a horseshoe, with two surfaces and two borders.
Mandible anatomy radiology
The mandible is made up of the body and two vertical rami. The body of mandible is divided into two halves, each with its outer and inner surfaces, as well as upper and lower borders. The mandibular symphysis or symphysis menti, which is where the right and left halves of the bone join, marked by a slight ridge. The chin, scientifically known as the mental protuberance , is a triangular projection at the bottom middle part. The inferolateral corners of this area are called mental tubercles. The mental foramen , located just below the interval between the premolar teeth. This allows for the passage of mental vessels and nerve. The oblique line starts from the sharp front edge of the ramus and runs downwards and forwards towards the mental tubercle. It affords attachment to the Quadratus labii inferioris and Triangularis; the Platysma is attached below it. The incisive fossa , a shallow depression found below the incisor teeth, which gives origin to the Mentalis and a small portion of the Orbicularis oris. The mylohyoid line , a distinct ridge that angles downwards and forwards from below the third molar tooth to a central area beneath the genial tubercles or mental spines. It gives origin to the mylohyoid muscle, contributing to the floor of the oral cavity. The posterior most part of this line also gives attachment to the superior constrictor muscle of pharynx and pterygomandibular raphe. Below this line, there's a slight depression called the submandibular fossa , which accommodates the submandibular gland. Above it, the sublingual fossa provides a space for the sublingual gland.
This case is an example of a mandible anatomy radiology mandible series comprising the anteroposterior axial Towne and bilateral axiolateral oblique views. Oral cancers can spread by the following routes: extension along the submucosa, direct invasion into adjacent structures, perineural spread and lymph node metastasis.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. Experiencing significant pain when articulating jaw after falling flat on face. Soft tissue tenderness on palpation. This case is an example of a normal mandible series comprising the anteroposterior axial Towne and bilateral axiolateral oblique views. These projections may differ in other departmental protocols.
Chapter 22 The Mandible Thomas L. At birth, the mandible consists of two lateral halves united in the midline at the symphysis by a bar of cartilage Fig. Bony fusion of the symphysis usually occurs before the second year, but segments of the fissures may persist beyond puberty. The body of the mandible is large at birth compared with the relatively short rami and poorly differentiated coronoid and condylar processes. The rami form an angle of about degrees with the body at birth. Figure Important anatomic features of the normal mandible. Figure Anatomy of a normal temporomandibular joint. The zygomatic arch and a portion of the ramus of the mandible are cut away to expose the articular disk.
Mandible anatomy radiology
The authors are well-known US anatomists, but also clinicians. The mandible concerns several surgical disciplines: oral and maxillofacial surgeons, dentists, but also ENT surgeons, plastic surgeons who perform microsurgical reconstructions of the jaws. The morphology and the structure of this bone mandibular canal and its numerous variations condition the way of carrying out a sagittal split osteotomy. Excellent control of the mandibular morphology optimizes the morphological and functional results of mandibular reconstruction with a free fibula flap. The book of Iwanaga and Tubbs provides valuable data for all these disciplines. It contains seven chapters: overview of the mandible, anterior mandible, mandibular body, ramus of the mandible, fetus, cone-beam computed tomography CBCT and teeth.
Authentic collectables
The root of tongue is bounded inferiorly by the mylohyoid muscle, anteriorly by the mandibular symphysis and along with the laterally positioned sublingual space forms the floor of the mouth. Normal left internal carotid artery thin arrow. Figure 3b: mandible in childhood Gray's illustrations Figure 3b: mandible in childhood Gray's illustrations. These are associated with chronic infection that progresses from the pulp of a tooth through its root into the alveolar bone. Concept 3: Cranial nerve pathology can lead to a pseudolesion Cranial nerve injury at a remote site can manifest in the oral cavity as acute or chronic denervation. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. Cranial nerve injury at a remote site can manifest in the oral cavity as acute or chronic denervation. Tags: Manual of Head and Neck Imaging. Sign Up. Minor salivary gland tumours adenoid cystic carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma , lymphoma, sarcoma liposarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma and mandibular neoplasms. Radiograph a and CT b images of dentigerous cysts.
The jaw is a pair of bones forming the framework of the mouth, including the movable lower jaw mandible and fixed upper jaw maxilla. The mandible consists of the horizontal arch, containing the teeth and the ascending arch ramus with the hinge joint at the end, articulating with the glenoid cavity of the temporal bone of the skull. This chapter illustrates the normal CT anatomy of the jaw.
The short, small mandible apparently causes a retrodisplacement of the tongue and obstruction to airflow Fig. The Pierre Robin association is nonspecific and occurs with several genetic and drug-induced syndromes and some loosely associated anomalies, as well as an isolated symptom complex. Get Clinical Tree app for offline access. It gives origin to the mylohyoid muscle, contributing to the floor of the oral cavity. At the time the case was submitted for publication Amanda Er had the following disclosures: Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees past These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. Contact Us. Figure 7. This syndrome is characterized by the appearance of nevoid basal cell carcinomas at a young age Fig. The body of the mandible is large at birth compared with the relatively short rami and poorly differentiated coronoid and condylar processes. Underlying structures: Base of mandible Alveolar part of mandible. Concept 3: Cranial nerve pathology can lead to a pseudolesion Cranial nerve injury at a remote site can manifest in the oral cavity as acute or chronic denervation. Head and neck imaging , 4th edn.

Excuse, the message is removed