Mbr or gpt for ssd
Choosing between them can be a challenging task, especially when selecting one to use with an SSD drive. In this blog post, we have done in-depth research on mbr or gpt for ssd differences between MBR and GPT, factors to consider while choosing one of them for your Solid State Drive, steps to convert from one type to another as well as some safety considerations before converting.
So, which one should you use? Well, it depends. To have more than four partitions, you'll need to create three primary partitions and an extended partition, which can be further subdivided into logical partitions. It supports up to primary partitions and unlimited numbers of logical partitions. MBR puts boot data and partitions together, while GPT separates data and the system into different partitions. If one partition is corrupted, you can use other partitions.
Mbr or gpt for ssd
These methods hold information about how the data is stored on the drive. But how do you know which one to use? Simply put, partitions are sections on the drive that store data. You always need at least one partition on a drive, or else you can't save anything. Although you might only have one physical drive, you can use partitions to split it up and assign a different drive letter to each partition. MBR only lets you create four primary partitions. However, you can circumvent this limitation by using logical partitions. This means you can create three primary partitions and an extended partition. Inside this extended partition, you can have logical partitions. The biggest limitation with this is that you cannot use logical partitions as boot volumes, a type of partition that holds Windows operating system files. For example, you could have Windows 10 on one partition and Windows 7 on another. This won't be a problem for most people unless you want to boot multiple operating systems from the same drive. It's also important to know about the risks when dual-booting operating systems. GPT doesn't have the same limitation. You can create up to partitions on a single GPT drive without using the logical partition workaround.
Read More. The disk can be easier to recover boot data if they get lost in some unexpected situations. Sometimes, Disk Management does not work.
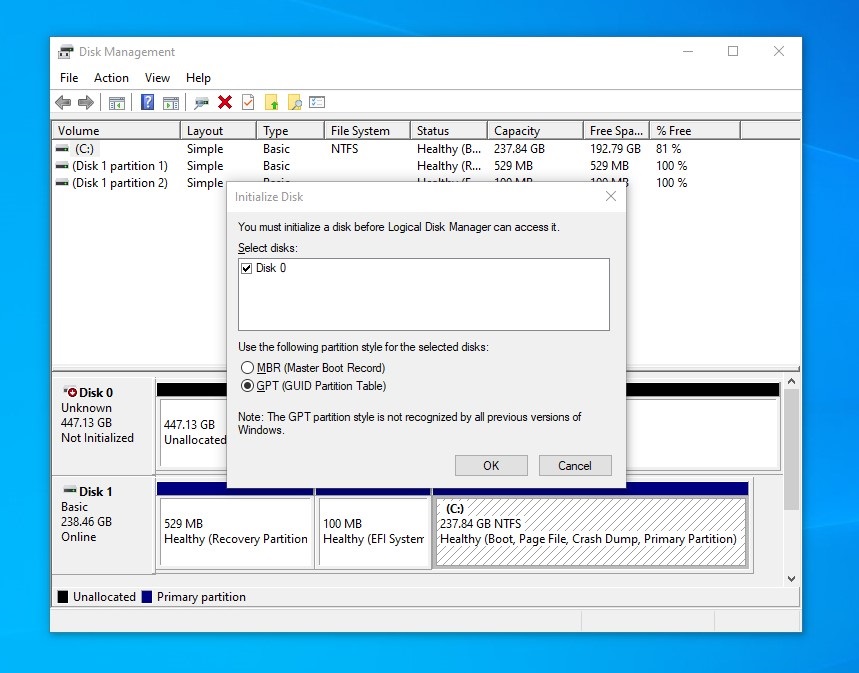
What partition style should I initialize for it? SSDs provide stable running performance, which is important for running a game, a bunch of programs, and commands. And a partition table is a table that is used to describe the partition on an HDD or SSD and help the disk locate a file so that the operating system can read data on the drive. So, what is the difference between them? When delving into the number of partitions, the MBR Master Boot Record imposes a limit of up to four primary partitions. To exceed this limit, workarounds include creating three primary partitions and introducing an extended partition for further subdivision into logical partitions. It can accommodate up to primary partitions and supports unlimited arrays of logical partitions.
These methods hold information about how the data is stored on the drive. But how do you know which one to use? Simply put, partitions are sections on the drive that store data. You always need at least one partition on a drive, or else you can't save anything. Although you might only have one physical drive, you can use partitions to split it up and assign a different drive letter to each partition. MBR only lets you create four primary partitions. However, you can circumvent this limitation by using logical partitions.
Mbr or gpt for ssd
So, which one should you use? Well, it depends. To have more than four partitions, you'll need to create three primary partitions and an extended partition, which can be further subdivided into logical partitions. It supports up to primary partitions and unlimited numbers of logical partitions. MBR puts boot data and partitions together, while GPT separates data and the system into different partitions. If one partition is corrupted, you can use other partitions. In short, GPT provides more capacity and better data protection. In general, newer versions of Windows are more likely to be compatible with GPT, while older versions are more likely to be compatible with MBR.
Mcdougall creek fire
At last, click " Apply " on the top corner of the main interface, and click " Proceed " to commit the operation. If it detects errors, GPT can try to repair itself. This article will show you how to do it and another easier way will be introduced too which can convert GPT to MBR without data loss. To ensure a smooth and successful transition, any other drives in the system should be formatted first before attempting to convert. On the contrary, GPT does not have any such limitation and allows over bootable partitions which makes it a superior choice for high-capacity storage needs. The boot processes for both are different which can have implications in terms of system start-up time, depending on the operating system. Firstly, GPT stores boot data across several partitions rather than having all partition and boot info together as in MBR. These include:. If one partition gets corrupted, it can use the other partitions to recover. It's now commonplace to buy SSDs that offer multiple terabytes.
What partition style should I initialize for it? SSDs provide stable running performance, which is important for running a game, a bunch of programs, and commands. And a partition table is a table that is used to describe the partition on an HDD or SSD and help the disk locate a file so that the operating system can read data on the drive.
The capacity offered by consumer SSDs continues to grow, too. In terms of data recovery in case of errors or corruption, GPT has a unique set of advantages that makes it the more reliable option. Thus, the same as what you do with DiskPart, you have to delete all partitions beforehand. Step 3. Disk Management is a Windows built-in utility similar to DiskPart. Choosing between them can be a challenging task, especially when selecting one to use with an SSD drive. This is because GPT stores its partition structures on multiple locations and has error-detecting code to check the partitions during the bootup process. So, what is the difference between them? For example, you could have Windows 10 on one partition and Windows 7 on another. However, you can circumvent this limitation by using logical partitions. But how do you know which one to use?

I can not participate now in discussion - it is very occupied. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion on this question.
I join. So happens. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
I am sorry, that has interfered... But this theme is very close to me. Write in PM.