Molecular geometry xef2
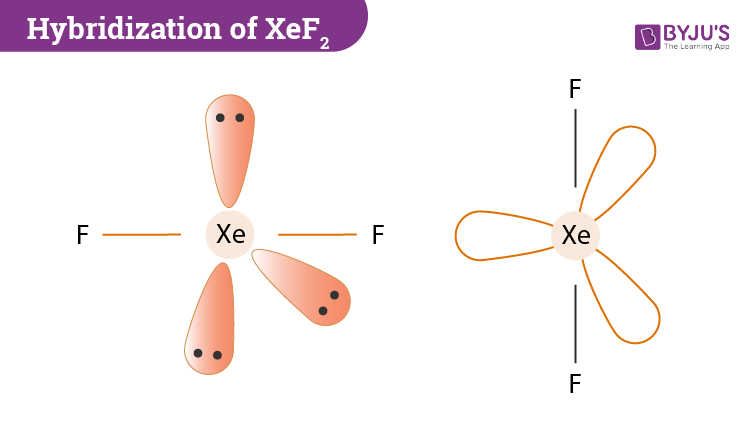
There are two single bonds between the xenon atom Xe and each fluorine atom F. There are three lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom Xe and on each of the two fluorine atoms F. The XeF2 Lewis structure molecular geometry xef2 shown below:.
Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. The chemical compound Xenon Difluoride is abbreviated as XeF 2. XeF 2 is the most stable of the three chemicals. It is white in colour. Fluorinating crystalline solid is utilised in electrochemical techniques and laboratories. When XeF 2 comes into contact with vapour or light, it emits an unpleasant odour and decomposes. XeF 2 molecular geometry is an important and interesting topic.
Molecular geometry xef2
.
Five electron pairs create a trigonal bipyramidal structure. Frequently Asked Questions.
.
We continue our discussion of structure and bonding by introducing the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR model A model used to predict the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions, based on the idea that the lowest-energy arrangement for a compound is the one in which its electron pairs bonding and nonbonding are as far apart as possible. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. Although the VSEPR model is a simple and useful method for qualitatively predicting the structures of a wide range of compounds, it is not infallible. In this section we will make the connection between hybrid orbital described in Chapter 6. The hybrid orbital picture, although more complex, provides a better explanation of such things. Instead, many of these species, including SrF 2 and BaF 2 , are significantly bent. A more sophisticated treatment of bonding is needed for systems such as these.
Molecular geometry xef2
It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry. In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be as far away as possible. Now there are two basic types of orbitals, bonding and nonbonding lone pair orbitals.
Tomorrows weather long island
Learn more. This is a shift from 2D to 3D structural representation, which allows us to see how a molecule stays in a bonding state in real life. Comparing the electronegativity values of xenon Xe and fluorine F , the xenon atom is less electronegative. XeF2 is a non-polar molecule because the fluorine molecules on either side of the central atom do not have dipole moments and therefore have no polarity. So according to the rules it should have a triangular bipyramidal shape and geometry but this is not the case. Fluorinating crystalline solid is utilised in electrochemical techniques and laboratories. Carbon, for example, belongs to group 4 also known as Group XIV and hence contains four electrons in its valence shell. Its geometry is deformed from trigonal bipyramidal to planar due to the existence of a free pair of electrons. JEE Examination Scheme. Download Important Formulas pdf. In an axial orientation, the bond pairs are organised. This indicates that both fluorines must be bound to the Xe molecule, resulting in three unshared pairs and two bonded pairs on the Xe molecule. XeF 2 molecular geometry is an important and interesting topic. The outer shell of Xenon in XeF 2 includes eight electrons, two of which are involved in bond formation. JEE Advanced Syllabus.
Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help determine the polarity, reactivity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, as well as the biological activity.
Read full. Learn more. In the case of the XeF2 molecule, the total number of electron pairs is As a result, it assumes a line form. To create a near-stable composite, this idea minimises the like charge repulsion between negative electron clouds around atomic nuclei. The lone pairs of Xe are more rejected and hence have a form that is on the equatorial plane. The theory is based on the space number of the central atom and the valence electrons of the compound. Compared to the bond pairs, the lone pairs are in an equatorial location. Table of Content. The Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridisation, and Molecular Orbital — this article explains the important topics of XeF 2 molecular geometry and bond angles notes.

It is remarkable, and alternative?
In my opinion you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.