Nadh2 full form in biology
NADH is preferred except in cases where the use Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription.
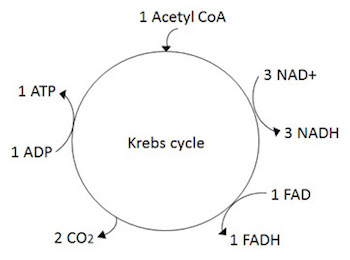
The process of using oxygen and food molecules to produce energy, carbon dioxide, water, and waste products is known as cellular respiration. Respiration is the process through which humans transform food into energy by utilising water and oxygen. Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three metabolic processes of respiration. The redox cofactor FADH 2 , which stands for Flavin adenine dinucleotide, is generated during the last steps of the electron transport chain process. FADH 2 , or flavin adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor that is produced throughout the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration. Electrons produced in the Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle are transported to the Electron Transport Chain by a high-energy electron carrier. In the last stage of respiration, when the majority of the energy is lost and created from mitochondria, these two chemicals are utilised in the movement of electrons in the electron transport chain.
Nadh2 full form in biology
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or from proteins , in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery. In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks de novo from either tryptophan or aspartic acid , each a case of an amino acid. Alternatively, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from nutritive compounds such as niacin ; similar compounds are produced by reactions that break down the structure of NAD, providing a salvage pathway that recycles them back into their respective active form. Some NAD is converted into the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate NADP , whose chemistry largely parallels that of NAD, though its predominant role is as a coenzyme in anabolic metabolism. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide consists of two nucleosides joined by pyrophosphate. The nucleosides each contain a ribose ring, one with adenine attached to the first carbon atom the 1' position adenosine diphosphate ribose and the other with nicotinamide at this position. The second electron and proton atom are transferred to the carbon atom adjacent to the N atom. In appearance, all forms of this coenzyme are white amorphous powders that are hygroscopic and highly water-soluble.
Trending Topics.
.
Life is possible only if molecules and cells remain organized. Organization requires energy, as governed by the laws of thermodynamics. Just about anything a living organism does requires energy. We most often think of energy as food or calories. Cells, however, think of energy as ATP.
Nadh2 full form in biology
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Overview of oxidative phosphorylation.
Synonym for as
Oxford: Clarendon Press. Because cancer cells utilize increased glycolysis , and because NAD enhances glycolysis, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase NAD salvage pathway is often amplified in cancer cells. The process of using oxygen and food molecules to produce energy, carbon dioxide, water, and waste products is known as cellular respiration. This ratio is an important component of what is called the redox state of a cell, a measurement that reflects both the metabolic activities and the health of cells. Please subscribe or login to access full text content. In bacteriology, NAD, sometimes referred to factor V, is used as a supplement to culture media for some fastidious bacteria. Biochemical Society Transactions. Sign in You could not be signed in, please check and try again. In cellular respiration and other activities such as photosynthesis, the electron transport chain is the principal source of energy. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription.
During cellular respiration, the cells use these coenzymes to turn fuel from food into energy. However, the brain cells may contain more than one mitochondrion, since they are involved in lot of processing and require more energy to perform multiple tasks. NADH is the reduced version of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD , which is essentially a co-enzyme form of niacin vitamin B3 , present in all living cells.
Your current browser may not support copying via this button. Let's look about its causes,symptoms and treatments in this article. Although it is important in catabolism, NADH is also used in anabolic reactions, such as gluconeogenesis. S2CID Further information: History of biochemistry. Retrieved 30 September CAS Number. An adenylate moiety is then transferred to form nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide NaAD. Username Please enter your Username. Access free live classes and tests on the app. Archived from the original PDF on 27 September

I think, that you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.
You commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.