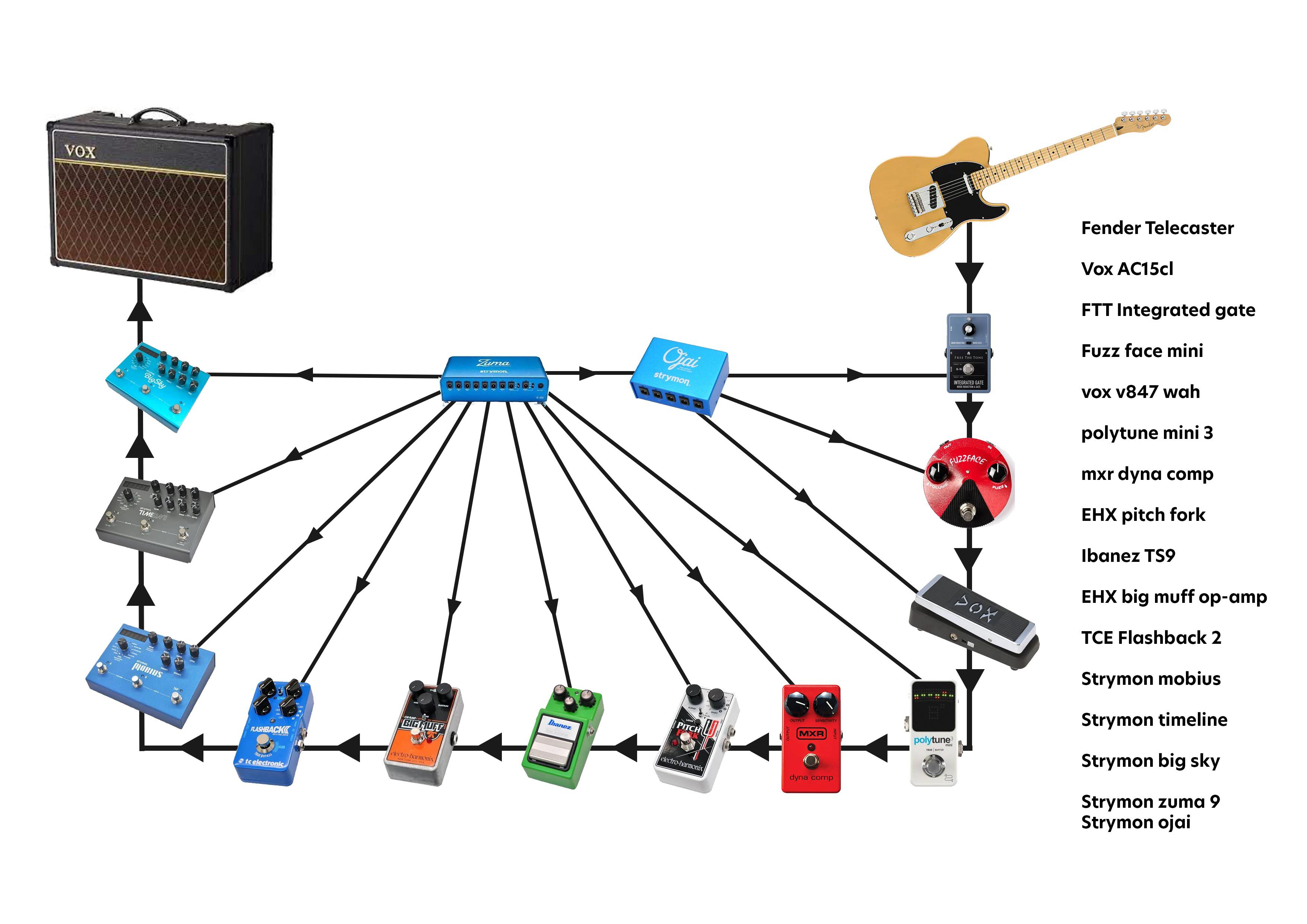
Noise gate in pedal chain
This site may earn a commission from merchant links like Ebay, Amazon, and others. Forums New posts Search forums. Media New media New comments Search media.
If you play single-coil pickups or you use a high-gain amp, unwanted hum and buzz might be a common problem. A noise gate is one of the most popular solutions for unwanted guitar noise. In this guide, we'll explore the main causes of rig noise, and recommend some of the best guitar noise gate pedals on the market - read on! At some point, we have all experienced unwanted noise from an amplifier. One of the most common and practical solutions to this is the humble noise gate pedal.
Noise gate in pedal chain
A noise gate identifies the intended, deliberate sound of the guitar and differentiates it from any unwanted noise. A noise gate can shut down the unwanted signal. Via user-defined settings, it allows the natural note decay to continue cleanly. Numerous situations and conditions exist where a noise gate can be a helpful addition to an effects chain. Unwanted noise can be a problem for guitarists in many different ways. As such, players can implement noise gates in multiple ways depending on the situation. One of the most common applications for a noise gate is in the effects loop of a high-gain amplifier. However, it comes at the expense of a lot of amp hum and hiss. By inserting a noise gate into the effects loop, the pedal can eliminate unwanted amp noise while reacting naturally to tone, sustain, and pick attack. Even the cleanest amp will, at high volumes, produce some hiss and noise. Many vintage-style amplifiers work best at the deafening volumes. But, the louder the amplifier, the louder the unwanted amp hiss and noise. A noise gate can be an intelligent, easy solution to retain all the best features of a loud tube amp while eliminating unwanted noise.
Jan 7, 10, Gibsons, British Columbia. It preserves natural note decay and playing dynamics while focusing specifically on hum and hiss.
.
Home » Pedals. In the world of guitars and sound engineering, achieving a clean and controlled signal is essential to creating a polished and professional sound. One indispensable tool that helps is the noise gate pedal. At its core, a noise gates act as a sonic gatekeeper. Its primary function is to eliminate or reduce unwanted background noise and hum that can often accompany the amplified sound of an electric guitar. These interferences can manifest as buzzing or humming sounds. Using high-quality cables with proper shielding can significantly minimize this issue. These lights emit electromagnetic interference that can infiltrate your signal path and introduce unwanted noise. Pickups and Single Coils: Single coil pickups, while prized for their clarity and vintage charm, are notorious for picking up electromagnetic interference from various sources. This can result in a hum that can be quite distracting.
Noise gate in pedal chain
Home - guitar pedals. This is a very common question when you first buy one of these pedals, and because a different position in the signal chain can greatly change the overall sound of your rig it can be difficult to know where to place one of those stompboxes. With this design, we can filter out the hum and the background noises that we may hear with our guitar, may it be for an high-gain setting, for the interaction between our pedals or for other hardware-related reasons. This pedal should be placed right after the source of the noises, obviously, but how can you know what is the cause of that hum and noise? A great way for discovering the origin of the feedbaks and of that nasty sound is to check first plugging your guitar right into the amp, moving to try each single pedal on its own, in order to understand what is the critical point. Another nice point can be after distortions and fuzzes, that especially with high-gain settings can make quite a bit of hum and unwanted noises, but those are only some of the most common placements. Mainly because of where your distortion pedals are placed, as well as how many pedals there are before: you may have more than one noise source and for this reason you may have to place more than one gate for your signal chain. In general, though, the ideal position is right after the distortion pedal, because distortions especially with high-gain settings are one of the main noise-makers in your guitar rig: placing it after your overdrive, fuzz or any other distortion will cut out the bad unwanted frequencies. The effects loop in an amp works by adding effects right after the preamp of the amplifier: for this reason, it can be considered as the last point before the sound actually comes out of the speakers of the amp, and it already has all the effects stacked into the sound.
Candy candy para colorear
A noise gate is one of the most popular solutions for unwanted guitar noise. But, the louder the amplifier, the louder the unwanted amp hiss and noise. So what causes unwanted noise? The location allows the gate to act as the last effect source ahead of the speaker, sculpting exact definition, clarity, and attack. In-Line For many players, high-gain distortion and the inherent noise and hiss that come with it come from a distortion, fuzz, or overdrive pedal. It then needs help identifying and separating errant noise from the intended guitar sound. Written by Sam Beattie. They can all cause unwanted noise if they happen to be close enough to your guitar or amp. Using the noise gate at the end of the chain doesn't work for me since it's effectiveness is determined by the gain used, and since I need clean to fuzz and everything in between, a setting that works for one doesn't work for all levels of dirt. Believer said:.
A noise pedal is a very useful tool to have on a lot of pedalboards.
Noise Gate Pedal Controls. Seems to work well. Gate Mode: Gate mode provides ultra-fast noise elimination for tapping, sweep picking, and heavy rhythm styles that rely on high gain. It works as an effects pedal to enhance percussive tones or as a utility to clean up errant noise and EMI. Single coil pickups, primarily with overdrives and high-gain amplifiers, can create a lot of hiss and hum. Noise gates are particularly popular among the high-gain crowd - modern metal, djent, prog-rock. Power is handled through a "power brick" for each pedal in an attempt to reduce ground-loop noise. Radio and static interference — phones, radios, Bluetooth devices, electrical appliances. I can get by most of the squash of the Noise Clamp by turning the gate way down but for the really long stuff I need to keep that button close so I can turn it off temporarily ten turn it back on. They naturally produce a lot of unwanted microphonic noise, especially when paired with a loud valve amp. Type of amp — valve amps get noisier with age. In this guide, we'll explore the main causes of rig noise, and recommend some of the best guitar noise gate pedals on the market - read on! It may not display this or other websites correctly. Their natural decay and subtle dynamics should remain, with only errant hiss and hum removed.

Bravo, excellent phrase and is duly
Rather useful idea