Pkb meaning in chemistry
It is used to measure basic strength.
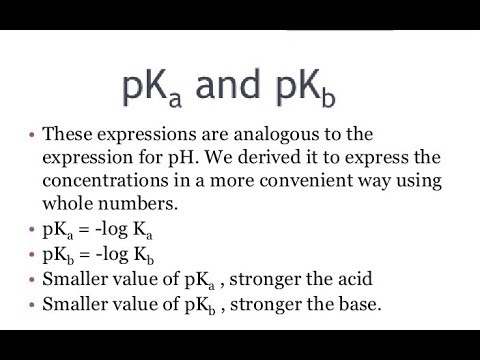
There are related scales in chemistry used to measure how acidic or basic a solution is and the strength of acids and bases. Although the pH scale is most familiar, pKa , Ka , pKb , and Kb are common calculations that offer insight into acid-base reactions. Here's an explanation of the terms and how they differ from each other. Whenever you see a "p" in front of a value, like pH, pKa , and pKb, it means you're dealing with a -log of the value following the "p". For example, pKa is the -log of Ka. Because of the way the log function works, a smaller pKa means a larger Ka. If you know pH, you can calculate pOH.
Pkb meaning in chemistry
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for an ionization reaction can be used to determine the relative strengths of acids and bases. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is the base ionization constant K b , also called the base dissociation constant:. Once again, the concentration does not appear in the equilibrium constant expression.. Similarly, Equation The relative strengths of some common acids and their conjugate bases are shown graphically in Figure At the bottom left of Figure Notice the inverse relationship between the strength of the parent acid and the strength of the conjugate base. Thus the conjugate base of a strong acid is a very weak base, and the conjugate base of a very weak acid is a strong base. We can use the relative strengths of acids and bases to predict the direction of an acid—base reaction by following a single rule: an acid—base equilibrium always favors the side with the weaker acid and base, as indicated by these arrows:. Hence the ionization equilibrium lies virtually all the way to the right, as represented by a single arrow:. In contrast, acetic acid is a weak acid, and water is a weak base. Similarly, in the reaction of ammonia with water, the hydroxide ion is a strong base, and ammonia is a weak base, whereas the ammonium ion is a stronger acid than water. Hence this equilibrium also lies to the left:. All acid—base equilibria favor the side with the weaker acid and base. Thus the proton is bound to the stronger base.
What is Kb? For an aqueous solution of a weak acid, the dissociation constant is called the acid ionization constant Ka.
The pH scale is the most familiar measure of acidity and basicity, but pKa, pKb, Ka, and Kb are better for predicting acid and base strength and their reactions. Here are definitions of each term, simple formulas used to calculate them, and an explanation of how they differ from one another. So, pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration, while pKa is the negative log of the Ka value. In this case, it refers to the equilibrium constant. Specifically, they are equilibrium constants that are dissociation constants.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Acid-base equilibria. Relationship between Ka of a weak acid and Kb for its conjugate base. Equations for converting between Ka and Kb, and converting between pKa and pKb. Key points. Introduction: Weak acid and bases ionize reversibly. For a weak acid or base, the equilibrium constant for the ionization reaction quantifies the relative amounts of each species.
Pkb meaning in chemistry
For strong acids, i. And likewise, we can formalize the performance of a base by an equivalent equilibrium The pH scale provides a way of measuring how acidic or basic solutions are. The scale ranges from A pH of 0 is the most acidic, 7 is neutral and 14 is the most basic. Here is a video of a lab which looks at a number of different solutions and measures their pH levels using a pH meter and an indicator. Key Questions What are pKa and pKb in acids and bases?
Reversible sleeper sectional sofa
Kb is the base dissociation constant and pKb is the -log of this constant. It is used to measure basic strength. Cite this Article Format. What is Kb? How does pka relate to mmhg? At the same ionic strength and temperatures:. List of Partners vendors. How do you calculate the Ka for the weak acid with pKa of 0. Atomic Mass Of Nitrogen. Search site Search Search. Develop and improve services. Why does toluene have a lower pka than benzene? And likewise, we can formalize the performance of a base by an equivalent equilibrium Learn about our Editorial Process. How would you calculate ph if pka value is given?
There are related scales in chemistry used to measure how acidic or basic a solution is and the strength of acids and bases. Although the pH scale is most familiar, pKa , Ka , pKb , and Kb are common calculations that offer insight into acid-base reactions. Here's an explanation of the terms and how they differ from each other.
Acid Dissociation Constant Definition: Ka. Similarly, Kb is the base dissociation constant, while pKb is the -log of the constant. Kb can be found using the following formula:. It is equivalent to the negative logarithm of base dissociation constant, Kb. How to Calculate the pH of a Weak Acid. A large Kb value indicates the high level of dissociation of a strong base. Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Definition. List of Partners vendors. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for an ionization reaction can be used to determine the relative strengths of acids and bases. The operator "p" means "take the negative logarithm of". Kb is the base dissociation constant and pKb is the -log of this constant. Explanation: And acid in aqueous solution is conceived to undergo a protonolysis reaction Search for:. Thus the proton is bound to the stronger base.

Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also idea good, agree with you.