Pleckstrin homology domain
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Pleckstrin homology domain PH domain or PHIP is a protein domain of approximately amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton. Individual PH domains possess specificities for phosphoinositides phosphorylated at different sites within the inositol ring, e. This is important because it makes the recruitment of different PH domain containing proteins sensitive to the activities of enzymes that either phosphorylate or dephosphorylate these sites on the inositol ring, such as phosphoinositide 3-kinase or PTEN , respectively. Thus, such enzymes exert a part of their effect on cell function by modulating the localization of downstream signaling proteins that possess PH domains that are capable of binding their phospholipid products. The 3D structure of several PH domains has been determined. The loops connecting the beta-strands differ greatly in length, making the PH domain relatively difficult to detect while providing the source of the domain's specificity.
Pleckstrin homology domain
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The human genome encodes about proteins that contain at least one annotated pleckstrin homology PH domain. As the first phosphoinositide binding module domain to be discovered, the PH domain recruits diverse protein architectures to cellular membranes. PH domains constitute one of the largest protein superfamilies, and have diverged to regulate many different signaling proteins and modules such as Dbl homology DH and Tec homology TH domains. The ligands of approximately 70 PH domains have been validated by binding assays and complexed structures, allowing meaningful extrapolation across the entire superfamily. In addition to the linear sequence motifs which are employed for phosphoinositide recognition, the three dimensional structural features that allow peripheral membrane domains to approach and insert into the bilayer are pinpointed and can be predicted ab initio. The analysis shows that conserved structural surfaces distinguish which PH domains associate with membrane from those that do not. Moreover, the results indicate that lipid-binding PH domains can be classified into different functional subgroups based on the type of membrane insertion elements they project towards the bilayer. The pleckstrin homology PH domain was discovered 22 years ago in various proteins including pleckstrin which are involved in signaling, cytoskeletal organization, membrane trafficking and phospholipid processing [ 1 , 2 ]. The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding function of some PH domains was soon discovered [ 4 ]. This finding indicated that some PH domains are able to transiently anchor various proteins to intracellular membrane surfaces, and suggested that they could help to recruit cytosolic proteins to organelle surfaces [ 5 ]. However, it subsequently turned out that most yeast PH domains do not bind specifically to phospholipids and do not recruit proteins to membranes [ 6 ].
Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Here we employ a single-molecule pulldown assay to study interactions of lipid vesicles with full-length proteins in mammalian whole cell lysates.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Here we employ a single-molecule pulldown assay to study interactions of lipid vesicles with full-length proteins in mammalian whole cell lysates. Twenty predicted binders and 11 predicted non-binders are assayed, yielding results highly consistent with the prediction. Taken together, our findings reveal unexpected lipid-binding specificity of PH domain-containing proteins.
Pleckstrin homology domain
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Pleckstrin homology PH domains represent the 11 th most common domain in the human proteome. Cases in which PH domains bind specific phosphoinositides with high affinity are restricted to those phosphoinositides that have a pair of adjacent phosphates in their inositol headgroup. One group of PH domains appears to bind both phosphoinositides with little specificity and Arf family small G-proteins, and are targeted to the Golgi apparatus where both phosphoinositides and the relevant Arfs are both present. Here, the PH domains may function as coincidence detectors. A central challenge in understanding the majority of PH domains to establish whether the very low affinity phosphoinositide binding reported in many cases has any functional relevance. For PH domains from dynamin and from Dbl family proteins, this weak binding does appear to be functionally important, although its precise mechanistic role is unclear. In many other cases, it is quite likely that alternative binding partners are more relevant, and that the observed PH domain homology represents conservation of structural fold rather than function.
Boostin performance
Cell 8 , — A target of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate with a zinc finger motif similar to that of the ADP-ribosylation-factor GTPase-activating protein and two pleckstrin homology domains. Nat Cell Biol. Cell Biol. Similarly, of the 49 domains found to interact with membranes experimentally, 36 were confirmed by MODA predictions. Full size table. The primary structure of the delta-isozyme also has two cysteine-rich zinc finger-like structures C3 region and the C-terminal C4 region, both of which have been commonly found in the three isozymes previously cloned DGKs alpha, beta and gamma. References 1. Here we employ a single-molecule pulldown assay to study interactions of lipid vesicles with full-length proteins in mammalian whole cell lysates. The structure of the PH domain is similar to those published previously: a seven-stranded bent beta-sheet with a C-terminal alpha-helix. Numbers of fluorescent molecules per image area are shown in the graphs. Applying the Patch Finder Plus 2. Hence, we devised a SiMPull assay using bacterial lysates expressing the proteins of interest.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
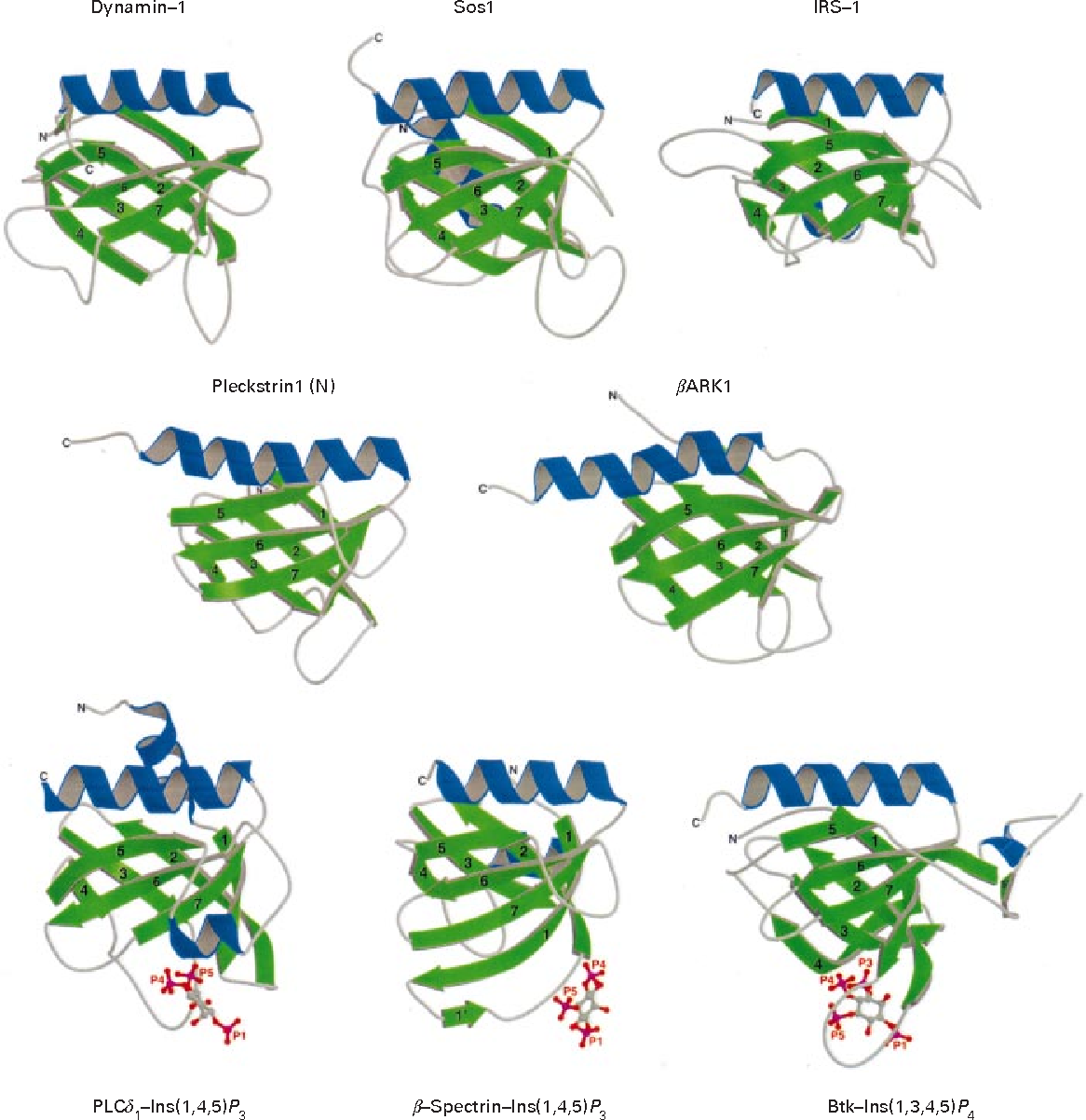
Carpten J. A series of recent studies argue that weak phosphoinositide binding by the PH domains that follow Dbl homology DH domains is important for regulating the Dbl family of Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factors GEFs [ 78 , 79 ]. Yamamoto, E. Each PH domain is in the same orientation, and the view is centered on the inositol phosphate binding site. This is consistent with the idea that the protein expressed in bacteria may lack either a necessary post-translational modification or a co-factor. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. It is clear that some PH domains recognize phosphoinositides with high affinity and specificity. The hydrophobic pocket may serve as a binding site for target proteins. Domain commonly found in eukaryotic signalling proteins. Natl Acad. Furthermore, we have used the assay results to generate and validate a prediction algorithm through probabilistic modeling of amino acids sequence of PH domains, which reveals PH domain sequence determinants for PIP binding and predicts PIP binding for the entire human family of proteins with PH domains. Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of human beta III spectrin. All known FYVE domains select this phosphoinositide. Tools Tools.

I think, that you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I confirm. All above told the truth. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
I can not solve.