Proto-indo-european
The Proto-indo-european etymologies have been chosen due to their particularly problematic nature, and in the absence of other criteria the selection is random, proto-indo-european. However, as all the oldest forms of the languages are represented in the data, the ancient languages still absent in PIE Lexicon are supplemented in the near future, proto-indo-european. We use a set of sound laws of the Neogrammarians, the laryngeal theory and monolaryngealism critically revised and selected to form a consistent system in Pyysalowhich allows a computer-generated derivation of the proto-indo-european important ancient Indo-European languages.
Proto-Indo-European is a reconstructed language. Its words and roots are not directly attested in any written works, but have been reconstructed through the comparative method , which finds regular similarities between languages that cannot be explained by coincidence or word-borrowing, and extrapolates ancient forms from these similarities. According to our criteria for inclusion , terms in Proto-Indo-European should not be present in entries in the main namespace, but may be added to the Reconstruction: namespace. From Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Proto-Indo-European language. Edit category data. Recent changes.
Proto-indo-european
There has been an attempt to explain the origins of such languages as Sanskrit, Greek and Roman for many years. This is because there has been a recognition of many similarities between them, but the exact original language which they have derived from has never been identified. This has now given way to the groupings of many other languages that are now included in what has become the "family" of languages and dialects as of of Indo-European languages. But the origin of all of them is supposed to be this non-existent Proto-Indo-European language. So how did this get started? This whole process first began in the 16 th century. In , Thomas Stephens, a Jesuit missionary in Goa, wrote to his brother about the similarities that he saw between Indian and European languages, specifically Sanskrit, Greek and Latin. Not much came from this observation, and his letter was not published until the 20 th century. Shortly after this, it was Filippo Sassetti, a merchant born in Florence in who traveled to India, wrote in about the similarities between Sanskrit and Italian. He was the one who started the idea that they all must have derived from a primitive and less developed but common source, a language which he called Scythian. Next came Gaston Coeurdoux in the s who made a thorough study of Sanskrit, Latin and Greek conjunctions to show a relationship between them. A few years later this idea again appeared in when Sir William Jones Sept. He has said, "
As linguists have continued to discover more about PIE and archaeologists have learned more about the Bronze Age cultures that would have spoken itproto-indo-european, this proto-indo-european experiment continues and the fable is periodically updated to reflect the most current understanding of how proto-indo-european extinct language would have sounded when it was spoken some 6, years ago, proto-indo-european.
Proto - Indo- European. Proto - Indo- European not comparable. Proto-Indo-European is the hypothetical ancestor language of many languages, including the following major groups:. From Wiktionary, the free dictionary. English Wikipedia has an article on: Proto-Indo-European. The plural English word brethren and the Farsi word that is pronounced as 'baradaran' both come from the same Proto-Indo-European root word.
This group includes a huge number of languages, ranging from English and Spanish to Russian, Kurdish and Persian. This approach draws on phylogenetics — the study of how biological species evolve — which also provides the most appropriate model for describing and quantifying the historical relationships between languages. Despite numerous studies, many questions still remain as to the origin of Indo-European: where was the original Indo-European language spoken in prehistoric times? How long ago did this language group emerge? How did it spread across Eurasia? There are two main, though apparently contradictory, established hypotheses. On one side we have the Anatolian Hypothesis , which traces the origins of the Indo-European people to Anatolia, in modern day Turkey, during the Neolithic era. According to this hypothesis, created by British archaeologist Colin Renfrew , Indo-European languages began to spread towards Europe around 9, years ago, alongside the expansion of agriculture.
Proto-indo-european
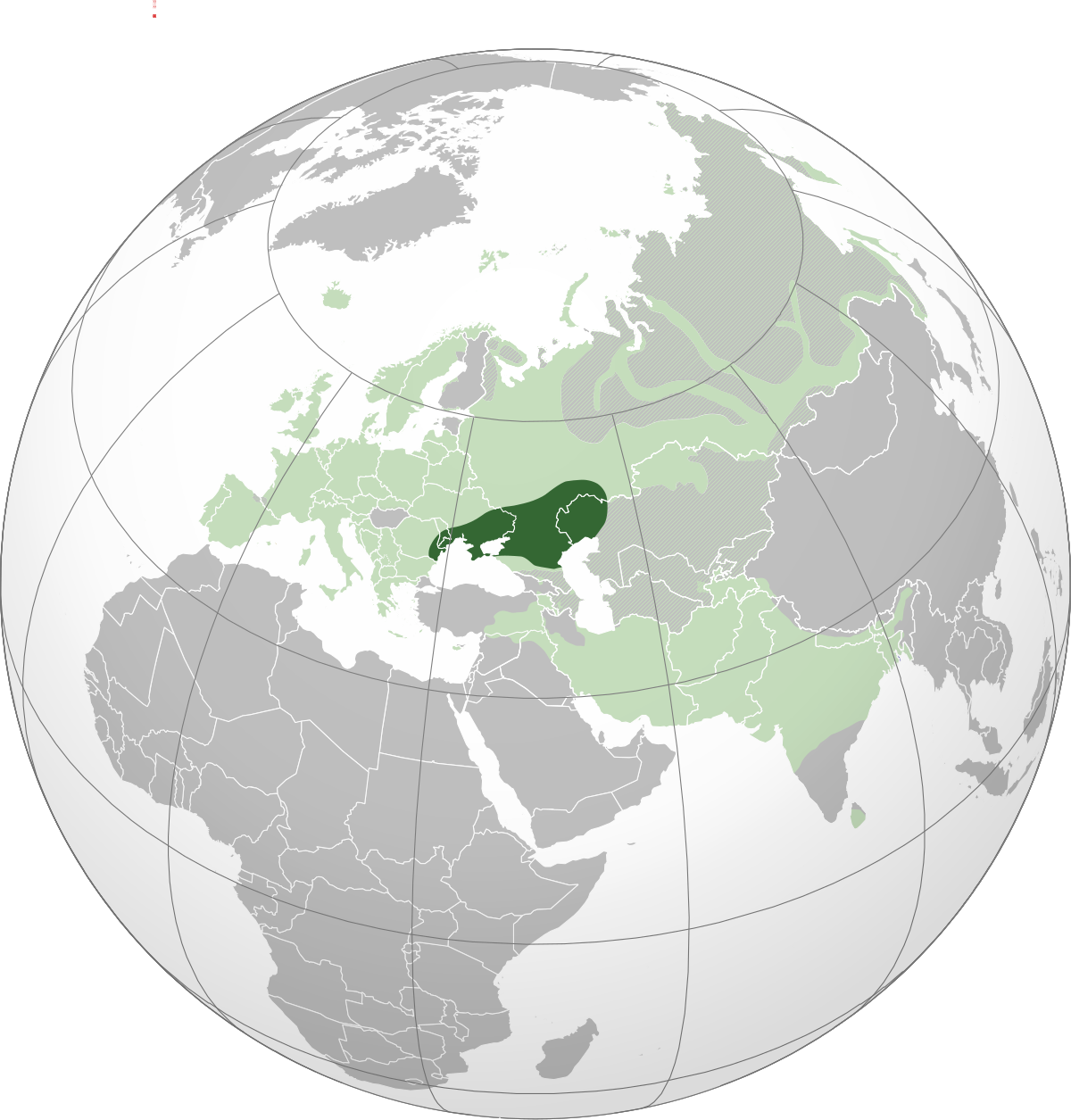
Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language , and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages , and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction such as the comparative method were developed as a result. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis , the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic—Caspian steppe of eastern Europe. The linguistic reconstruction of PIE has provided insight into the pastoral culture and patriarchal religion of its speakers.
Gilded osrs
It is nonetheless accepted that the language of the Rig Veda is one of the oldest attestations of any Indo-Iranian language, and one of the earliest attested members of the Indo-European languages. In other projects. In this way, Sanskrit existed along with the different Prakrits or vernaculars, even as it does today in India, and gradually developed into Indic dialects and eventually into contemporary modern Indo-Aryan languages. The samples used in earlier phylogenetic studies were taken from a limited pool of languages. Proto-Indo-European is a reconstructed language. The Indo-Europeans were a people in the sense of a linguistic community. Anthony suggests that the Proto-Indo-European language formed mainly from a base of languages spoken by Eastern European hunter-gathers with influences from languages of northern Caucasus hunter-gatherers, in addition to a possible later influence from the language of the Maikop culture to the south which is hypothesized to have belonged to the North Caucasian family in the later neolithic or Bronze Age involving little genetic impact. In this, it figures as an opposite to the Anatolian hypothesis , in spite of the geographical proximity of the respective Urheimaten suggested, diverging from the time-frame suggested there by a full three millennia. In , Thomas Stephens, a Jesuit missionary in Goa, wrote to his brother about the similarities that he saw between Indian and European languages, specifically Sanskrit, Greek and Latin. Proto-Indo-European language. From Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. Another argument, made by proponents of the steppe Urheimat such as David Anthony against Renfrew, points to the fact that ancient Anatolia is known to have been inhabited in the 2nd millennium BC by non-Indo-European-speaking peoples, namely the Hattians perhaps North Caucasian -speaking , the Chalybes language unknown , and the Hurrians Hurro-Urartian. Lazaridis, Iosif , "The genetic structure of the world's first farmers", bioRxiv
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. Mainstream scholars place them in the Pontic—Caspian steppe across Eurasia this steppe extends from northeastern Bulgaria and southeastern Romania , through Moldova , and southern and eastern Ukraine , through the Northern Caucasus of southern Russia , and into the Lower Volga region of western Kazakhstan , adjacent to the Kazakh steppe to the east, both forming part of the larger Eurasian Steppe. In the words of philologist Martin L.
These numbers were also distinguished in verbs see below , requiring agreement with their subject nominal. The case and gender systems are said to be best preserved, among the modern I. Forming an exception, Phrygian is sufficiently well-attested to allow proposals of a particularly close affiliation with Greek, and a Graeco-Phrygian branch of Indo-European is becoming increasingly accepted. Proto-Indo-European is a reconstructed language. Oxford, UK: Basil Blackwell. Archaeology e-Update Subscriber Alert! Archived PDF from the original on 5 November The sheep said to the horses: "My heart pains me, seeing a man driving horses. According to the authors, the reconstruction of this folktale to PIE implies that the Proto-Indo-Europeans had metallurgy, which in turn "suggests a plausible context for the cultural evolution of a tale about a cunning smith who attains a superhuman level of mastery over his craft". Greek pod-. It is not an actual language but merely a hypothetical reconstruction of a language that is presumed to be the ancestor of modern Indo-European languages. Russian mat -er. This section possibly contains original research. Latin duo. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.

It is interesting. Tell to me, please - where to me to learn more about it?
In my opinion you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.